Chapter: Mechanical : Advanced IC Engines : Alternate Fuels
LPG as Alternate fuels
LPG as Alternate fuels:
LPG is
typically a mixture of several gases in varying proportions. Major constituent
gases are propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10), with minor quantities of propane
(C3H6), various butanes (C4H8), iso-butane, and small amounts of ethane (C2H6).
The composition of commercial LPG is quite variable. About 55% of the LPG
processed from natural gas purification. The other 45% comes from crude oil
refining. LPG is derived from petroleum; LPG does less to relieve the country’s
dependency on foreign oil than some other alternative fuels. The gaseous nature
of the fuel/air mixture in an LPG vehicle’s combustion chambers eliminates the
cold-start problems associated with liquid fuels. LPG defuses in air fuel
mixing at lower inlet temperature than is possible with either gasoline or diesel.
This leads to easier starting, more reliable idling, smoother acceleration and
more complete and efficient burning with less unburned hydrocarbons present in
the exhaust. In contrast to gasoline engines, which produce high emission
levels while running cold, LPG engine emissions remain similar whether the
engine is cold or hot. Also, because LPG enters an engine’s combustion chambers
as a vapor, it does not strip oil from cylinder walls or dilute the oil when
the engine is cold. This helps to have a longer service life and reduced
maintenance costs of engine.
Also
helping in this regard is the fuel’s high hydrogen-to-carbon ratio (C3H8),
which enables propane-powered vehicles to have less carbon build-up than
gasoline and diesel-powered vehicles. LPG delivers roughly the same power,
acceleration, and cruising speed characteristics as gasoline. Its high octane
rating means engine’s power output and fuel efficiency can be increased beyond
what would be possible with a gasoline engine without causing Destructive Knocking. Such fine-tuning
can help compensate for the fuel’s lower energy density. The higher ignition
temperature of gas compared with petroleum based fuel leads to reduced auto
ignition delays,less hazardous than any other petroleum based fuel and expected
to produce less CO, NOx emissions and may cause less ozone formation than
gasoline and diesel engines.
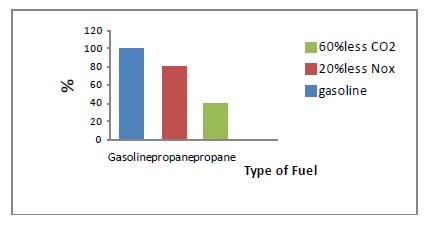
LPG engines similar to petrol engines, and deliver nearly similar performance and good in combustion characteristics than Gasoline. In the short term, LPG as a alternative fuels reviewed could displace 10 per cent of current usage of oil, or bring significant reductions in CO, CO2 emissions and help to reduce harmful greenhouse gas emissions. In the next five to ten years, LPG will be more widely available and gaining market share across vehicle ranges.
Related Topics