Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : The Applet Class
AppletContext and showDocument( ) - The Applet Class
AppletContext and showDocument( )
One
application of Java is to use active images and animation to provide a graphical
means of navigating the Web that is more interesting than simple text-based
links. To allow your applet to transfer control to another URL, you must use
the showDocument( ) method defined
by the AppletContext interface. AppletContext is an interface that lets
you
get
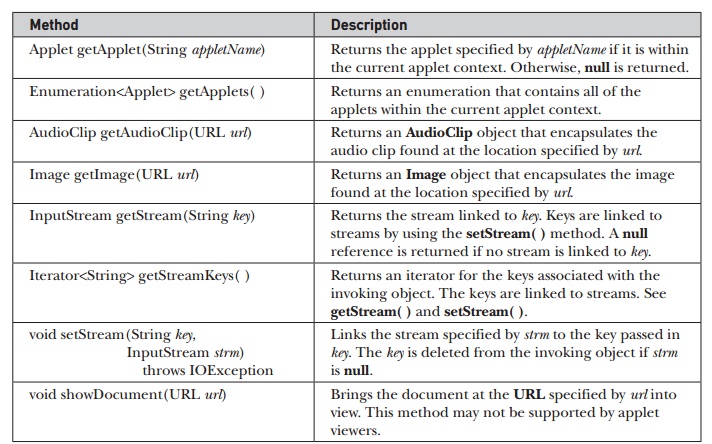
information from the applet’s execution environment. The methods defined by AppletContext are shown in Table 23-2.
The context of the currently executing applet is obtained by a call to the getAppletContext(
) method defined by Applet.
Method :
Description
Applet
getApplet(String appletName) : Returns the applet specified by appletName if it
is within the current applet context. Otherwise, null is returned.
Enumeration<Applet>
getApplets( ) : Returns an enumeration that contains all of the applets within
the current applet context.
AudioClip
getAudioClip(URL url) : Returns an AudioClip object that encapsulates the audio
clip found at the location specified by url.
Image
getImage(URL url) : Returns an Image object that encapsulates the image found
at the location specified by url.
InputStream
getStream(String key) : Returns the stream linked to key. Keys are linked to
streams by using the setStream( ) method. A null reference is returned if no
stream is linked to key.
Iterator<String>
getStreamKeys( ) : Returns an iterator for the keys associated with the
invoking object. The keys are linked to streams. See getStream( ) and
setStream( ).
void
setStream(String key, InputStream strm) throws IOException : Links the stream
specified by strm to the key passed in key. The key is deleted from the
invoking object if strm is null.
void
showDocument(URL url) : Brings the document at the URL specified by url into
view. This method may not be supported by applet viewers.
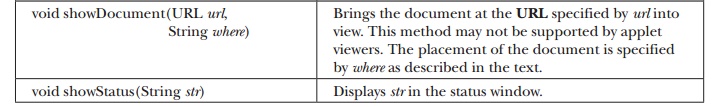
void
showDocument(URL url, String where) : Brings the document at the URL specified
by url into view. This method may not be supported by applet viewers. The
placement of the document is specified by where as described in the text.
void
showStatus(String str) : Displays str in the status window.
Table 23-2 The Methods Defined by the AppletContext Interface (continued)
Within
an applet, once you have obtained the applet’s context, you can bring another
document into view by calling showDocument(
). This method has no return value and throws no exception if it fails, so
use it carefully. There are two showDocument(
) methods. The method showDocument(URL)
displays the document at the specified URL.
The method showDocument(URL, String)
displays the specified document at the specified location within the browser
window. Valid arguments for where are
"_self" (show in current frame), "_parent" (show in parent
frame), "_top" (show in topmost frame), and "_blank" (show
in new browser window). You can also specify a name, which causes the document
to be shown in a new browser window by that name.
The
following applet demonstrates AppletContext
and showDocument( ). Upon execution,
it obtains the current applet context and uses that context to transfer control
to a file called Test.html. This
file must be in the same directory as the applet. Test.html can contain any valid hypertext that you like.
/* Using an
applet context, getCodeBase(), and showDocument() to display an HTML file.
*/
import java.awt.*; import
java.applet.*; import java.net.*;
/*
<applet
code="ACDemo" width=300 height=50> </applet>
*/
public class ACDemo extends
Applet { public void start() {
AppletContext ac =
getAppletContext();
URL url = getCodeBase(); //
get url of this applet
try {
ac.showDocument(new
URL(url+"Test.html"));
} catch(MalformedURLException
e) { showStatus("URL not found");
}
}
Related Topics