Example Programs in C++ - C++: Defining methods of a class | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 14 : Classes and objects
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 14 : Classes and objects
C++: Defining methods of a class
Defining methods of a class
Without defining the methods (functions), class definition will become incomplete. The member functions of a class can be defined in two ways.
(1) Inside the class definition
(2) Outside the class definition
(1) Inside the class definition
When a member function is defined inside a class, it behaves like inline functions. These are called Inline member functions.
If a function is inline, the compiler places a copy of the code of that function at each point where the function is called at compile time.
(2) Outside the class definition
When Member function defined outside the class just like normal function definition (Function definitions you are familiar with ) then it is be called as outline member function or non-inline member function. Scope resolution operator (::) is used for this purpose. The syntax for defining the outline member function is
Syntax
return_type class_name :: function_name (parameter list)
{
function definition
}
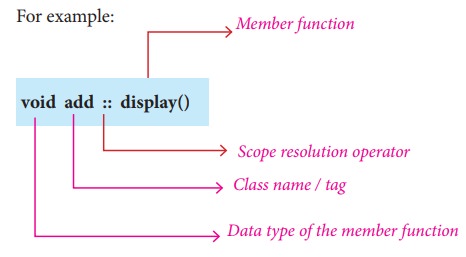
Illustration 14.1 Inline and Outline member function
Absence of access specifier means that members are private by default..
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
double width; // no access specifier mentioned
public:
double length;
void printWidth( ) //inline member function definition
{
cout<<”\n The width of the box is...”<<width;
}
void setWidth( double w ); //prototype of the function
};
void Box :: setWidth(double w) // outline member function definition
{
width=w;
}
int main( )
{
Box b; // object for class Box
b.setWidth(10.0); // Use member function to set the width.
b.printWidth( ); //Use member function to print the width.
return 0;
}
Output:
The width of the box is... 10
Declaring a member function having many statements, looping construct, switch or goto statement as inline is not advisable.
Related Topics