Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy
What changes in preload, afterload, heart rate, and contractility will optimize hemodynamic performance in a patient with HOCM?
What changes in preload, afterload, heart rate, and contractility
will optimize hemodynamic performance in a patient with HOCM?
Determinants of the severity of the ventricular
obstruc-tion in HOCM are:
·
systolic
volume of the ventricle
·
force of
ventricular contraction
·
transmural
pressure distending the outflow tract
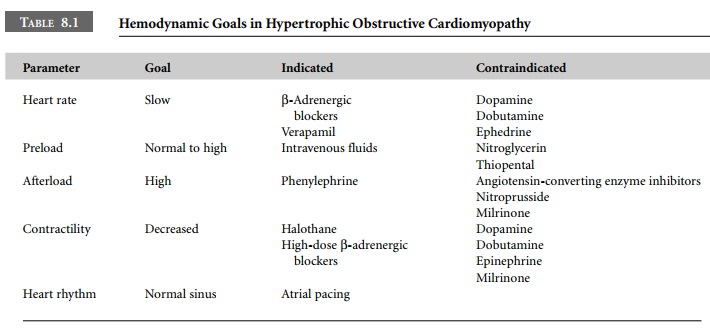
Large systolic volumes in the ventricle distend
the out-flow tract and reduce the obstruction. Paradoxically, when ventricular
contractility is increased, the outflow tract is narrowed, which increases the
obstruction and decreases cardiac output. When aortic pressure (afterload) is
ele-vated, there is an increased transmural pressure distending the LVOT during
systole and this reduces the degree of obstruction. However, during periods of
systemic vasodila-tion the outflow tract is narrowed. This results in marked
decreases in cardiac output and even mitral regurgitation as the mitral valve
becomes the relief point for ventricular pressure (Table 8.1).
Related Topics