Definition, Classifications, Effects, Therapeutic Uses, Principles, Complications and Contraindications - Hot and Cold Applications | 11th Nursing : Chapter 8 : Nursing Procedures
Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 8 : Nursing Procedures
Hot and Cold Applications
Hot and Cold Applications
Definition
Hot application is the
application of hot agent, warmer than skin either in a moist or dry form on the
surface of the body to relieve pain and congestion, to provide warmth, to
promote suppuration, to promote healing, to decrease muscle tone and to softens
the exudates.
Cold application is
the application of cold agent, cooler than skin either in a moist or dry form
on the surface of the body to relieve pain and body temperature, to
anaesthetize an area, to check hemorrhage, to control growth of bacteria, to
prevent gangrene, to prevent oedema and reduce inflammation.
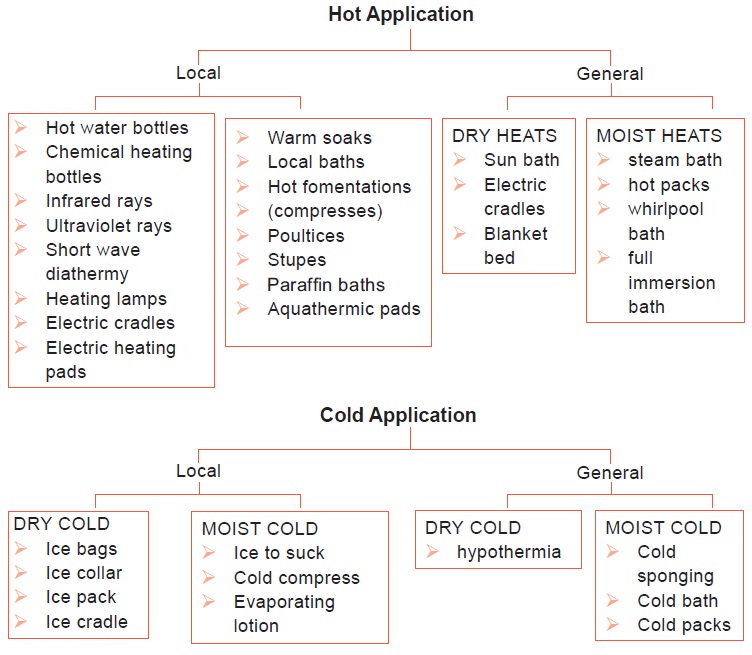
Classifications
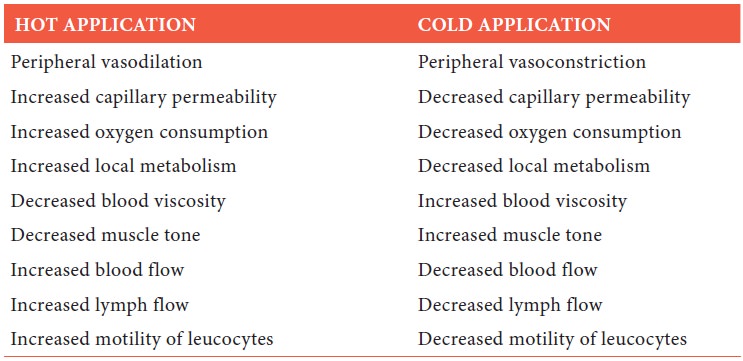
Effects of Hot and Cold Applications
Therapeutic Uses of Local Hot Applications
·
Heat decreases pain
·
Heat decreases muscle tone
·
Heat promotes healing
·
Heat promotes suppuration
·
Heat relieves deep suppuration
·
Heat provides warmth
·
Heat stimulates peristalsis
Therapeutic Uses of Local Cold Applications
·
Cold relieves pain
·
Prevents gangrene
·
Prevents edema and reduce inflammation
·
Controls hemorrhages
·
Checks the growth of bacteria
·
Reduce the body temperature
·
Cold anaesthetize an area
Principles of Hot and Cold Applications
1.
Water is good conductor of heat.
2.
Air is poor conductor of heat.
3.
Heat always flows from hotter area to the less hot area.
4.
Prolong exposure to moisture increases the skin susceptibility
to maceration and skin breakdown, reducing the protection of the intact skin.
5.
Moisture left on the skin cause rapid cooling due to evaporation
of the moisture.
6.
Presence of steam increases the temperature of the hot
application
7.
Oil acts as the insulator and delays the transmission of the
heat.
8.
Woolen materials absorb moisture slowly, but hold the moisture
longer and cold off less quickly than the cotton materials.
9.
When immersed in water the body becomes buoyant therefore the
exercises are performed under water with less effort.
10.
The temperature tolerance varies with individuals and according
to the site and area covered.
11.
The end organs of the sensory nerves of the skin convey the
sensation of cold, heat pain and pressure. The sensation is interpreted in the
brain.
12. Friction produces
heat.
Contraindications of Hot Applications
·
Heat is not used in malignancies
·
Heat is not used in patients with heart, kidney and lung
diseases
·
Should not used in acute inflamed areas.
·
Should not be applied on patients with paralysis.
·
Should not be applied on open wounds
·
Should not be applied when there is an edema associated with
venous or lymphatic diseases.
·
Should not be applied on patients with metabolic disorders.
·
Should not be applied on very young and very old patients.
· Should not be applied on clients with high temperature.
Contraindications of Cold Applications
·
Cold should not be applied on clients who are in the stage of
shock and collapse
·
Cold should not be applied when there is edema.
·
Cold should not be applied on clients with circulatory
disorders.
·
Cold should not be applied on patients with decreased sensation
·
Patients with shivering and very low temperature,
·
Cold should not be applied when there is infected wound.
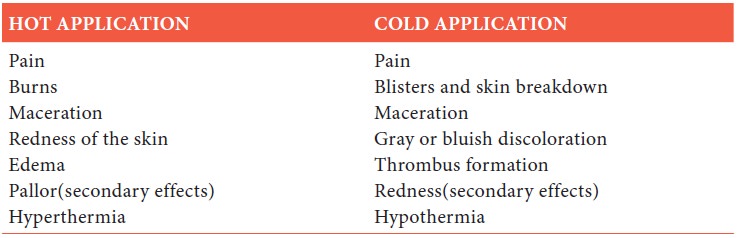
Complications of Hot and Cold Applications
General Instructions
·
Asses the condition the clients before and after the hot and
cold applications.
·
Maintain the correct temperature for the entire duration of the
application
·
Expose the client only to the safe temperature.
·
Do not allow the clients to adjust the temperature control of
appliance such as short wave diathermy, electric heating pads etc.
·
Never ignore the complaints of clients however small they appear
to be.
·
Always make sure that the client is in position to remove the application
·
The client must have a calling signal within reach
·
Never leave a client alone even for a short period that cannot
move from the appliances.
·
A thin layer of petroleum jelly or oil should be applied to the
skin prior the application of moist heat application.
·
Do not use electrical appliances near to open oxygen. A small
spark may cause explosion.
·
Do not handle electrical appliances with the wet hands.
·
Hot and cold applications must be very carefully used when the
clients is unconscious, anaesthetized or otherwise unable to respond pain.
·
Any signs of complications should be recognized early, the
procedure should be stopped immediately.
·
After the procedure, dry the part gently by patting and not by
rubbing to remove the moisture.
·
In hyperpyrexia, the temperature of the body should be brought
down gradually and steadily, sudden cooling is dangerous to the client.
Related Topics