Chapter: Pharmaceutical Drug Analysis: Non-Aqueous Titrations
Acidimetry in Non-Aqueous Titrations
ACIDIMETRY IN NON-AQUEOUS TITRATIONS
In order to perform feasible titrations of weak bases,
the solvent system should be selected specifically in such a fashion so as to
eliminate as far as possible the competing reaction of water for the proton
besides enhancing the strength of the basic species.
1. Titration of primary, secondary and tertiary amines
1.1. Methlyldopa
In general, the reaction taking place between a primary
amine and perchloric acid may be expressed as follows :
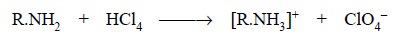
The specific reaction between methyldopa and perchloric
acid is expressed by the following equation :
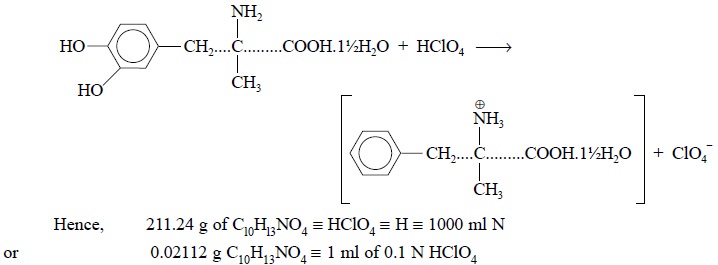
Materials Required : Methyldopa 0.2 g ; anhydrous
formic acid : 15 ml ; glacial acetic acid : 30 ml ; dioxane : 30 ml ; 0.1 N
perchloric acid and crystal violet solution.
Procedure : Weigh accurately about 0.2 g
and dissolve in 15 ml of anhydrous formic acid, 30 ml of glacial acetic acid and 30 ml of dioxane. Add 0.1 ml of crystal
violet solution and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid. Perform a blank
determination and make any necessary correction. Each ml of 0.1 N perchloric
acid is equivalent to 0.02112 g of C10H13NO4.
Calculations : The percentage of methyldopa
present in the sample is given by :
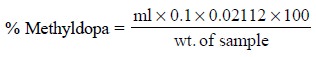
1.2. Methacholine Clloride
Materials Required : Methacholine chloride : 0.4 g ;
glacial acetic acid : 50 ml ; mercuric acetate solution : 10 ml ; 0.1 N
perchloric acid and crystal violet solution.
Procedure : Weigh accurately about 0.4 g,
previously dried and stored in a vacuum desiccator, and dissolve in 50 ml of glacial acetic acid, add 10 ml of mercuric
acetate solution, one drop of crystal violet solution and titrate with 0.1 N
perchloric acid to a blue-green end point. Perform a blank determination and
make any necessary correction. Each ml of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent
to 0.01957 g of C8Hl8ClNO2.
Equation :
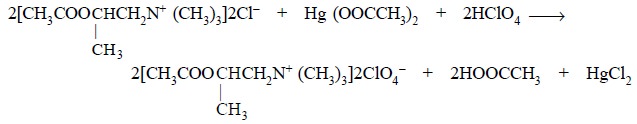
Mercuric acetate : It is essentially added to
prevent the interference of the hydrochloric acid dis-placed through the
formation of the relatively un-ionized HgCl2, thereby making a
predominant shift in the equilibrium so that the titrimetric reaction is
quantitative.
Blank Titration : It is usually carried out to
account for the possible reaction of atmospheric moisture with the titrant perchloric acid and also to check the titrant
being employed to bring about the blue-green end-point.
Calculations : The percentage of methacholine
chloride in the sample may be calculated by
the following expression :
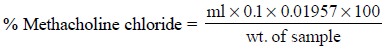
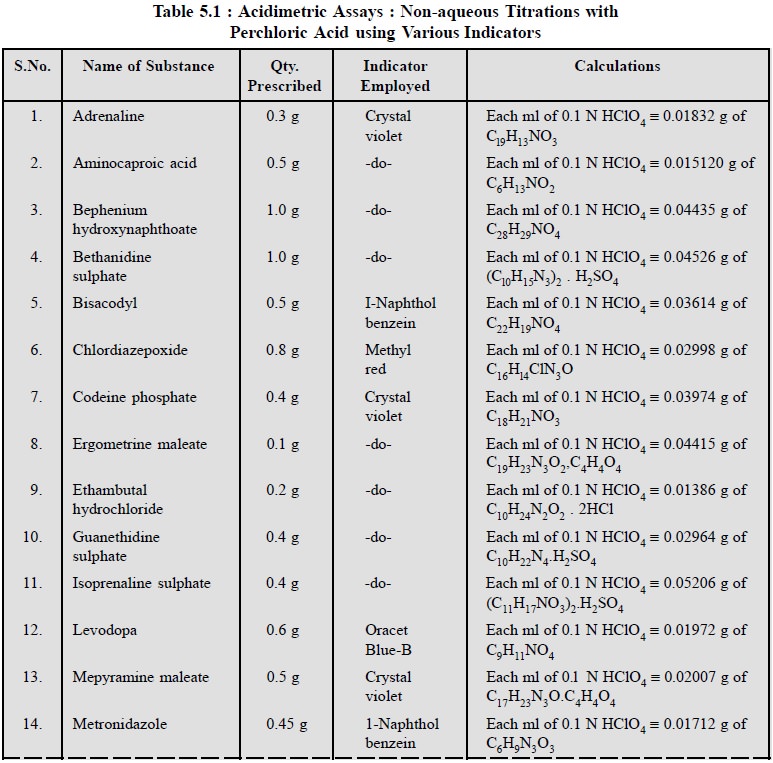
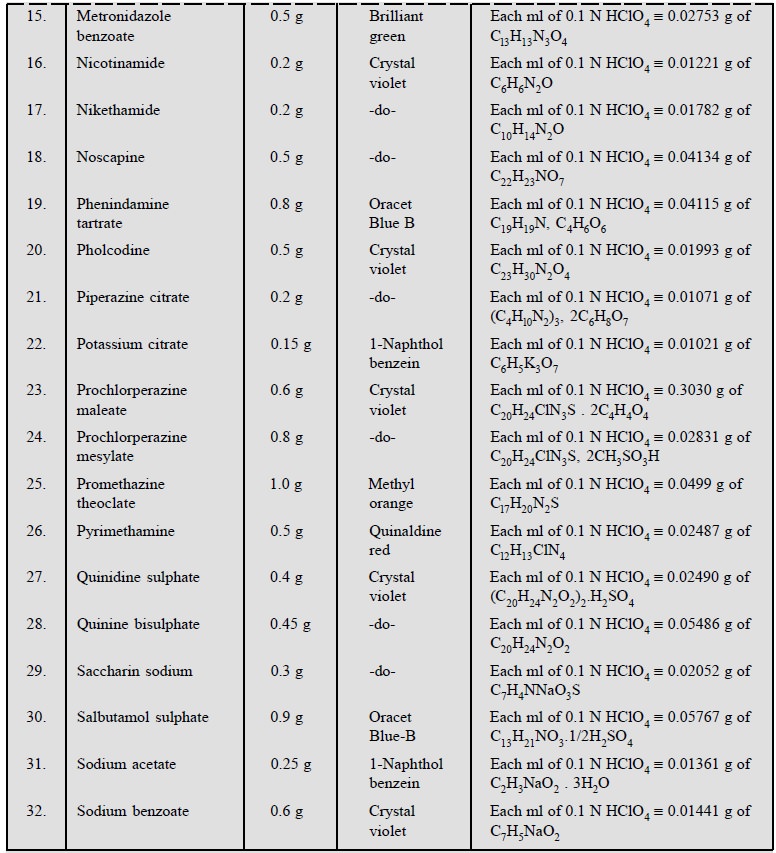
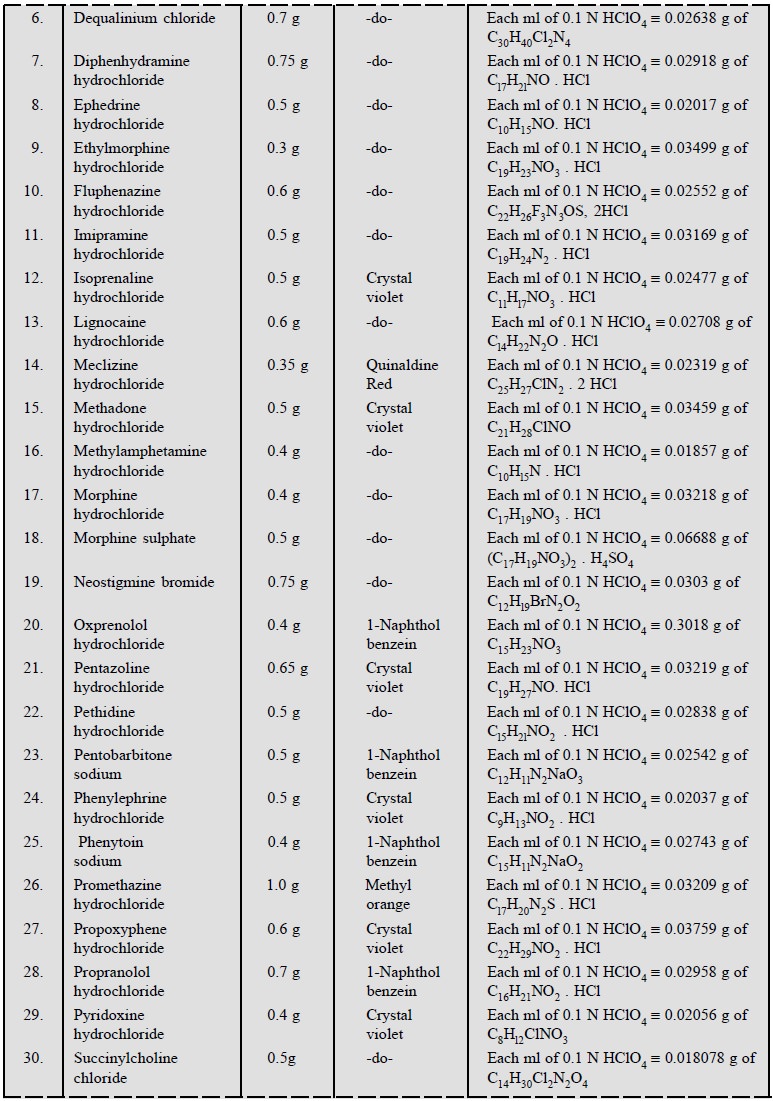
1.3. Cognate Assays
Table 5.1, enlists the various cognate determinations
using different indicators but employing the same titrant i.e., 0.1 N perchloric acid.
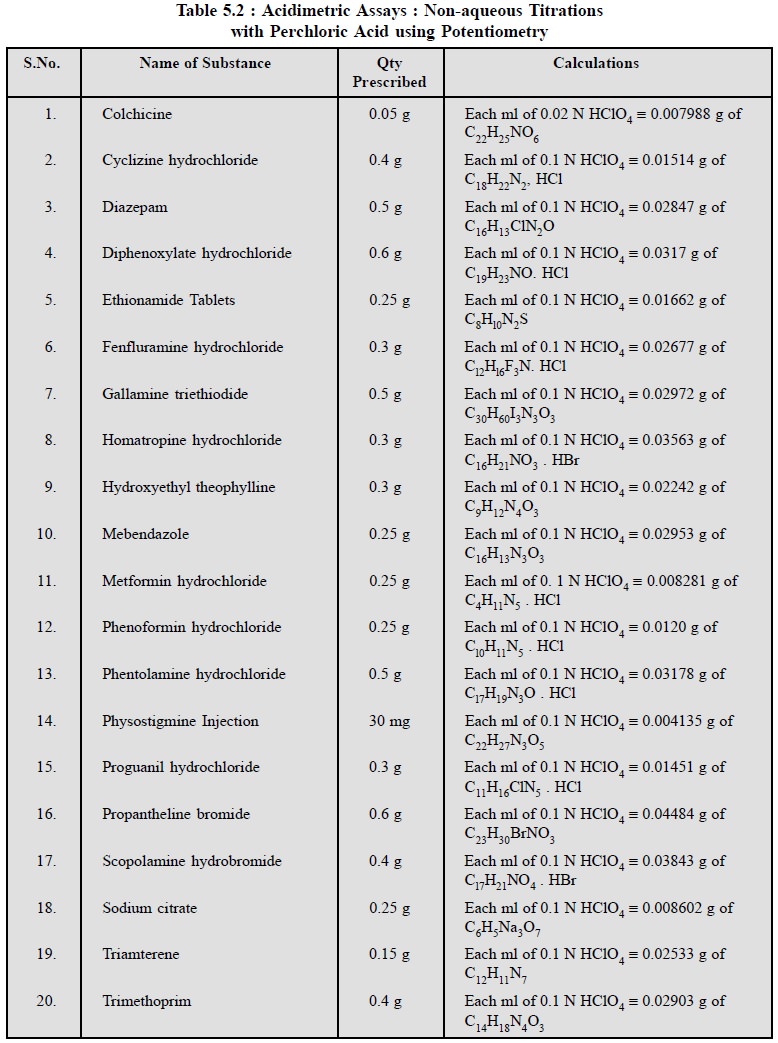
1.4. Potentiometric Titrations
These non-aqueous titrations may also be carried out with
the help of potentiometric titrations which technique shall be discussed at
length elsewhere in this book.
It is always preferred to first ascertain the equivalence
point of a given neutralization reaction potentiometrically (i.e., an instrumental method of
analysis) ; and secondly, by selecting an appropriate indicator that will
ensure the sharpest colour change for the least increment of volume of titrant
added near the equivalence point.
In actual practice, however, there are quite a number of
non-aqueous titrations of pharmaceutical substances either in pure or in dosage
forms that can be successfully performed potentiometrically.
2. Titration of Halogen Acid Salts of Bases
In general, the halide ions, namely : chloride, bromide
and iodide are very weakly basic in character so much so that they cannot react
quantitatively with acetous perchloric acid. In order to overcome this problem,
mercuric acetate is usually added (it remains undissociated in acetic acid
solution) to a halide salt thereby causing the replacement of halide ion by an
equivalent amount of acetate ion, which serves as a strong base in acetic acid
as shown below :
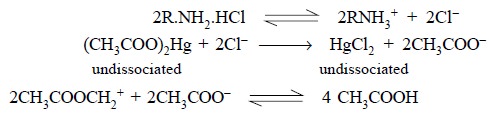
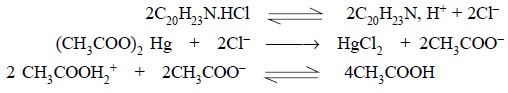
2.A. Amitriptyline Hydrochloride
Materials Required : Amitriptyline hydrochloride :
1.0 g ; mercuric acetate ; crystal violet ; 0.1 N perchloric acid ; glacial acetic acid.
Procedure : Weigh accurately about 1.0 g
and dissolve in 50 ml of glacial acetic acid, warming slightly, if necessary, to affect the solution. Cool, add 10 ml of
mercuric acetate solution, two drops of crystal violet solution and titrate
with 0.1 N perchloric acid to a green end-point. Perform a blank determination
and make any necessary correction. Each ml of 0.1 N perchloric acid is
equivalent to 0.03139 g of C20H23N. HCl.
Equations :
Calculations :
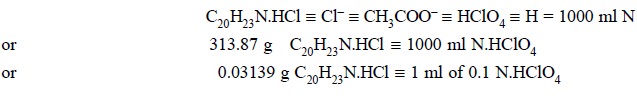
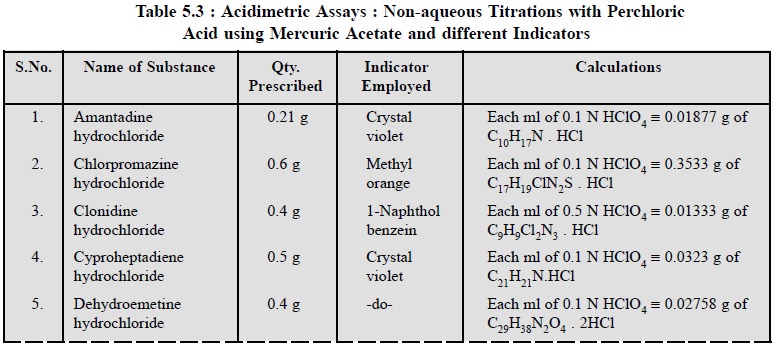
3. Cognate Assays
The following estimations of various pharmaceutical
substances can also be carried out by the aforesaid procedure (Table 5.3) :

Related Topics