Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 14 : Classes and objects
C++: Introduction to Classes
Introduction
to Classes
The
most important feature of C++ is the “Class”. It is significance is highlighted
by the fact that Bjarne Stroustrup initially gave the name 'C with classes'.
C++ offers classes, which provide the four features commonly present in OOP
languages: Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, and Polymorphism.
Need for Class
Class is a way to bind the data and its associated functions together. Classes are needed to represent real world entities that not only have data type properties but also have associated operations. It is used to create user defined data type
Declaration of a class
A
class is defined in C++ using the keyword class
followed by the name of the class. The body of the class is defined inside the
curly brackets and terminated either by a semicolon or a list of declarations
at the end.
The only difference between structure and class is the members of
structure are by default public
where as it is private in class.
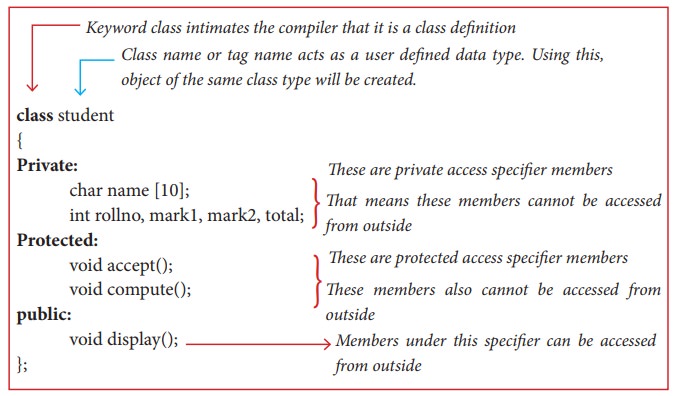
The General Form of a class definition
class class-name
{
private:
variable declaration;
function declaration;
protected:
variable declaration;
function declaration;
public:
variable declaration;
function declaration;
};
•
The class body contains the declaration of its members (Data member and Member
functions).
• The class body has three access specifiers (visibility
labels) viz., private , public and protected.
Class Access Specifiers
Data hiding is one of the important features of Object Oriented
Programming which allows preventing the functions of a program to access
directly the internal representation of a class type. The access restriction to
the class members is specified by public, private, and protected sections within
the class body. The keywords public, private, and protected are called access
specifiers. The default access specifier for members is private.
The Public Members
in child classes which are called derived classes
A public member is accessible from anywhere outside the class but within a program.You can set and get the value of public data members even without using any member function.
The Private Members
A
private member cannot be accessed from outside the class. Only the class member
functions can access private members.By default all the members of a class
would be private.
The Protected Members
A protected member is very similar to a private member but it Provides one additional benefit that they can be accessed (inherited classes).
Example
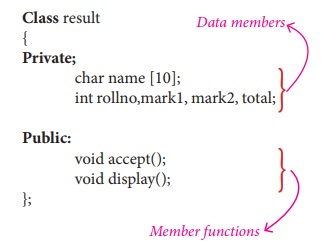
Definition of class members
Class
comprises of members. Members are classified as Data Members and Member
functions. Data members are the data variables that represent the features or
properties of a class. Member functions are the functions that perform specific
tasks in a class. Member functions are called as methods, and data members are
also called as attributes.
Example
Classes also contain some special member functions called as
constructors and destructors.
Defining methods of a class
Without
defining the methods (functions), class definition will become incomplete. The
member functions of a class can be defined in two ways.
(1)
Inside the class definition
(2)
Outside the class definition
(1) Inside the class definition
When
a member function is defined inside a class, it behaves like inline functions.
These are called Inline member functions.
If a function is inline, the compiler places a copy of the code of
that function at each point where the function is called at compile time.
(2) Outside the class definition
When Member function defined outside the class just like normal function definition (Function definitions you are familiar with ) then it is be called as outline member function or non-inline member function. Scope resolution operator (::) is used for this purpose. The syntax for defining the outline member function is
Syntax
return_type class_name
:: function_name (parameter list)
{
function definition
}
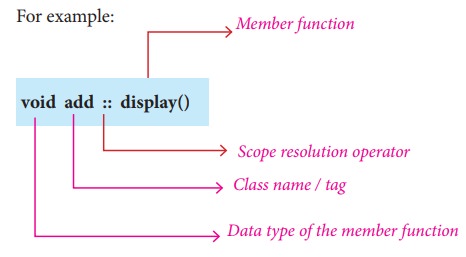
Illustration 14.1 Inline and Outline member function
Absence
of access specifier means that members are private by default..
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
double width; // no
access specifier mentioned
public:
double length;
void printWidth( )
//inline member function definition
{
cout<<”\n
The width of the box is...”<<width;
}
void setWidth( double w );
//prototype of the function
};
void Box :: setWidth(double
w) // outline member function definition
{
width=w;
}
int main( )
{
Box b; //
object for class Box
b.setWidth(10.0); //
Use member function to set the width.
b.printWidth( ); //Use
member function to print the width.
return 0;
}
Output:
The width of the box
is... 10
Declaring a member function having many statements, looping
construct, switch or goto statement as inline is not advisable.
Related Topics