Chapter: Pharmaceutical Drug Analysis: Radioimmunoassay
Applications of Radioimmunoassay (RIA) in Pharmaceutical Analysis
APPLICATIONS OF RADIOIMMUNOASSAY (RIA) IN PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS
The scope of applicability of radioimmunoassay is rapidly
expanding with the dawn of each day as RIA is being developed for newer
pharmaceutical substances. It has attained wide recognition and application
both in vitro and in vivo measurements of compounds of interest like insulin,
gastrin, glucagon, and growth hormones on
one hand ; whereas drugs like :
Morphine — Narcotic analgesic,
Hydromorphone and — Narcotic analgesic, antitussive and
antipyretic, Hydrocodone on the other
hand
Clonazepam — Sedative and anticonvulsant,
Flurazepam — Hypnotic and anticonvulsant,
Chlordiazepoxide — Sedative
Barbiturates — Hypnotic and anticonvulsant,
Flunisolide — A steroid having marked anti-inflammatory
activity,
Neobentine — A novel antidysrhythmic and antifibrillatory
agent,
Carteolol — B1-Adrenoreceptor blocker used in
hypertension and
RIA of some of these drugs will be discussed in the
sections that follows :
1. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY OF MORPHINE
Synthesis of Immunogen :
Morphine
is first converted to 3-o-carboxymethymorphine
by reacting the free base with
sodium-p-chloroacetate in absolute
ethanol
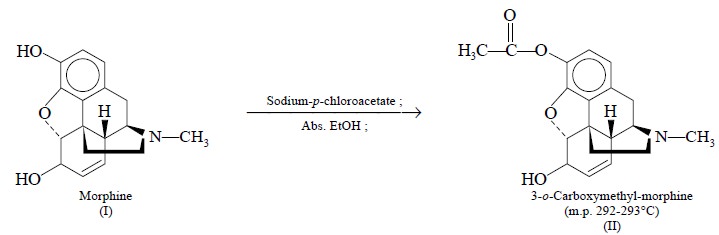
The product (II) is coupled to bovine-serum albumin by
dissolving the former in distilled water contain-ing the latter, maintaining
the pH of the resulting mixture to 5.5 and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl-aminopropyl)
carbidiimide was added. The mixture is incubated overnight at room temperature
and then dialyzed against distilled water to cause purification. The resulting
purified product carboxy-methyl-bovine-serum conjugate is then labelled with
tritium.
Antiserum Production : The immunogen,
carboxymethylmorphine-bovine-serum-albumin, is emulsi-fied with equal volume of
complete Freund’s adjuvant*. Initial immunization doses are injected into the
New Zealand albino rabbits and later on this followed up with booster
injections after a period of 6 weeks. The antiserum titer is determined with
each booster dose injection and is duly harvested when the titre value is
maximum. This is diluted suitably and employed in the radioimmunoassay**.
RIA-Procedure : The various steps followed are
as stated below, namely :
1)
Various dilutions of antiserums are incubated in the
presence of fixed concentration of (3H)-dihydromorphine, and after
incubation, a neutral saturated ammonium sulphate solution is added to all the
tubes,
2)
The complete precipitate, sedimented by centrifugation at
5000 rpm is washed twice with 50% ammonium sulphate solution,
3)
The washed-precipitate, containing antibody-bound
morphine, is dissolved in NCS-solubilizer, and the radioactivity is counted
with the help of a Packard-Iri-card Liquid Scintillation Spectrometer, The tube
which contained radioactive dihydromorphine and antiserum but no unlabelled
mor-phine, served as a measure of maximum antibody-bound radioactivity,
4)
The addition of increasing amount of unlabelled morphine
to a fixed amount of (3H) dihydromorphine and antiserum results a
competitive inhibition of the labelled dihydromorphine for the formation of the
antibody-hapten complex, and
5)
The assay sensitivity limit is found to be 100 pg of
unlabelled-morhine per tube that caused 20% binding inhibition of
labelled-dihydromorphine, (see Figure 32.3).
2. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY OF HYDROMORPHONE AND HYDROCODONE IN HUMAN PLASMA
Hydromorphone (I) and hydrocodone (II) belong to the
morphine group of drugs and are used
invariably in combination with other ingredients in a number of proprietory
antitussive and analgesic antipyretic mixtures. However, interest in the
pharmacokinetics of hydromorphone and hydrocodone in human subjects required an
adequate assay for drug levels in plasma.
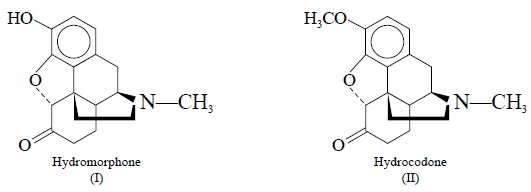
RIA for hydromorphone*, ** and hydrocodone***
are fairly sensitive in the nanogram per millilitre range but essentially
require the preparation of a specific antibody. The laid-out RIA method is
quite capable of estimating the above drugs within a range of 2.5-20 ng ml–1
using standard 100 μ l plasma sample only.
RAI is carried out using morphine-6-antiserum and
tritiated dihydromorphine (commercially avail-able). The free-drug is separated
from bound drug using dextran coated charcoal and an aliquot of the supenate
containing the antiserum-bound-drug is subsequently counted for radioactivity.
However, the radioactivity measurements are normally ascertained in a Liquid
Scintillation Counter provided with 20-ml glass scintilla-tion vials.
Materials Required
(i) Lyophilized morphine-6-antiserum : It
is diluted 1 : 20 with phosphate buffer prior to use,
(ii) 3H-Dihydromorphine Solution :
It is prepared by diluting 2 μ l of the radiolabelled
compound in ethanol to 10 ml with phosphate buffer so that each 0.1 ml of
solution contained 83 pg (0.5 mole),
(iii) Dextran-coated chrocoal suspension : It
is prepared by mixing 2.5 g of charcoal in 100 ml of distilled water with 2.5 g
of dextran in 100 ml of distilled water, and eliminating the fine particles by
centrifugation, and
(i)
Preparation of Saturated
Solutions :
Individual stock solutions containing the equivalent of 200 μ g of I or II base line are prepared using weighed quantities
of the respective powders dissolved in distilled water. Dilutions of the drugs
are made in individual 10 ml volumetric flasks to yield drug concentrations of
2.5, 5.0, 10.0 and 20 ng ml–1 for I and 10.0, 20.0, 40.0 and 80.0 ng
ml–1 for II. The dilutions are made using blank plasma and phosphate
buffer solutions
RIA-Procedure : The different steps to be
followed are stated below, namely :
a)
Various dilutions of unknown plasma,
morphine-6-antiserum, 3H-dihydromorphone are prepared afresh,
b)
The unknown plasma (0.1 ml) is incubated directly with
morphine-6-antiserum (0.1 ml) and buffer (0.3 ml) for a duration of 50 minutes
at room temperature (20 ± 2 °C) and immediately followed by 10 minutes at 4°C,
c)
The ice-cold dextran-coated-charcoal suspension (0.1 ml)
is added to all the above tubes, followed by immediate mixing and incubation
for 10 minutes at 4°C,
d)
All the tubes are then centrifuged for a period of 15
minutes at 3000 rpm,
e)
A small portion (0.2 ml) of the supernate is removed and
placed in a scintillation vial containing 0.5 ml of distilled water and 5 ml of
scintilation fluid,
f)
The contents of the scintillation vial are mixed
thoroughly, and the radioactivity is measured in a Liquid Scintillation Counter
for 10 minutes,
g)
Duplicate hydromorphone 2.5, 5.0, 10.0 and 20.0 ng ml–1
or hydrocodone 10.0, 20.0, 40.0, and 80.0 μ g ml–1 standards are accurately assayed
concurrently and the data is plotted in a graph, and
h)
The regression equation, calculated from the standard
solutions in each collection, is employed to determine quantitatively the drug
concentration present in individual plasma samples.
3. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY OF CLONAZEPAM
Colonazepam belongs to the class of 1, 4-benzodiazepines that has been
found to be therapeutically effective
in controlling minor motor seizures i.e.,
petitmal epilepsy in humans*
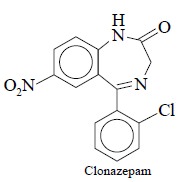
Synthesis of Immunogen : The 3-hemisuccinyloxy
derivative of clonazepam is covalently coupled to bovine serum albumin employing the mixed-anhydride method
suggested by Erlanger and coworkers** (1959). After successive dialysis against
dioxane-water borate buffer and water, the immunogen i.e., clonazepam-bovine-serum-albumin conjugate is isolated by
lyophilization.
Preparation of 3H-Labelled
Clonazepam : 3H-Clonazepam is prepared by tritium exchange employ-ing
dimethyl formamide-titrated water having a specific activity*** of 100 ci g–1.
The resulting product is subsequently purified by
silica-gel-column-chromatography, thereby yielding a material which has a
specific activity of 4.32 mci mg–1. This specific method of
introducing 3H (tritium) probably provided exchange chiefly at C-3
position****.
Antibody Production : A thick emulsion of the
immunogen (clonazepam-bovine-serum-albumin-con-jugate) is prepared employing
complete Freund’s adjuvant and two New Zealand white female rabbits are
immunized intradermally at multiple sites with the immunogen emulsion. The
animals are then administered with booster doses intravenously with immunogen
emulsion at monthly intervals, and serum is harvested 10-14 days after each
administration. Both rabbits produced satisfactory titers of antibodies to
clonazepam within a period of three months following the initial immunization.
The resulting serum is pooled, diluted suitably and employed in the
radioimmunoassay.
RIA-Procedure : The various steps involved in
the RIA-procedure for clonazepam are enumerated below, namely :
1)
A constant small (volume) portion of the control plasma
is added to constant small (volume) portion of standard clonazepam in small
test-tubes to generate a calibration (standard) curve,
2)
Appropriate controls are included by adding the control
plasma to small portion of buffer solutions,
3)
Each unknown plasma sample is added to tubes containing
buffer solution then the titrated (3H)-colnazepam solution followed
by diluted antiserum is added,
4)
The contents of each tube are mixed thoroughly and
allowed to stand at room temperature for sometime,
5)
Saturated ammonium sulphate solution is added to
precipitate the globulin-bound-3H- clonazepam and after mixing, the
tubes are allowed to stand for 15 minutes at 0 °C,
6)
The tubes are subsequently centrifuged at 3000 rpm,
7)
Each supernate, containing the unbound 3H-clonazepam,
is decanted into a scintillation vial and toluene is added,
8)
The samples are assayed for 3H-activity in a
liquid scintillation counter, and
9)
All samples including the standards, unknowns and
controls are assayed in duplicate and the aver-age of the 3H-counts
is employed for the percentage of binding.
4. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY OF FLURAZEPAM IN HUMAN PLASMA
Flurazepam belongs to the class of hypnotic agent used for the treatment
of insomnia.
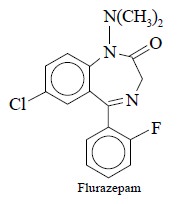
Synthesis of Immunogen
(Hapten) : 3-Hydroxy
flurazepam is refluxed with succinic anhydride in dichloromethane containing triethylamine to produce the desired
hapten, 3-hemisuccinyloxy-flurazepam. It is coupled covalently to
bovine-serum-albumin by the mixed-anhydride procedure developed by Erlanger et al (1959). The resulting conjugate is
purified by dialysis against sodium bicarbonate solution followed by dialy-sis
against distilled water and finally isolated by lyophilization.
Immunization and Antibody
Production : The
immunogen 3-hemisuccinyloxyflurazepam, is emulsi-fied with complete Freund’s
adjuvant. It is injected intradermally into two female New Zealand albino
(white) rabbits. Repeated doses are administered twice at interval of two
weeks. Subsequently, booster injections of the thick-immunogen-emulsion-paste
are administered after a span of 6-weeks. The antibody is harvested when its
titer level is high enough, diluted to the suitable-level and employed in the
RIA.
RIA-Procedure : The different steps followed
in the RIA-procedure are as given below :
A calibration curve is generated by adding 3H-Flurazepam
in 0.1 ml of buffer containing 0.03-0.2 ng range of flurazepam in buffer,
·
Following preparation of the standards, duplicate
portions of the reconstituted unknown flurazepam fractions are added to tubes
containing 3H-Flurazepam,
·
Diluted antiserum is added to all tubes except the
non-specific-binding control specimen to which buffer is added,
·
The contents of each tube is mixed gently on a Vortex
Mixer and allowed to stand at room tempera-ture,
·
Following incubation, the antibody-bound radio ligand is
separated from the unbound fraction by precipitation with saturated ammonium
sulphate,
·
After the pellet is dissolved in water add 3 ml of
scintillation fluid to produce a clear solution, and
·
The radioactivity in each tube is quantified in a
modified scintillation liquid counter.
RIA-Specificity* : The specificity of the
antiserum initially is evaluated by cross-reactivity** studies involving all the flurazepam metabolites known to be present in plasma. The mono-as
well as di-desethylmetabolites exhibited a cross-reactivity of 17 and 3.7%
respectively, while other possible competitors cross-reacted less than 1% as
shown in Table 32.1.
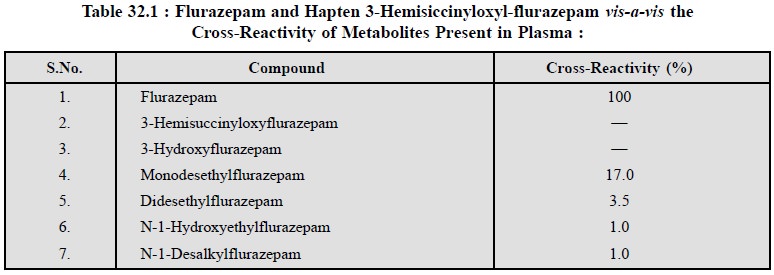
Evidently, due to the cross-reactivity of both mono- and
di-desethyl metabolites, a specific assay of flurazepam could not be developed
successfully without first separating it from its metabolites effectively by
the help of column chromatography.
5. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY OF CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE IN PLASMA
Chlordiazepoxide is the pioneer member of the 1, 4-benzodiazepines to be employed
clinically as an antianxiety agent
in humans***. A number of methods based on extraction processes are available
for the assay of this drug, namely : spectrofluorometry,
polarography and electron-capture GC-technique ; but RIA measures it directly in the
blood without involving extraction and possesses very low sensitivity.
Synthesis of Immunogen : Chlordiazepoxide as suspension
in N-methylformamide is treated with HCl
in dioxane to yield a pale-yellow solution. The resulting mixture is cooled
to -30 °C and isoamyl nitrite in dioxane is added. The solution is stirred at –
30° to – 40 °C and aqueous ammonium sulfamate is added with continuous
stirring.
The chilled azide solution is added slowly, dropwise with
constant vigorous stirring into a solution of bovine-serum albumin. The pH is
maintained at 8.0 to 8.7 by the careful addition of NaOH solution. The
resulting pale-yellow solution is kept at 4°C for a duration of 36 hours and
then dialysed against trimethamine buffer. After further dialysis for two days
against distilled water, the immunogen is isolated by lyophilization.
Immunization and Antibody
Production : The
lypphilized immunogen obtained above is dissolved in normal saline and emulsified with equal volumes of complete
Freund’s adjuvant into a thick paste. Three New Zealand albino rabbits are
immunized with the immunogen-paste through intradermal injections. The process
is repeated twice at 2-weeks intervals followed by booster doses at monthly
intervals. The antiserum is harvested when the plasma titer value is attained
maximum.
RIA-Procedure : The various steps involved in
the RIA procedure are enumerated below :
1)
A constant volume of control human plasma is added to a
constant volume of each standard of chlordiazepoxide to produce a calibration
curve of 2 to 100 ng per tube,
2)
The same volume of the unknown plasma samples is added to
tubes containing constant volume of the solution of the labelled
chlordiazepoxide and constant volume of the antiserum solution is now added to
all the tubes,
3)
The volumes in all the tubes are made upto 1 ml with
buffer solution, mixed thoroughly on a Vortex Mixer, and each tube is immersed
in an ice-water bath,
4)
An equal volume of saturated ammonium sulphate solution
is added to enable complete precipitation of globulin-bound chlordiazepoxide 14C,
5)
After mixing the contents of the tubes thoroughly on a
Vortex Mixer and allowing them to stand for a while at 4°C, the tubes are
centrifuged at 3000 rpm,
6)
The supernate thus obtained containing unbound
chlordiazepoxide-14C is decanted into a count-ing vial and toluene
is added, and
7)
The radioactivity in the supernate and that in the
precipitate are separately counted in a scintilla-tion counter.
Specificity of Antibody
binding of Chlordiazepoxide : A good number of benzodiazepines are tested for their ability to complete with labelled
chlordiazepoxide for the respective antibody binding site. The various
competitors are adequately tested at a concentration of 200 ng i.e..,10-times the concentration of
chlordiazepoxide required to produce a 50% inhibition of binding as shown in
Table 32.2.
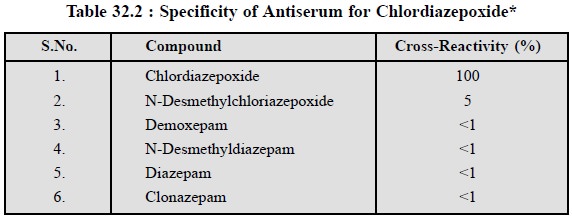
From table 32.2 it is evident that the highest
cross-reaction is 5% with N-desmethylchlordiazepoxide while demoxepam,
N-desmethyldiazepam, diazepam and clonazepam displayed less than 1% inhibition.
How-ever, the RIA method appears to be reliable over a range of 2-100 ng per
tube of chlordiazepoxide and, there-fore, the sensitivity limit stands at 20 ng
ml–1 using a 1.0 ml sample of plasma.
6. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY OF BARBITURATES
Barbiturates represent a class of sedative and hypnotic drugs employed
extensively in medicine. RIA
provides a rapid, sensitive specific and reliable means for their determination
in plasma levels upto 5 ng without indulging in any type of extraction,
filtration or evaporation as required for other conventional analyti-cal
methods**.
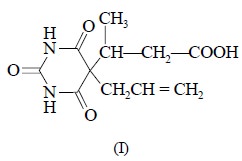
5-Allyl-5-(1-carboxyisopropyl) barbituric acid.
Synthesis of Immunogen
(Hapten) : The
barbiturate, 5-allyl-5-(1-carboxyisopropyl) barbituric acid (1) is first
converted to 5-allyl-5-(1-p-nitrophenyloxycarbonylisopropyl)
barbituric acid (II) by the interaction of the base with p-nitrophenol in N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as shown below :
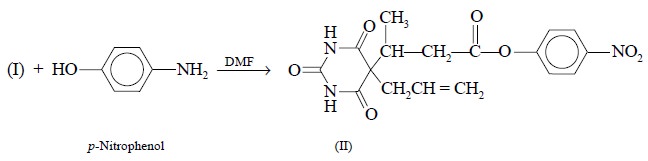
The resulting product (II) is subsequently coupled to
bovine-serum-albumin in a glycerol-water mixture in the presence of
dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. The mixture is incubated overnight at 4°C, and the
protein-hapten complex is dialysed against distilled water thereby causing its
purification. Conjugation of the respective bar-biturate to the protein
carrier, comparison of the barbiturate BGG-conjugate to control BGG-solution
and preparation of 14C-pentobarbital sodium are carried out
respectively.
Preparation of Antiserum : The
barbiturate-bovine-serum-albumin conjugate is duly emulsified with an equal volume of complete
Freund’s adjuvant and New Zealand albino rabbits are subsequently im munized
with this particular emulsion. Six weeks after the initial does, booster doses
are administered to the animals in each of their foot pads. Blood samples are
collected 5-7 days after the booster injections and the serum is examined for
antibodies to barbiturates. The antiserum is harvested when the serum antibody
titer has attained its maximum level.
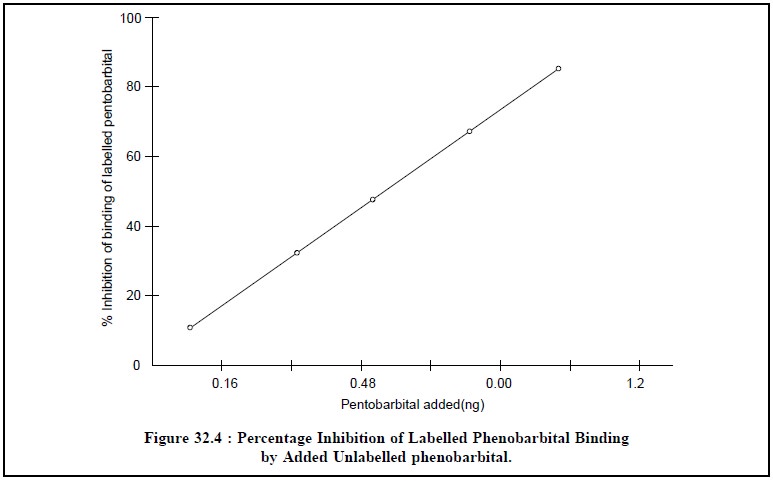
It has been observed that while normal, rabbit serum
failed to bind labelled phenobarbital, the serum from immunized rabbits bound
75 to 80% of the added pentobarbital and there exists a linear relationship
between 14C-phenobarbital and the concentration of added antibody.
Besides, when variable quantities of 14C-pentobarbital are added to
a constant quantity of antibody, there exists a linear relationship between
added and bound 14C-phenobarbital as depicted in Figure 32.4.
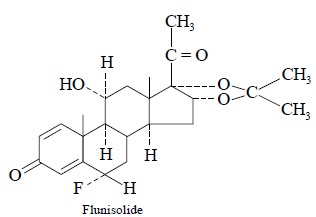
7. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY OF FLUNISOLIDE IN HUMAN PLASMA
Flunisolide is a fast-acting corticoid
designed for the treatment of allergic rhinitis, asthma, and other allied respiratory disorders in
humans*. As the quantum of drug delivered by inhalation (i.e., the usual route of administration of the drug), is invariably
small, the plasma-levels attained can also be fairly small. Hence, there is a
dire need for a sensitive method of plasma concentration evaluation which is
satisfied by radioimmunoassay.
Synthesis of Hapten Immunogen
and Antiserum Production : The hapten, flunisolide-bovine-se-rum-albumin conjugate
is prepared by coupling the 21-hemisuccinate of flunisolide to
bovine-serum-albumin with a water-soluble carbodiimide coupling reagent*. The
reaction mixture is dialysed exhaustively against normal saline to cause
purification and the extent of conjugation is estimated by measuring the
protein concen-tration**. However, the flunisolide residues are determined by
UV-absorption method.
An emulsion of the hapten (i.e., conjugate) in normal saline is prepared by mixing with an
equal volume of Freund’s complete adjuvant. The prepared emulsion is injected
subcutaneously into four different sites in New Zealand albino rabbits. Six
weeks after the initial injection, all the animals are placed on a regimen of
weekly booster shots. After a period of six months, antiserum from these
animals are harvested and dilutions of 1 : 10,000 to 1 : 30,000 produced 50%
binding or more and is employed in the RIA.
RIA-Procedure : The following steps are to be
adopted in a sequential manner, namely :
·
Flunisolide standards required for the preparation of the
standard curve are obtained by dilution of a stock solution of 10 mg of it in
10 ml of ethanol,
·
A series of standard solution viz., 20, 50, 100, 200, 300, 500 and 600 pg per 0.1 ml in
tris-(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane/hydrochloric acid buffer and stored duly at 0
°C temperature,
·
An ethanolic solution of 3H-Flunisolide is
diluted with tris-(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane/hydro-chloric acid buffer and
0.1% gelatin such that 0.1 ml portion contains 8,000 to 10,000 cmp activity,
·
The antiserums are diluted in the said buffer with 0.1%
gelatin to give rise to a total binding of between 35-50%,
·
The charcoal stock solution is diluted as and when
required with the aforementioned buffer immedi-ately before, use,
·
RIA is conducted by mixing together various dilutions of
antiserum, buffer solution, 3H-Flunisolide and various dilutions of
flunisolide standard solutions in a set of test tubes,
·
A second set of test tubes containing various dilutions
of antiserum, buffer solution, 3H-Flunisolide and various dilutions
of the plasma being analysed of flunisolide content are prepared separately,
·
The two sets of test tubes are incubated at temperature
of 0 °C after adding constant volume of charcoal suspension to each of the
tubes and mixing them thoroughly on a Vortex Mixer,
·
The incubation is done overnight,
·
The tubes are then centrifuged at 2500 rpm for 4 minutes
and immediately 0.5 ml of the supernate is transferred into scintillation
vials, and
·
The scintillation fluid is added and the solutions are
counted for 10 minutes in Scintillation Counter***.
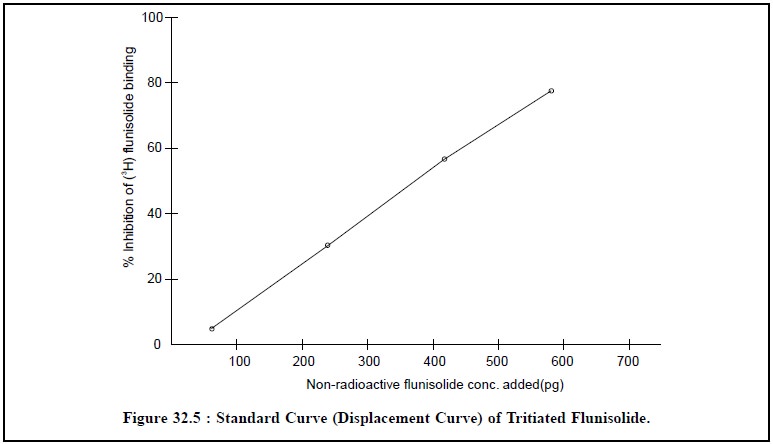
The percentage inhibition is calculated and the values
obtained from the first set of tubes is used to plot a standard curve. The
concentrations of flunisolide from the standard curve values from their
calulated percent-age inhibition value as depicted in figure 32.5 below :
Related Topics