Term 3 Chapter 2 | 5th Social Science - Agriculture | 5th Social Science : Term 3 Unit 2 : Agriculture
Chapter: 5th Social Science : Term 3 Unit 2 : Agriculture
Agriculture
UNIT 2
Agriculture

Learning Objectives
Students will be able to:
*
describe the features of agriculture.
*
list and explain differnt types of farming and irrigation.
*
name the various crops grown in Tamil Nadu.

Introduction
Agriculture is the art and science of preparing
the soil for cultivation, growing crops andraising livestock. It has become a
necessity for the humans. Agriculture led to the development of human
civilisation.

India
is an agricultural country. One-third of our nation‛s income comes from
agriculture. Agricultural development contributes to the economy of our country.
Farmers in India
A
farmer is a person who cultivates crops and rears animals (poultry and other
livestock). India is a land of farmers. It is called so because majority of
Indians are directly or indirectly involved in agricultural activities. Agriculture
is the backbone of our economy.
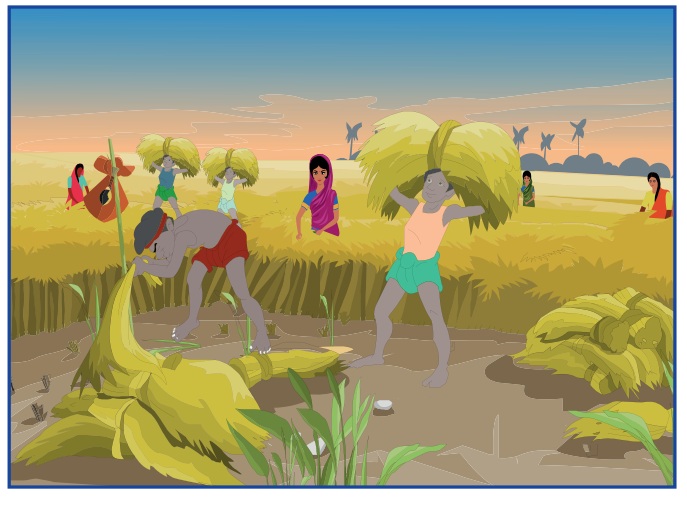

Farmers who cultivate in an area less than 1 hectare are called micro farmers.
Types of Farming
There are several types of farming.
* Subsistence farming
* Commercial farming
* Plantation farming
* Mixed farming

Subsistence Farming
In subsistence farming, crops are cultivated and used only for own family consumption. Such type of farming is adopted by small and marginal farmers on fragmented land holdings. The cultivated crops are usually food crops. The method of this farming is generally archaic.

Commercial farming
Unlike subsistence farming, here the
crops are cultivated for commercial use and is sold in markets. This method of
farming is done by using modern tools and techniques

Plantation Farming
Plantation Farming is done in an
estate where a single cash crop is cultivated on a large scale. Examples: Tea,
Coffee and Rubber.

Mixed Farming
Mixed farming refers to the rearing
of animals along with the cultivation. This type of farming is economical.

LET US KNOW
The Government has set
up agencies like the Food Corporation of
India to purchase the farm products directly from the farmers at reasonable
rates.
ACTIVITY
Let us do
Help the farmer to reach his filed.
In order to eliminate the middlemen between farmers and consumers, the Government of Tamil Nadu introduced the new concept, namely UZHAVAR SANTHAI
Water Resource for Agriculture
There are no perennial rivers in
Tamil Nadu. Tamil Nadu depends on Northeast and Southwest monsoon. Hence,
agriculture in Tamil Nadu is dependent on ground water.
Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) monitors the level and nature of
ground water.
Irrigation
Irrigation is the supply of water to land or crops for the purpose of
agricultural production.
Types of Irrigation
* Well Irrigation
* Canal Irrigation
* Sprinkler Irrigation
* Drip Irrigation
Well Irrigation
Well irrigation has been practised in Tamil Nadu
for many generations. It is a less expensive type of irrigation.

Canal Irrigation
Canal irrigation is the most important
form of irrigation in India. Most of the North Indian canals are perennial. The
main canal irrigated areas are in the northern plains of India such as Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Bihar.
Canal Irrigation
Green revolution is a process which
brought an increase in crop production by using new varieties of seeds,
pesticides and new agricultural techniques.

Dr.M.S. Swaminathan of Tamil Nadu is known as Father of Green Revolution in India.

Sprinkler Irrigation
Sprinkler irrigation is similar to natural
rainfall. Water is sprayed through pipes in the air through sprinklers.

Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is a type of
micro-irrigation system that saves water and soil nutrients. In this system
water drips slowly into the roots of plants through pipes. Pipes can be either
above the soil surface or buried below the surface. The water directly reaches
the roots and minimises evaporation.![]()

ACTIVITY
Let us write
(Tractor, Winnower, Farmer)
Find out the following.
1. One who produces
food for us. Farmer
2. It is used for
ploughing. Tractor
3. It is used for
separating grain from hay. Winnower
LET US KNOW
Animal husbandry is the branch of
agriculture. It is to raise animals for meat, fur, milk, eggs and other
products.

Horticulture is the science or art of cultivating fruits, vegetables, flowers or ornamental plants.
Important crops in Tamil Nadu
Tamil
Nadu has different types of soil, rainfall and weather across its districts. It
is suitable for the production of fruits, vegetables, spices, plantation crops,
flowers, medicinal and aromatic plants. Horticulture is the fastest
growing sector within agriculture in Tamil Nadu.
Paddy is grown in large areas because rice is the
main staple food of the state.
The principal food crops are rice, maize, jowar
(cholam), bajra (Kambu), ragi,
and pulses (bengalgram, redgram, greengram blackgram
and horsegram).
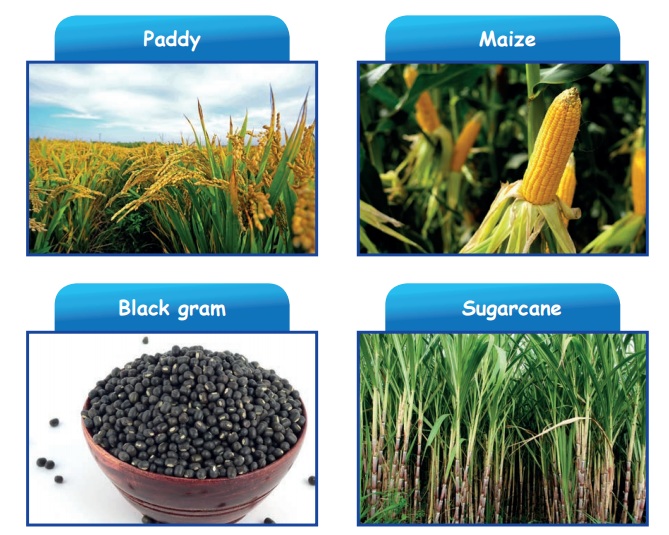

The cash crops include cotton,
sugarcane, oilseeds, coffee, tea, rubber, coconut, gingelly and chillies.
Mango and Banana are the leading fruit
crops of Tamil Nadu.
The main flowers grown in Tamil Nadu
are Jasmine, Chrysanthemum, Marigold and Rose.
Thanjavur is an important agricultural centre located in the Cauvery Delta. It is known as the Rice bowl of Tamil Nadu.
Think
Which State is known
as the Rice bowl of India?![]()
Answer: Andhra Pradesh is known as the Rice bowl of
India.
LET US KNOW
Cropping seasons in
Tamil Nadu
* Navarai
* Sornavari
* Kar
* Kuruvai
* Samba
* Thaladi
Coimbatore is the largest cotton producing district in Tamil Nadu. It is known as the Manchester of South India.
Glossary
1. Archaic: Ancient
2. Minimize: Reduce
3. Perennial : Everlast
Recap
* India is an agricultural country.
* Indian farmers are the backbone of
the Indian economy.
* There are several methods of
farming systems in India.
* There are four basic types of
irrigation.
* The principal food crops are rice, maize, jowar, bajra, ragi and pulses.
Related Topics