Probability Distributions - Summary | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 7 : Probability Distributions
Chapter: 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 7 : Probability Distributions
Summary
Summary
·
Conditions for the binomial probability
distribution are
(i) the trials are independent
(ii) the number of trials is finite
(iii) each trial has only two possible
outcomes called success and failure.
(iv) the probability of success in each
trial is a constant.
·
The probability for exactly x success in
n independent trials is given by
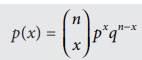 where x = 0,1,2,3…..n and
q = 1 – p
where x = 0,1,2,3…..n and
q = 1 – p
·
The parameters of the binomial
distributions are n and p
·
The mean of the binomial distribution is
np and variance are npq
·
Poisson distribution as limiting form of
binomial distribution when n is large, p is small and np is finite.
·
The Poisson probability distribution is
p(x) = 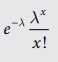 X = 0,1,2,3… Where λ = np
X = 0,1,2,3… Where λ = np
·
The mean and variance of the poisson
distribtution is λ.
·
The λ is the only parameter of poisson
distribution.
·
Poisson distribution can never be
symmetrical.
·
It is a distribution for rare events.
·
Normal distribution is the limiting form
of binomial distribution when n is large and neither p nor q is small
·
The normal probability distribution is
given by 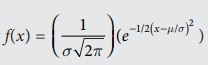
·
The mean of the distribution is μ
·
The sd of the distribution is σ.
·
It is a symmetrical distribution
·
The graph of the distribution is bell
shaped
·
In normal distribution the mean, median
and mode are equal
·
The points of inflexion are μ – σ and μ
+ σ
·
The normal curve approaches the horizontal
axis asymptotically
·
Area Property : In a normal distribution
about 68% of the item will lie between μ – σ and μ + σ. About 95% will lie
between are μ –2 σ and μ + 2σ . About 99% will lie between μ –3 σ and μ +3 σ.
·
Standard normal random variate is
denoted as Z = (X – μ)/σ
·
The standard normal probability
distribution is 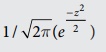
·
The mean of the distribution is zero and
SD is unity
·
The points of inflexion are at z = –1
and z = +1
Related Topics