in Agriculture, Industries, Medicine - Applications of Microbes | 9th Science : World of Microbes
Chapter: 9th Science : World of Microbes
Applications of Microbes
Applications of Microbes
Microorganism s
contribute to human welfare in many ways. In this section we will study about
the diversified usefulness of microbes.
1. Microbes in Agriculture
Microbes play an
important role in agriculture as biocontrol agents and biofertilizers. Microbes
play a vital role in the cycling of elements like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen,
sulphur and phosphorus.
(i) Microbes as
biocontrol agents Microorganisms used for controlling harmful or pathogenic
organisms and pests of plants are called as biocontrol agents (Biopesticides). Bacillus
thuringiensis (Bt) is a species of bacteria that produces a protein called
as ‘cry’ protein. This protein is toxic to the insect larva and kills them.
Spores of B.thuringiensis are available in sachets, which are dissolved
in water and sprayed on plants infected with insect larva.
(ii) Microbes as biofertilizers
Microorganisms which
enrich the soil with nutrients are called as biofertilizers. Bacteria,
cyanobacteria and fungi are the main sources of biofertilizers. Nitrogen is one
of the main source of plant nutrients. Atmospheric nitrogen has to be converted
to available form of nitrogen. This is done by microbes either in free living
conditions or by having symbiotic relationship

with the plants. e.g. Nitrosomonas,
Nostoc (free living), symbiotic microbes like Rhizobium, Frankia,
mycorrhizae.
2. Microbes in Industries
Microorganisms play an
important role in the production of wide variety of valuable products for the
welfare of human beings.
·
Production of fermented beverages: Beverages like
wine are produced by fermentation of malted cereals and fruits by Saccharomyces
cerevisiae.
·
Curing of coffee beans, tea leaves and tobacco leaves: Beans of coffee and
cocoa, leaves of tea and tobacco are fermented by the bacteria Bacillus
megaterium. This gives the special aroma.
·
Production of curd: Lactobacillus sp. converts
milk to curd.
·
Production of organic acids, enzymes and vitamins: Oxalic acid, acetic
acid and citric acid are produced by fungus Aspergillus niger.
Enzymes like lipases, invertase, proteases, and glucose oxidase are
derived from microbes. Yeasts are rich source of vitamin-B complex.
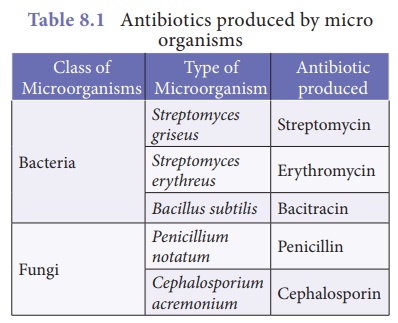
3. Microbes in Medicine
Antibiotics are metabolic products
of microorganisms, which in very low concentration are inhibitory or
detrimental to other microbes. In 1929, Alexander Fleming produced the first
antibiotic pencillin. In human beings antibiotics are used to control
infectious diseases like cholera, diptheria, pneumonia, typhoid, etc.
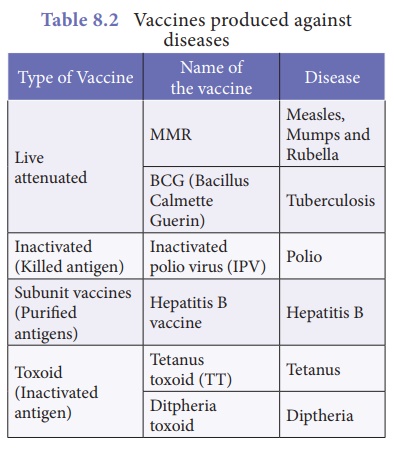
Vaccines are prepared by killing
or making the microbes inactive (attenuated). These inactive microbes
are unable to cause the disease, but stimulate the body to produce antibodies
against the antigen in the microbes.
Related Topics