Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 14 : Transportation in Plants and Circulation in Animals
Blood
Blood
Blood is the main
circulatory medium in the human body. It is a red coloured fluid connective
tissue.
Components of Blood: The blood consists of
two main components. The fluid plasma and the formed elements
(blood cells) which are found suspended in the plasma.
Plasma: It is slightly alkaline,
containing non-cellular substance which constitutes about 55% of the
blood. Organic substances like proteins, glucose, urea, enzymes, hormones,
vitamins and minerals are present in the plasma.
Formed Elements of
Blood: Blood
corpuscles are of three types
1. Red blood corpuscles (RBC) or Erythrocytes
2. White blood corpuscles (WBC) or Leucocytes
3. Blood platelets or Thrombocytes.
Red blood corpuscles (Erythrocytes)
They are the most
abundant cells in the human body. RBCs are formed in the bone marrow. The RBCs
impart red colour to the Erythrocytes blood due to presence of respiratory
pigment haemoglobin. Matured mammalian RBCs do not have cell
organelles and nucleus. They are biconcave and disc -shaped. Their life span is
about 120 days. RBC is involved in the transport of oxygen from lungs to tissues.

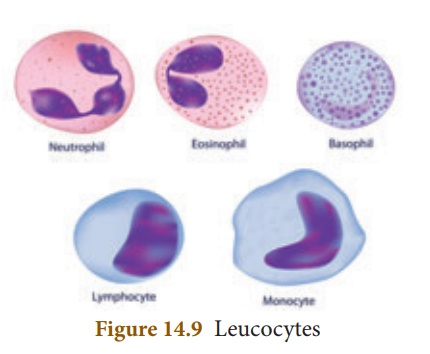
White blood corpuscles (Leucocytes)
WBC's are colourless.
They do not have haemoglobin and are nucleated cells. It is found in the bone
marrow, spleen, thymus and lymph nodes. They are capable of amoeboid movement
The white blood
corpuscles can be grouped into two categories:
1. Granulocytes 2. Agranulocytes.
Granulocytes
They contain granules in
their cytoplasm. Their nucleus is irregular or lobed. The granulocytes are of
three types
(i) Neutrophils
(ii) Eosinophils
(iii) Basophils
(i) Neutrophils
They are large in size
and have a 2 - 7 lobed nucleus. These corpuscles form 60% - 65% of the total
leucocytes. Their numbers are increased during infection and inflammation.
(ii) Eosinophils
It has a bilobed nucleus
and constitute 2% - 3% of the total leucocytes. Their number increases during
conditions of allergy and parasitic infections. It brings about
detoxification of toxins.
(iii) Basophils
Basophils have lobed
nucleus. They form 0.5-1.0% of the total leucocytes. They release chemicals
during the process of inflammation.
Agranulocytes
Granules are not found
in the cytoplasm of these cells. The agranulocytes are of two types:
(i) Lymphocytes (ii) Monocytes
(i) Lymphocytes
These are about 20-25%
of the total leucocytes. They produce antibodies during bacterial and
viral infections.
(ii) Monocytes
They are the largest of
the leucocytes and are amoeboid in shape. These cells form 5 - 6 % of the total
leucocytes.They are phagocytic and can engulf bacteria.
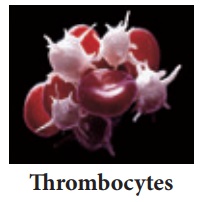
Blood Platelets or Thrombocytes
These are small and
colourless. They do not have nucleus. There are about 2,50,000 – 4,00,000 platelets/cubic
mm Thrombocytes of blood. Life span of platelets is 8–10 days. They play an important
role in clotting of blood. Platelets form clot at the site of injury and
prevent blood loss.
Functions of blood
a)
Transport of respiratory gases (Oxygen and CO2).
b)
Transport of digested food materials to the different body cells.
c)
Transport of hormones.
d)
Transport of nitrogenous excretory products like ammonia, urea and
uric acid.
e)
It is involved in protection of the body and defense against
diseases.
f)
It acts as buffer and also helps in regulation of pH and body
temperature.
g)
It maintains proper water balance in the body.
Related Topics