Definition, Methods, Description, Advantages, Disadvantages, Articles, Procedure - Oxygen Therapy | 11th Nursing : Chapter 8 : Nursing Procedures
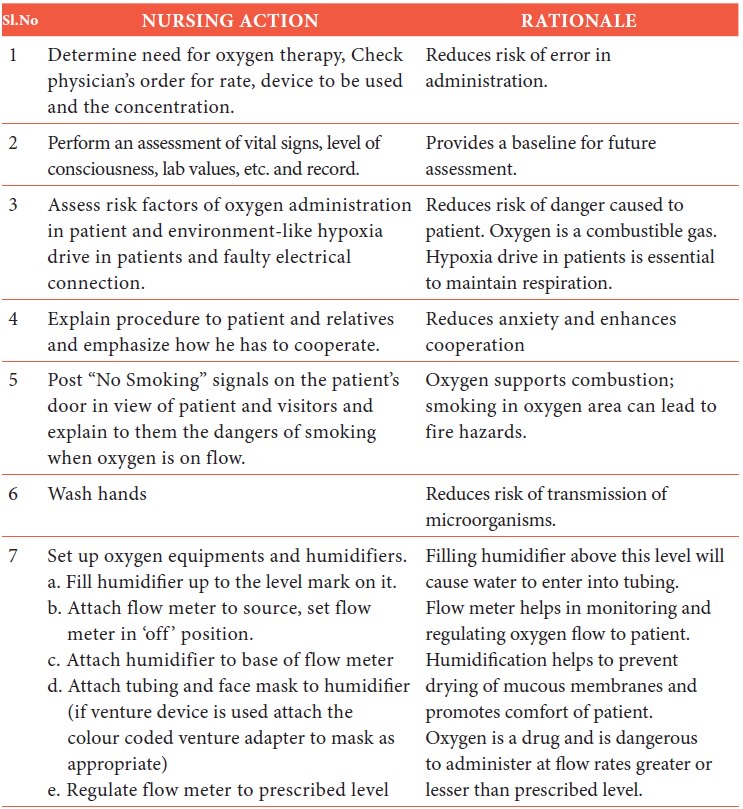
Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 8 : Nursing Procedures
Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen Therapy
Definition
Oxygen therapy refers
to supplemental oxygen given to people with breathing disorders.
Methods
·
Nasal Cannula method
·
Oxygen tent method/Oxyhood method Simple mask method
·
Venture mask method
Sources
·
Oxygen cylinder
·
Oxygen wall outlet
Indications
·
Shock
·
Poisoning Trauma
·
Anaesthesia Cardiac failure
·
Respiration failure
Cannula Method
Definition
A method by which
oxygen is administered in low concentration through a cannula, which is
disposable plastic device with two protruding prongs for insertion into the
nostrils.
Purpose
·
To relieve dysponea.
·
To administer low concentration of oxygen to patients.
·
To allow uninterrupted supply of oxygen during activities like
eating, drinking, etc.
Procedure
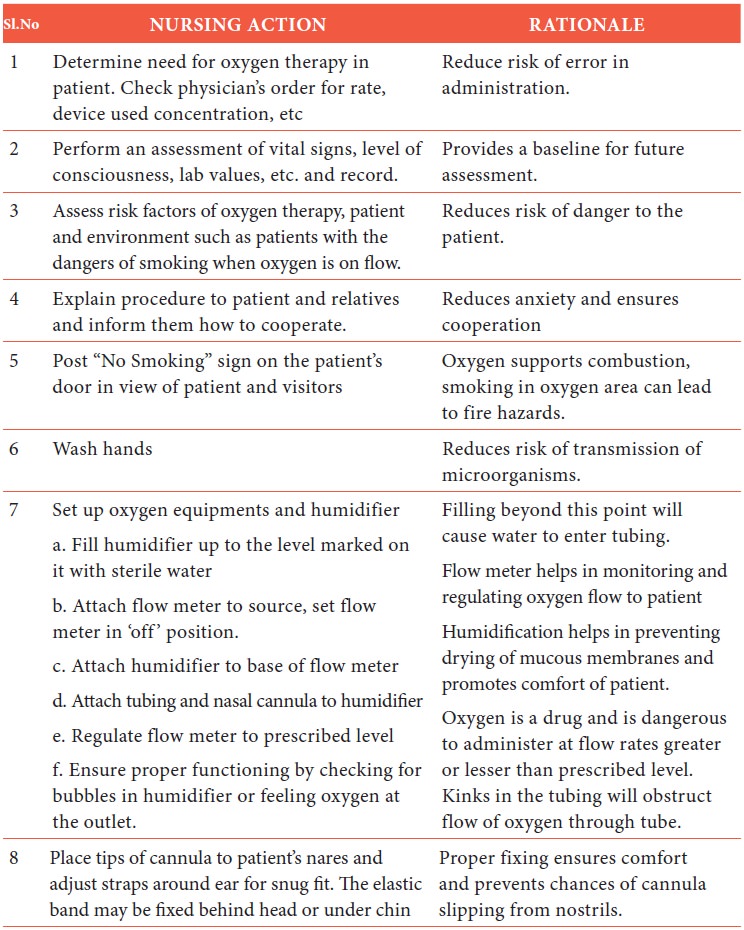
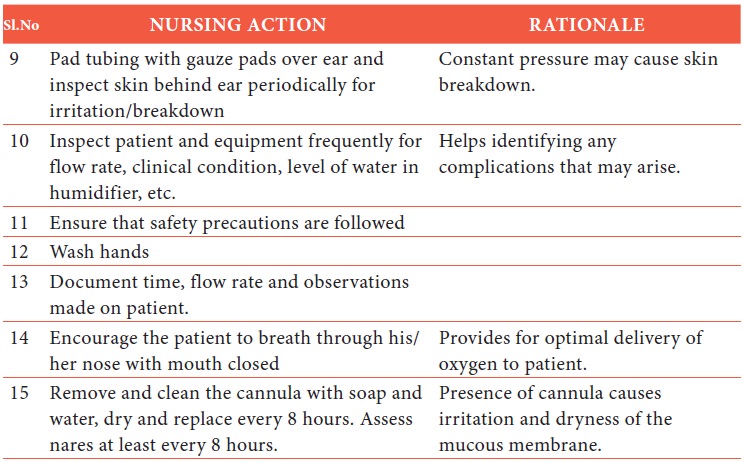
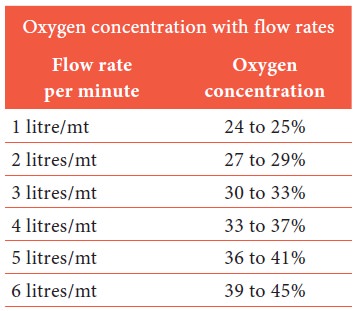
Oxygen concentration
will vary on many factors like patient’s tidal volume and ventilator pattern.
Special Precautions
1.
Never deliver more than 2-3 litres of oxygen to patients with
chronic lung disease, e.g. COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
2.
Check frequently that both prongs are in patient’s nares.
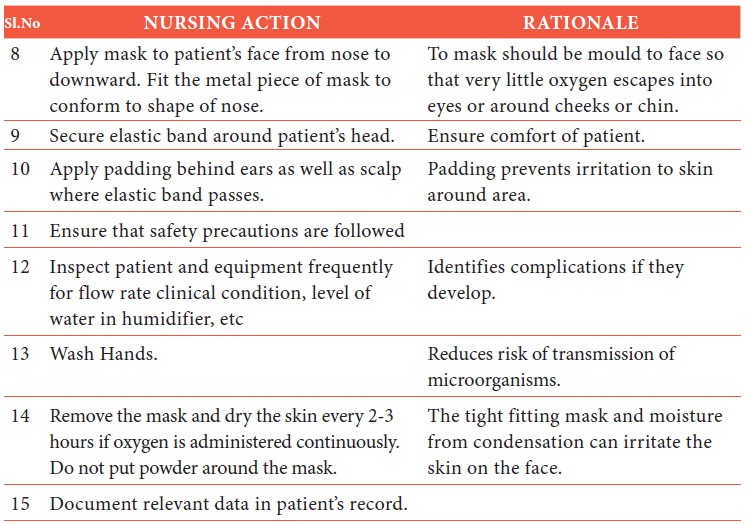
Administering Oxygen By Mask Method
Definition
Administering oxygen
to the patient by means of a mask (simple / venturi) according to requirement
of patient.
Purpose
1.
To relieve dyspnoea.
2.
To administer higher concentration of oxygen.
Articles
1.
Oxygen source
2.
Mask (simple / or with venture adaptor high flow device of
appropriate size)
3.
Humidifier with distilled water
4.
Flow meter
5.
Gauze pieces
6.
“No Smoking” sign.
Procedure
Venturi mask
Special Considerations
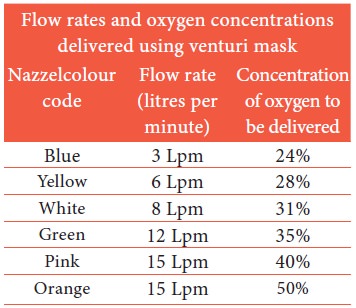
1.
The dosage of oxygen may be ordered as an FIO (Fraction of
Inspired Oxygen) which is expressed as a percentage or as litres per minute.
2.
The venturi mask will have colour-coded inserts that list the
flow rate necessary to obtain the desired percentage oxygen.
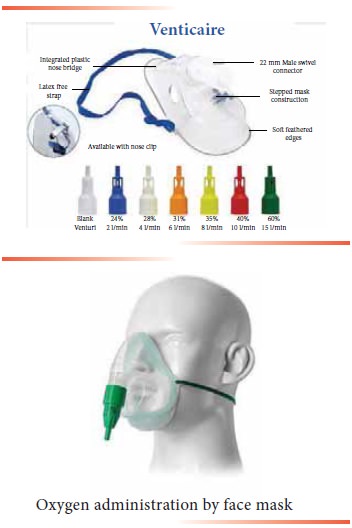

Administering Oxygen Using Oxygen Tent
Definition
Process of
administering oxygen by means of tent, usually for infants which gives maximum
comfort and most satisfactory results.
Description
An Oxygen tent
consists of a canopy over the baby’s bed that may cover the baby fully or
partially and is connected to a supply of oxygen. The canopies are transparent
and enables the nurse to observe the sick baby.
Advantages
1.
provides an environment for the patient with controlled oxygen concentration,
temperature regulation and humidity control.
2.
It allows freedom of movement in bed.
Disadvantages
1.
It creates a feeling of isolation.
2.
It requires high level of oxygen (10-12 litres per minute)
3.
Loss of desired concentration occurs each time the tent is
opened to provide care for the infant.
4.
There is an increased chance of hazards due to fire.
5.
It requires much time and effort to clean and maintain a tent.
Articles
Oxygen tent and oxygen
source, humidifier.
Procedure
Note
1.
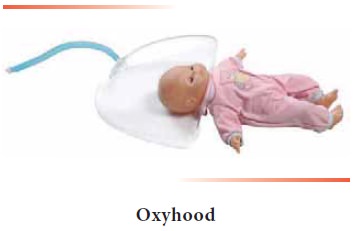
Oxygen can be administered to babies using oxygen hood
(Oxyhood).
2.
Oxygen hood is a plastic device, which is kept over the head of
the infant. It permits easy access to the child without loss of oxygen. It
helps in efficient delivery of oxygen.
3.
While placing hood over the head of the child, the edges of the
hood should not rub against the child’s chin, neck and shoulders.
Special Considerations
1.
Mist is prescribed with oxygen therapy to liquefy secretions.
2.
Humidified air may condense into water droplets on the inside
walls of the tent, it is important to examine the child’s clothing and bedding
and change them as necessary to prevent chilling.
3.
Electrical equipment used within or near the tent should be
grounded properly.
4.
It is preferable to monitor SpO2 (oxygen saturation) of patient
continuously.
5.
Avoid the use of volatile, inflammable materials such as oils,
grease, alcohol, either and acetone near the tent.
6.
Nurses should be knowledgeable about the location and technique
for using a fire extinguisher.
7.
For the baby in oxygen tent, toys selected should be such that
they retard absorption are washable and will not produce static electricity,
e.g. woolen and stuffed toys. This ensures baby’s safety.
Related Topics