Human Development and its Challenges - Adulthood - Domains and Stages of Development | 11th Home Science : Chapter 2 : Human Development and its Challenges
Chapter: 11th Home Science : Chapter 2 : Human Development and its Challenges
Adulthood - Domains and Stages of Development
Adulthood
Adulthood is usually divide into subdivisions
or stages
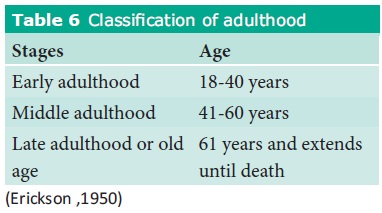
Expectations and developmental tasks during adulthood:
• Achieving
a measure of personal autonomy
• Molding
an identity
• Developing
emotional stability
• Establishing
and consolidating a career
• Becoming
a part of a social group or community
• Selecting
a mate and adjusting to marriage
• Establishing
residence and managing a home
• Becoming
a parent and rearing a child
Physical and Cognitive Changes during Adulthood
Physical Changes It has been found that the organ system of most per-sons show a 0.8 to 1 percent
decline per year in functional ability after the age of 30. Major physical
changes with ageing are described as (1) external changes (2) internal changes,
and (3) changes in sen-sory capacities.
1. External Changes
External changes refer to the outward
symp-toms of growing old. The more observable changes are those associated with
the skin, hair, teeth, and general posture.
·
Skin also becomes thick, hard, less elas-tic, brittle and dry
and wrinkled. With advancing age, the hair of the person continues to turn
white and loses its luster and continues to thin.
·
Baldness and loss of teeth is common for many, dentures become a
way of life.
·
Most weakening occurs in the back and leg muscles, less in the
arm muscles.
·
There is a progressive decline in energy production. Muscle
tissue decreases in size and strength.
2. Internal Changes
Internal changes refer to the symptoms of
growing old that are not visible or obvious.
The Respiratory System:
With increasing age, there is reduction in
breathing efficiency. Decreased oxygen supply makes the old person less active,
less aware and less strong.
The Gastrointestinal System:
With increasing age there is decreased
capacity for biting and chewing, decrease in the production of digestive
enzymes, decreased gastric and intestinal mobility and lack of appetite.
The Cardiovascular System:
With the aging process, there is a decrease in
the elasticity of blood vessels and blood cell production as well.
The Central Nervous System (CNS): Beginning at about age 60, there is a reduction of cerebral
blood flow. There is also a decline in oxygen and glucose con-sumption. The
most definite change is the slowing down of responses.
3. Changes in Sensory Capacities
With advancing age, there is gradual slow down
in the sensory abilities.
Vision:
·
Increasing age brings in several prob-lems in vision.
·
The lens continue to lose elasticity.
·
The pupils become smaller and irregu-lar in shape.
·
The eyelids have a tendency to sag.
·
Colour vision becomes less efficient.
Cognitive Changes during Adulthood and Aging
The four major aspects of cognition includes
memory, learning, attention and intelligence. Old persons are found to perform
poorer than young ones on long-term memory tasks which require pro-cessing of
information and organization of material. They are not in a position to learn
skills. Attention span is also found to be lower than younger individuals.
Intelligence tests indicate that old persons are slower on reaction time. Among
the elderly, we often can find reduced abilities for complex decision making
and slowing of performance.
Related Topics