Human Development and its Challenges - Adolescence - Growth and Development | 11th Home Science : Chapter 2 : Human Development and its Challenges
Chapter: 11th Home Science : Chapter 2 : Human Development and its Challenges
Adolescence - Growth and Development
Adolescence - Growth and Development
WHAT WILL YOU LEARN IN THIS LESSON?
·
Who is an adolescent?
·
Classification and definition of the adolescent period
·
Characteristicchanges during adolescence
Definition
Adolescence is derived from the Latin word
“adolescere” meaning to grow into maturing. The World Health Organisation
defines adolecence as any person between the age of 10 and 19. It is between
child-hood and adulthood and is closely related to the teen age years.
ADOLESCENTS : Persons between 10and 19 years of age

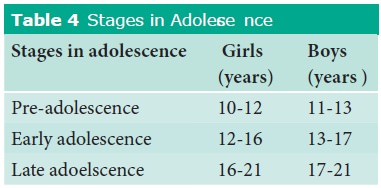
Stages of adolescence in boys and girls
Adolescence may be divided into three stages
namely pre adolescene, early ado-lescence and late adolescence.
The period of adolescence is extremely
important in one’s life because at this stage, one moves from childhood to the
onset of maturity. In every period of devel-opment from birth onwards a person
may face many challenges due to the changes that occur during that period. Each
phase in life has distinct characteristics.
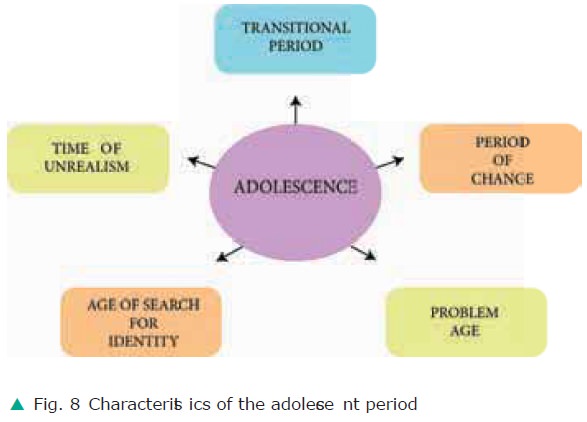
Characteristics of the Adolescent Period
(i) Transitional period
Adolescence is a period of transition. During
this phase the individuals status is vague and there is a confusion about the
roles they are expected to play as they are neither children nor adults.
(ii) Period of change
The stage of adolescence is characterized by
changes in physical, cognitive, social and emotional areas of their lives. This
sets them apart and uniquely distinguishes them from other stages
(a) Physical changes
During adolescence, primary sex
charac-teristics (the reproductive organs) develop and mature and secondary sex
character-istics appear.
Primary Sex characteristics- In males, the testes grow rapidly during the first year or two of
puberty. After that, the penis starts to grow in length and the seminal ducts
and the prostate gland enlarge. The female uterus, fallopian tube and vagina
grow rap-idly through puberty. The ovaries produce ova and secrete the hormones
needed for pregnancy, menstruation and the develop-ment of secondary sex
characteristics.

The secondary sex characteris tics are those which are not directly tied to reproduction yet distinguish the male from the female species. The secondary sex characteristics between boys and girls are given in the table above:
(b) Cognitive changes in adolescents .
In this stage, adolescents develop the
abil-ity to process Information, improve in areas of decision making, memory,
criti-cal thinking and self-regulatory learning. This is known as the ‘Formal
Operation Stage of Development’
(c) Social Changes and Development During Adolescence
Friendship during adolescence is based on
similarities and interests . The com-mon social groups in adolescence is as
follows:
Chums- close friends – They are inseperable
companions as confidants Cliques – They are made up of groups of close friends
Crowds – they are made up of cliques and close
friends
Organised groups – These groups are planned by
orgainised sectors like schools, churches or community centres
Gangs- They are a group of boys and/or girls
who are poorly adjusted to society
Individual activity 3
Who
are your chums? – What criteria do you have to select your confidants?
How
many members are there in your clique? What are your common interests?
Are
you part of an organized group? List any three social causes addressed by your
group.
DO YOU KNOW?
Every
5th person in India is an adolescent
–
Hence adolescents are a very precious segment of the population.
Significant changes in the area of social
development occur in the period of ado-lescence with regard to their peers and
relationship with adults.
Relationship with peers-
Adolescents are very much
influenced by their peer group. Their behaviour and attitude are affected by
peers.
Relationship with adults- Adoles-cents develop values different from the ones held by adults because the influence of peer group is more than that of adults. Hence the adolescent is torn between his loyalty to his parents and peers. Their values often clash with those of adults and many rebel against parental authority.
(d) Emotional changes
Adolescence is said to be a period of
heightened emotionality. Heightened emotionality is a state of more than normal
emotional experience. This period is often known as the “period of storm and
stress”. The word storm and stress suggest anger and turmoil.

Causes for Heightened Emotionality
The major causes for heightened emotion-ality
are as follows:
· Psychological problems due to phys-ical changes – Sudden spurt in
height, appearance of secondary sex characteris-tics, voice change,
appearance of pimples and acne, on the face. etc. cause much embarrassment to
them and they become worried about their physical appearances.
· Social expectations- Adolescents are treated neither as a
child nor as an adult. The constant pressure to live up to social expectations
causes a generalized state of anxiety in them.
· Unrealistic aspirations- Adolescent aspirations are
sometimes unrealistic. When they are not able to attain them they feel inferior
and frustrated.
· Urge for sex- Reproductive hor-mones are active and so there
is the presence of sex urge. This may lead to anxiety.
·
Identity crises- The adolescent is expected to form a realistic self-concept. They have to try out
different roles and develop a holistic idea of their future role. Until they
find their role they are often confused and anxious
·
Unfavorable family
relationships- Conflicts often occur between adults and adolescents due to the
generation gap between them.
(iii) Adolescence is a problem age
Adolescence is known as a problem age because
they are faced with many chal-lenges that arise due to the anatomical,
psychological changes. This is further enhanced by peer pressure and conflicts
with parents and elders. Most of these problems are aggravated due to
mislead-ing and misguiding parents, teachers and friends, ignorance of elders,
being half informed or ill-informed about the real-ities in life and wrong
messages and con-cepts depicted though the media
(iv) Adolescence is period when there is search for identity
Adolescence is the period of transition
between childhood and adulthood. It is a stressful and confusing period because
at times they are expected by the society to think and behave in mature manner.
At the same time, they are often reprimanded for the same and are demanded to
be meek and submis-sive as they are under the control of parents, elders and
teachers. The conflicts that arise due to this, cause a lot of stress among
ado-lescents as they are confused whether they should be like children or
behave as adults.
(v) Adolescence is a time of unrealism
Many adolescents have unrealistic goals and
aspirations. They live in an imaginary world. These unrealistic thinking
pattern may often lead to anxiety and depression especially when they are not
able to fulfill their goals. For this purpose, it is impor-tant for parents,
teachers and elders to guide adolescents into identifying their strengths,
weakness, opportunities and challenges and help them set realistic goals based
on available resources.
National Youth Day is celebrated in India on 12 January on the birth-day
of Swami Vivekananda. In 1984 the Government of India declared the day as the
National Youth Day and since 1985 the event is celebrated in India every year.
To quote from the Government of India's communica-tion, 'it was felt that the
philosophy of Swamiji and the ideals for which he lived and worked could be a
great source of inspiration for the Indian Youth.'
JUVENILE DELINQUENCY
Delinquency is a problem associated with the
period of adolescence. It is engaging in activities which are against law and
are pun-ishable. When a delinquent act is committed by a child or young person
before the age of age of 18 it is called juvenile delinquency.
A list of delinquent act by minors include
committing theft of valuables, burglary, looting, black mailing, murdering,
rap-ing, leading immoral life like prostitu-tion, drinking, gambling,
smuggling, drug addiction and anti-social acts like damag-ing public utilities
etc.
Causes of delinquency
i. Personal causes- A person’s physi-cal defects, aggressiveness
and low intelligence make a person prone to delinquency.
ii.
Family causes- Children from bro-ken
homes lack love and affection and a feeling of security. They tend to seek the
comfort from peers involving antisocial activities
iii.
Community factors- Numerous of community factors are proved to insti-gate the adolescents
towards delinquency. They are
a.
Poor housing – Poor housing is a symbol of poor economic and social status. Overcrowding in poor
houses and lack of privacy is said to be a cause for committing sex offences.
b.
Poor recreational facilities – In absence of good recreational facil-ities, delinquency itself
becomes a recreational activity.
c.
Poor schools – Many factors in school contribute to delinquency. Nagging by peers, lack of
under-standing from teachers, unhappy home- school relationship make children
dislike the school and engage in antisocial behaviour
d.
Unemployment – Unemployment among school dropouts and those who have no secured jobs tend to
cause delinquency.
e.
Movies and comic books- Crime, gangster movies, glamour and sex movies stimulate young people
to commit offences.

Prevention of delinquency
·
Satisfactory adult-adolescent relation-ship, absence of feeling
of rejection and presence of love and affection among members of the family
will be of much help in preventing delinquency.
·
Community efforts by parent teachers association, schools,
religious institu-tions, social workers, counselors and voluntary organizations
play a major role in guiding children.
·
Mass media such as radio, television and newspaper should
educate parents and the society on proper treatment of children.
·
Educational Institutions can have pro-grammes such as “Earn
While You Learn” by engaging adolescents in use-ful activities.
Related Topics