Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 12 : Biodiversity and its conservation
Biodiversity and its conservation: Summary
Summary:
Biodiversity is the variety of all life on
Earth, encompassing genetic, species and ecosystem diversity. Today’s
biodiversity is the fruit of billions of years of evolution, shaped by natural
processes and, increasingly, by the influence of humans. To date, about two
million species have been identified on Earth.
Biodiversity supplies a large number of goods
and services that sustain human life, including the provision of food, fuel and
building materials; purification of air and water; stabilization and moderation
of the earth’s climate; moderation of floods, droughts, temperature extremes
and wind forces; generation and renewal of soil health; maintenance of genetic
resources as inputs to crop varieties and livestock breeds, medicines, and
other products; and cultural, recreational and aesthetic benefits.
Over the past few hundred years, biodiversity
has faced major challenges, including a growing demand for biological resources
caused by population growth and increased consumption. This increased
exploitation of biological resources has resulted in the loss of species at
levels currently estimated to be 100 times faster than the natural rate of loss
prior to significant human intervention. Though many species were lost and new
ones formed, it is likely we will lose all this natural wealth in less than two
centuries, if the present rate of biodiversity losses persist.
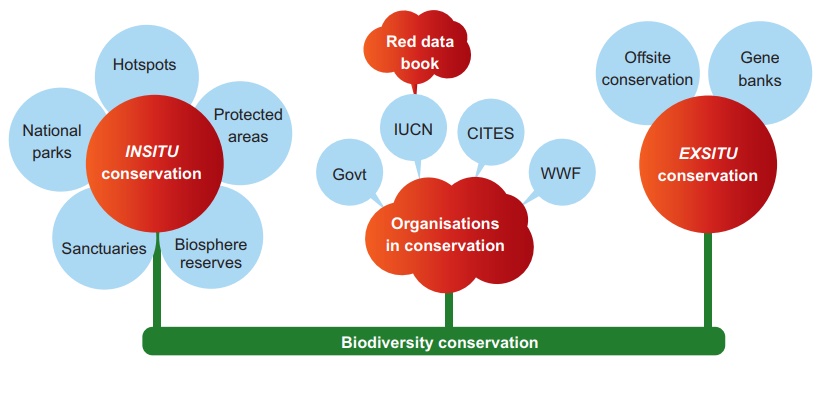
The biodiversity and its conservation is the
important global issue of international concern. Recognition of this problem
has made scientists and policy makers to work and develop mechanisms to
document, conserve and sustainably use biodiversity.
The younger generation should be made to realize
the critical state of biodiversity today and volunteer to protect and conserve
it, so as to enable the future generations get to enjoy the benefits of Nature.
Related Topics