Chapter: Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Diet and Cardiovascular Disease
Atherosclerosis
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
Arteriosclerosis is the general term
for vascular disease in which
arteriesharden (become thickened), making the passage of blood difficult and
some-times impossible. Atherosclerosis is the form of arteriosclerosis that
most frequently occurs in developed countries. It is believed to begin in
childhood and is considered one of the major causes of heart attack.
Atherosclerosis
affects the inner lining of arteries (the intima), where deposits of
cholesterol, fats, and other substances accumulate over time, thickening and
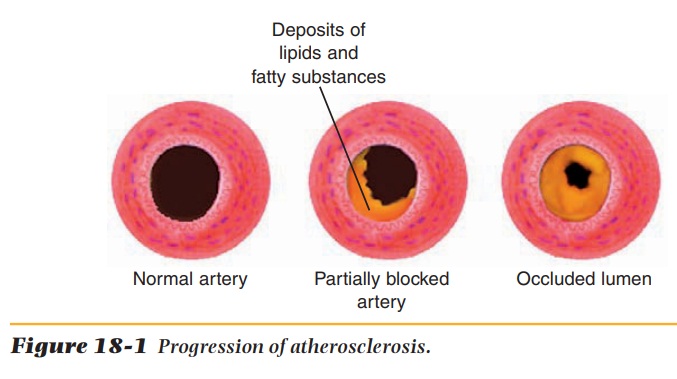
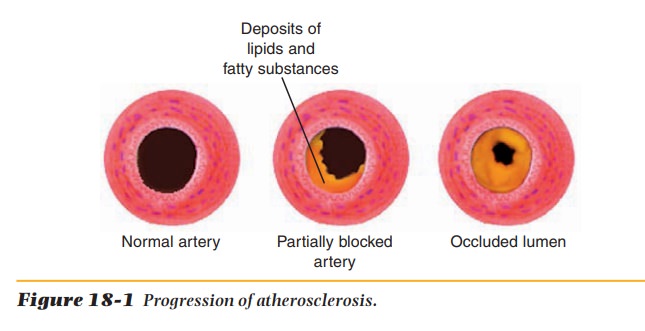
weakening artery walls. These deposits are called plaque (Figure 18-1). Plaque
deposits gradually reduce the size of the lumen of the artery and,
consequently, the amount of blood flow. The reduced blood flow causes an
inadequate supply of nutrients and oxygen delivery to and waste removal from
the tissues. This condition is called ischemia.
The reduced oxygen
supply causes pain. When the pain occurs in the chest and radiates down the
left arm, it is called angina pectoris and should be
consid-ered a warning. When the lumen narrows so that a blood clot (thrombus) occurs in a coronary
artery and blood flow is cut off, a heart attack occurs. The dead tissue that
results is called an infarct. The heart muscle that
should have
Thus, such an attack is commonly called an acute myocardial
infarction (MI). Some clients who experience an MI will require surgery to
bypass the clogged artery. The procedure is a coronary artery bypass graft
(CABG), which is commonly referred to as bypass surgery.
When blood flow to the
brain is blocked in this way or blood vessels burst and blood flows into the brain,
a stroke, or cerebrovascular
accident(CVA), results. When it occurs in tissue some distance from the heart,
it iscalled peripheral vascular
disease (PVD).
Risk Factors
Hyperlipidemia, hypertension (high
blood pressure), and smoking are majorrisk factors for the development of
atherosclerosis. Other contributory factors are believed to include obesity,
diabetes mellitus, male sex, heredity, personality type (ability to handle
stress), age (risk increases with years), and sedentary lifestyle. Although some
of these factors are beyond one’s control, some factors are not.
It is known that
dietary cholesterol and triglycerides (fats in foods and in adipose tissue)
contribute to hyperlipidemia. Foods containing saturated fats and trans fats
increase serum cholesterol, whereas unsaturated
fats tend to reduce it.
Lipoproteins carry
cholesterol and fats in the blood to body tissues. Low-density lipoprotein
(LDL) carries most of the cholesterol to the cells, and elevated blood levels
of LDL are believed to contribute to atherosclerosis. High-density lipoprotein
(HDL) carries cholesterol from the tissues to the liver for eventual excretion.
It is believed that low serum levels of HDL can contribute to atherosclerosis.
Diet can alleviate
hypertension, reduce obesity, and help control diabetes mellitus. A sedentary
lifestyle can be changed. Exercise can help the client lose weight, lower blood
pressure, and increase the HDL (“good”) cholesterol level. Exercise must be
done in consultation with the physi-cian and be increased gradually. Also, one
can stop smoking. In sum, a person can considerably reduce the risk of
atherosclerosis and thus an MI, CVA, and PVD.
Related Topics