Zoology - Activity, Case Study and Summary - Kingdom Animalia | 11th Zoology : Chapter 2 : Kingdom Animalia
Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 2 : Kingdom Animalia
Activity, Case Study and Summary - Kingdom Animalia
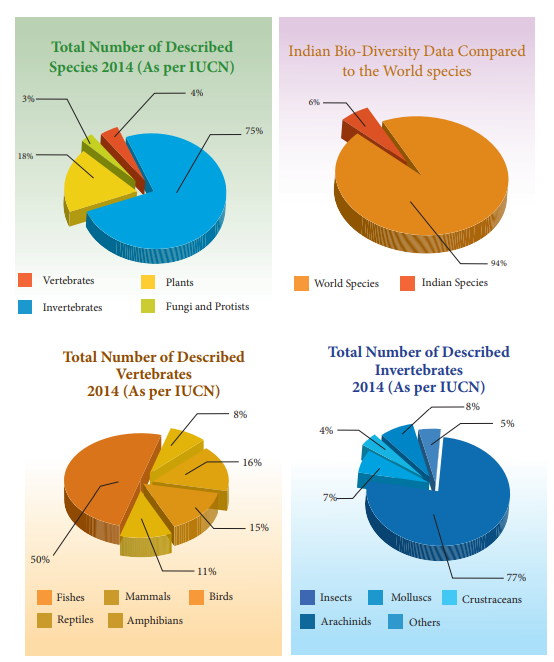
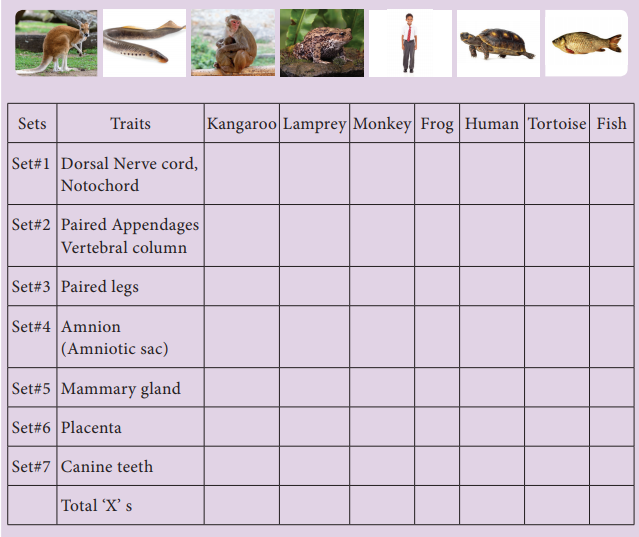
Activity
Objectives:
Some
Groups of organisms with their distinguishing characteristics are given.
Con-struct a cladogram, interpret and analyze the cladogram in terms of how it
shows common ancestry and degrees of evolutionary relationship.
Procedure:
Step 1.
Refer your text book and identify the characteristics of the given animals. In
the data table provided, place an “x” in the box if the animal has the
characteristic.
Step 2:
Below the Data Table on the Worksheet, make a Venn diagram, placing animals in
groups to illustrate those characteristics which different animals have in
common.
Step 3:
Using the Venn diagram draw a cladogram to illustrate the ancestry of these
animals. The diagram should reflect the shared characteristics as time
proceeds.
Step 4:
Draw the Venn diagram to reflect the shared characteristics of the given
ani-mal and draw a cladogram.
CASE STUDY
Sálim
Moizuddin Abdul Ali is the leading pioneer of Indian Ornithology and generally
referred as Bird Man of India. He was born on 12 November 1896 in Bombay and he
was the most respected and influential naturalist of 20th century in India, He
passed away on 20 June 1987. Young Salim got interested in birds when he was at
the age of ten. Later he has conducted many systematic bird surveys across
India and the neighboring countries. He authored many bird books and popularized
ornithology in India. ‘Book of Indian birds’ and the ‘Hand book of Birds of
India and Pakistan’ are the most important books he has written. His
autobiography ‘Fall of a sparrow’ narrates the beginning and experience of his
life with birds. Government of India honoured him with the award of Padma
Bhusahan in 1958 and Padma Vibhushan 1976. He was nominated to Rajyasabha in
1985. Salim Ali through his books motivated thousands of people to the field of
ornithology and natural history. Most of the environmentalists in India trace
back their initial motivation to bird watching and Salim Ali’s books.
In 1990,
Government of India started a national research institution in his honour
called Sálim Ali Centre for Ornithology and Natural History (SACON) in Coimbatore,
Tamil Nadu. SACON is a Centre of excellence in research supported by the
Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India. All
the researches and activities of SACON is devoted to the cause of conservation
of India’s Biodiversity with focus on birds. The main campus of SACON is
situated in the sylvan surrounding of Anaikatty, 24 kilometers northwest of
Coimbatore city, within the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve. SACON’s mission is to
help conserve India’s biodiversity and its sustainable use through research,
education and people’s participation with birds at the centre stage. SACON
conducts research in Ornithology covering all aspects of biodiversity and
natural history. More than 50 research scholars have completed PhD in Ornithology
and Natural history from SACON in its 25 years of existence. SACON is known for
its many research papers published in national and international journals.
Nature Education programme of SACON is very popular in the region which is
inculcating love for birds and nature to thousands of people especially to
school children every year. Children’s Ecology Congress of SACON and Salim Ali
Trophy Nature Competitions are flagship events. Salim Ali Naturalist Forum of
SACON is the people’s bird watching movement in Coimbatore facilitated by
SACON.
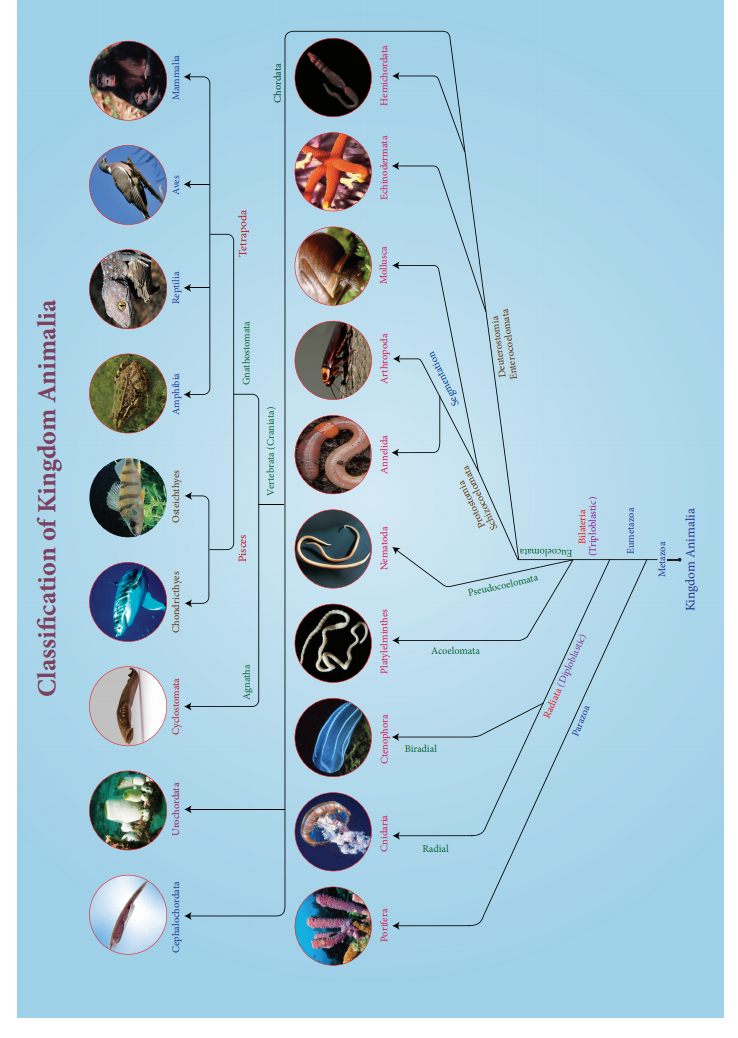
Summary
Kingdom
Animalia comprises of a broad range of animal species, from tiny parasitic
nematodes to the largest mammal the blue whale. The basic fundamental features
such as levels of organisation, diploblastic and triploblastic organisation,
patterns of symmetry, coelom, segmentation and notochord have enabled us to
broadly classify the animal kingdom. Besides the fundamental features, there
are many other distinctive characters which are specific for each phyla or
class.
Animals
are broadly classified into invertebrates and chordates. The animals which lack
vertebral column are called invertebrates. The chordates are characterized by
the presence of notochord, solidventralnervecordandgillslits.Kingdom Animalia are
classified into eleven animal phyla as Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora,
Platyhelminthes, Aschelminthes, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata,
Hemichordata and Chordata. Chordata is the largest phylum with three sup phyla
Urochordata, Cephalochordata and Vertebrata. Subphylum Vertebrata includes two
divisions, Agnatha and Gnathostomata. Agnatha comprises of the class
Cyclostomata. Gnathostomata includes jawed fishes (Pisces) and Tetrapoda which
includes the classes amphibia, reptilia, aves and mammals.
Related Topics