Chapter: Surgical Pathology Dissection : Breast
Breast Biopsies for Mammographic Abnormalities: Surgical Pathology Dissection
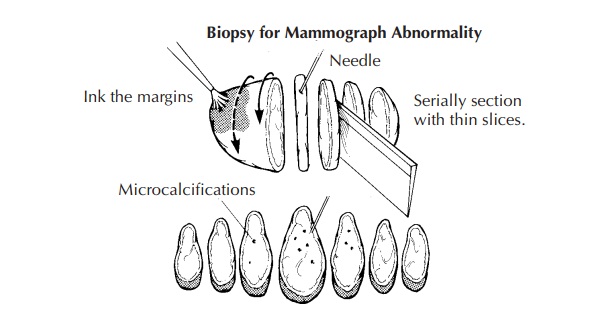
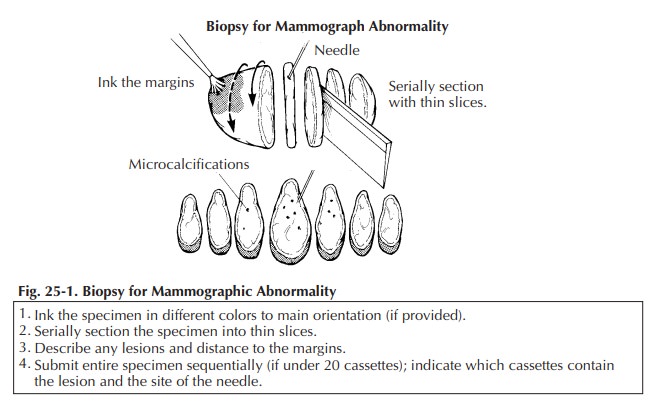
Biopsies for Mammographic Abnormalities
Nonpalpable
lesions detected mammographically are often biopsied by the surgeon and the
specimen then sent to radiology, where a specimen radiograph is obtained to
confirm that the surgeon has indeed biopsied or excised the lesion detected on
the clinical mammogram. In these cases the radiologist frequently marks the
lesion with a needle or dye, and both the biopsy and the specimen mammogram are
then sent to the surgical pathology laboratory.
Once
received in pathology, the specimen should be measured, inked, and serially
sectioned (Figure 25-1). Take care to slice the breast thinly (2 mm). Take
advantage of the specimen radiograph; the gross findings can be correlated with
the lesion seen radiographically. If a lesion is seen, note the largest
dimension of the lesion and carefully note the relationship of the lesion to
the inked margins as well as the circumscription and nature of the border of
the lesion.
Sequentially
submit the entire specimen, up to 20 blocks of tissue, for histologic
examination. Sequential sectioning allows one to better reconstruct the
distribution of the lesion from the slides. When taking these sections, be sure
that the sections demonstrate the relation of the lesion to the closest inked
margin. Be sure also to designate which block contains the area marked by the
radiologist’s needle as containing calcification.
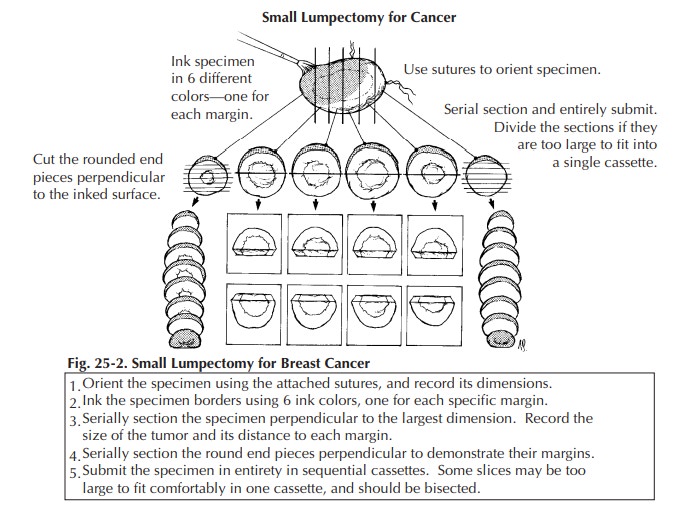
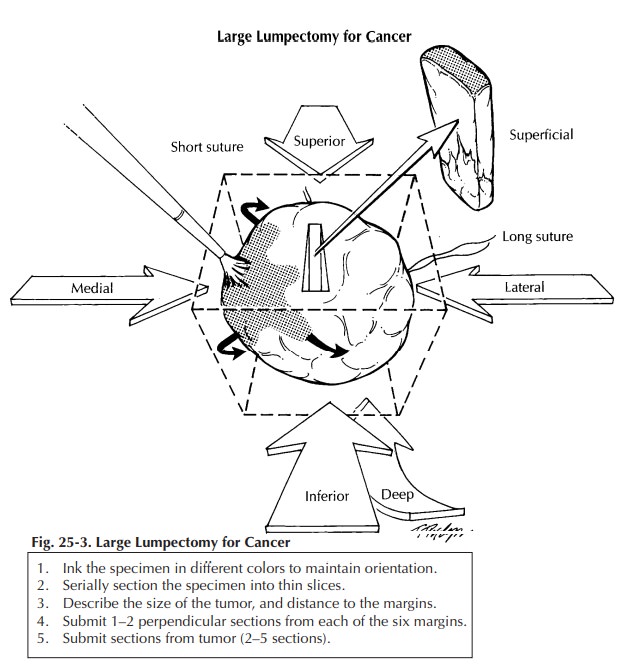
For large biopsy specimens that cannot be completely submitted in 20 or fewer sections, the extent of tissue sampling is not clear. Owings et al. suggested a method for selective tissue sampling in these large specimens. According to their method, initial sampling should include the submission of all tissue corresponding to radiographic calcifications and all surrounding fibrous tissue.
If carcinoma or atypical
duct hyperplasia is identified in these initial sections, the remaining tissue
should be submitted in its entirety to determine the extent of the lesion and
the status of the margins and to exclude inva-sion in cases of ductal carcinoma
in situ.
Related Topics