Chapter: Essentials of Psychiatry: Substance Abuse: Alcohol Use Disorders
Screening - Alcohol Use Disorders
Screening
Systematic clinical assessment often begins with
routine screen-ing to identify active cases, as well as persons at risk. During
the past 25 years a number of self-report screening tests have been developed
to identify alcoholics as well as persons at risk of alco-hol problems. The
Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test (MAST), developed by Selzer (1971), is one
of the most often cited instru-ments. It contains 25 items that ask about
drinking habits, as well as social, occupational and interpersonal problems associated
with excessive drinking. A total score is calculated, placing the individual
along a continuum from “nonalcohol dependent” to “definitely alcohol
dependent”. There are several shortened ver-sions of the MAST (e.g., the
10-item Brief MAST, the 13-item Short MAST and the 35-item Self-Administered
Alcohol Screen-ing Test – SAAST). Perhaps the most widely used alcohol
screen-ing test is the CAGE (Ewing, 1984), which contains only four questions:
1) Have you ever felt you ought to Cut
(the “C” in CAGE) down on your drinking? 2) Have people Annoyed (A) you by criticizing your drinking? 3) Have you ever felt
bad or Guilty (G) about your
drinking? 4) Have you ever had a drink first thing in the morning to steady
your nerves or get rid of a hangover that is, an Eye opener (E)? Reliability and validity studies of this test have
been conducted in diverse samples (e.g., psychiatric inpatients, ambulatory
medical patients, prenatal clinics), with generally acceptable levels of
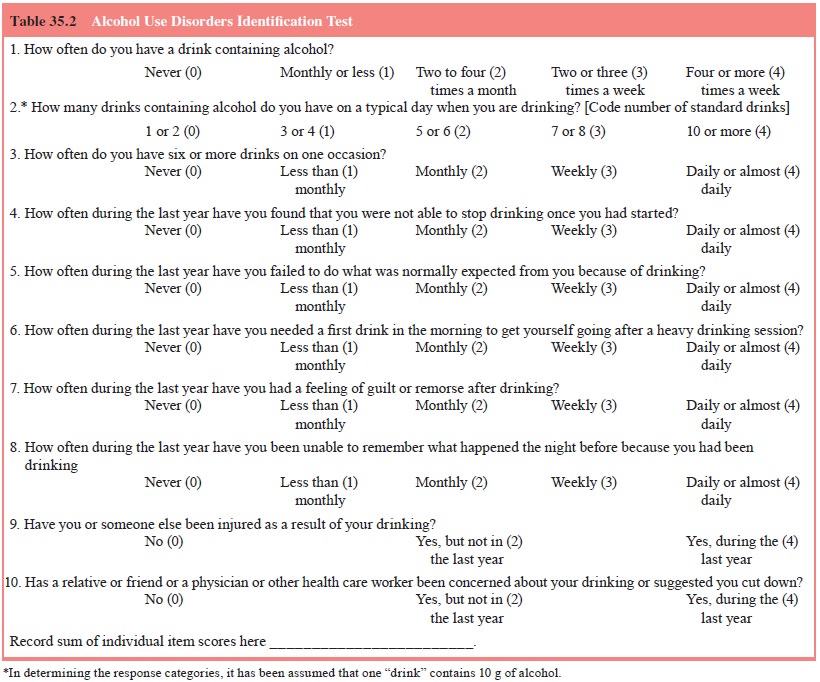
sensitivity. The Alcohol Use Dis-orders Identification Test (AUDIT) (Saunders et al., 1993; Babor), a 10-item
screening instrument, may be used as the first step in a comprehensive and
sequential alcohol use history. The AUDIT (Table 35.2) covers the domains of
alcohol consumption, symp-toms of alcohol dependence and alcohol-related
consequences. It has been shown to be sensitive and specific in discriminating
alcoholics from nonalcoholics, and is superior to the MAST in identifying
hazardous drinkers, that is, those heavy drinkers who have not yet experienced
serious harm from their drinking (Bohn et
al., 1995). The AUDIT total score increases with the severity of alcohol dependence and related
problems, and can be used as part of a comprehensive approach to early
identification and pa-tient placement. Because the misuse of both prescribed
and illicit.
drugs is common among alcoholics, screening should
include other psychoactive substances, including tobacco products.
Related Topics