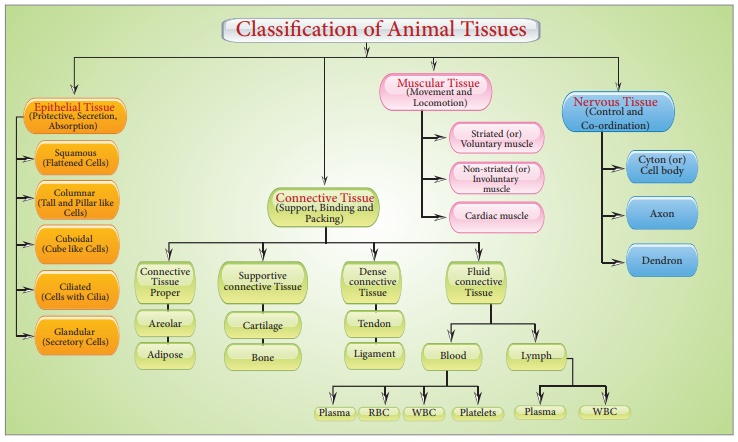
Classification/Types, Functions | Animal Tissue - Epithelial Tissues | 9th Science : Organization of Tissues
Chapter: 9th Science : Organization of Tissues
Epithelial Tissues
Epithelial Tissues
It is the simplest tissue. An epithelial tissue is composed of one or more layers of cells covering the external surface of the body and internal organs. The cells are arranged very close to each other with less extracellular material. Epithelial cells lie on a non-cellular basement membrane and contain a special form of matrix protein called collagen. The epithelial tissue generally lacks blood vessels. The epithelium is separated by the underlying connective tissue which provides it with nutrients. The skin and lining of buccal cavity, blood vessels, organs of the alimentary canal, digestive glands like the pancreas and liver, alveloli of lungs and kidney tubules are all made up of epithelial tissues.
Types of epithelial tissue
1. Simple epithelium is composed of single layer of cells resting on a basement membrane.
2. Compound epithelium are composed of several layers of cells. Only the cells of the deepest layer rest on the basement membrane.
Functions of epithelial tissues
i. The skin which forms the outer covering of the body is composed of epithelial cells.These cells protect the underlying cells from drying, injury and microbial infections.
ii. Inside the body, they are found lining the mouth and alimentary canal and give protection to the organs
iii. They help in absorption of water and nutrients
iv. They are involved in elimination of waste products
v. Some epithelial tissues perform secretory function. They secrete a variety of biochemical substances such as sweat, saliva, mucus and enzymes.
1. Simple Epithelium
It is formed of single layer of cells. It forms a lining for the body cavities and ducts. It is also found on the secretory and absorptive surfaces. On the basis of structural modification of the cells, simple epithelium is further divided into following types.
(i) Squamous epithelium
(ii) Cuboidal epithelium
(iii) Columnar epithelium
(iv) Ciliated epithelium
(v) Glandular epithelium
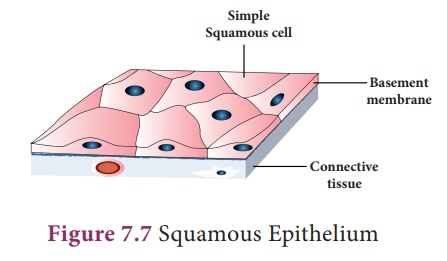
i. Squamous Epithelium is made up of thin, flat cells with prominent nuclei. These cells have irregular boundaries and bind with neighbouring cells. The squamous epithelium is also known as pavement membrane, which form delicate lining of the buccal cavity, alveoli of lungs, proximal tubule of kidneys, blood vessels and covering of the skin and tongue.
It protects the body from mechanical injury, drying and invasion of germs. It also helps in filtration by forming a selectively permeable membrane surface.
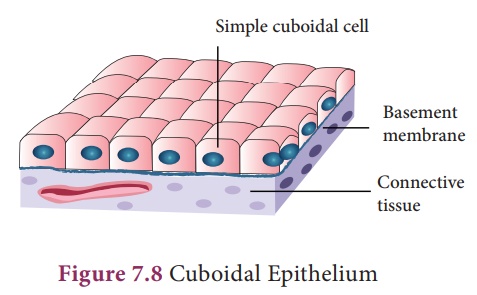
ii. Cuboidal Epithelium is composed of single layer of cubical cells. The nucleus is round and lies in the centre. This tissue is present in the thyroid vesicles, salivary glands, sweat glands and exocrine pancreas. It is also found in the intestine and tubular part of the nephron (kidney tubules) as microvilli that increase the absorptive surface area. Their main function is secretion and absorption.
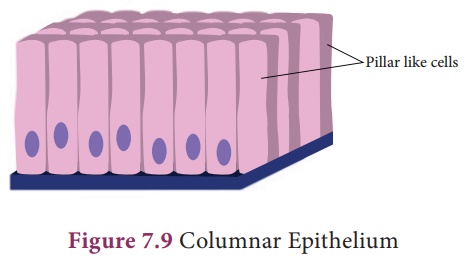
iii. Columnar Epithelium is composed of a single layer of slender, elongated and pillar like cells. Their nuclei are located at the base. It is found lining the stomach, gall bladder, bile duct, small intestine, colon, oviducts and also forms the mucous membrane. They are mainly involved in secretion and absorption.
iv. Ciliated Epithelium Certain columnar cells bear numerous delicate hair like out growths called cilia and are called ciliated epithelium. Their function is to move particles or mucus in a specific direction over the epithelium. It is seen in the trachea of wind-pipe, bronchioles of respiratory tract, kidney tubules and fallopian tubes of oviducts.
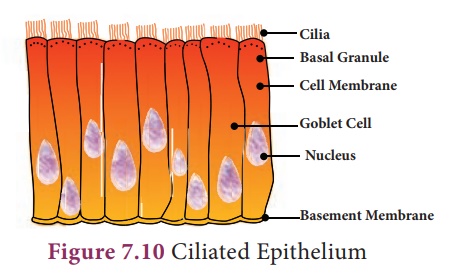
v. Glandular Epithelium Epithelial cells are often modified to form specialized gland cells which secrete chemical substances at the epithelial surface. Sometimes a portion of the epithelial tissue folds inward to form a multicellular gland, which lines the gastric glands, pancreatic tubules and intestinal glands.
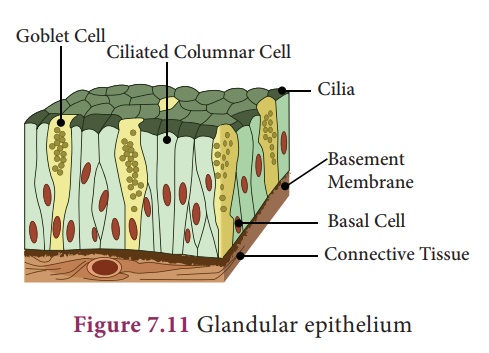
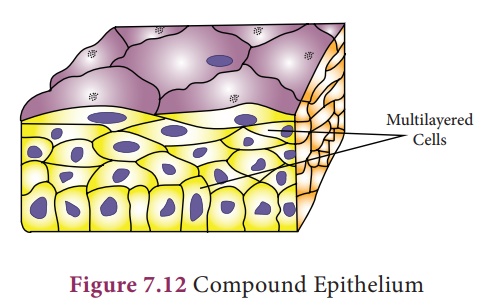
2. Compound Epithelium
It consists of more than one layer of cells and gives a stratified appearance. Hence , they are also known as stratified epithelial cells. Being multilayered, they have limited role in secretion and absorption. The main function of this epithelium is to give protection to the underlying tissues against mechanical and chemical stress. They also cover the dry surface of the skin, the moist surface of the buccal cavity and pharynx.
Related Topics