Human Development and its Challenges - Babyhood - Domains and Stages of Development | 11th Home Science : Chapter 2 : Human Development and its Challenges
Chapter: 11th Home Science : Chapter 2 : Human Development and its Challenges
Babyhood - Domains and Stages of Development
Babyhood
Babyhood continues from infancy to the second
year. It is the true foundation age with rapid growth and development.
a. Physical Development during Babyhood
Height
During babyhood, changes in the over-all size
of the child’s body are more rapid than any other time after birth. The baby
measures between 23 and 24 inches at four months, by the end of one year the
baby measures between 28 and 30 inches and between 32 and 34 inches at two
years.
Weight
During the first year, weight changes are more
than height changes. At four months the babies weight will double their birth
weight and triple it at 1 year. At one year, babies weigh, on the average,
three times as much as they did at birth, or approx-imately 10 kilograms.
Increase in weight during babyhood comes mainly from an increase in fat tissue.
Physical Proportions
Growth of the head slows down in babyhood
while the trunk and limb growth increases. Thus, the baby gradually becomes
less top-heavy and appears more slender and less chubby by the end of babyhood.
Bones
The fusion of bones increases during babyhood.
Calcification begins in the early part of the first year but is not completed until
puberty. The soft spot on the skull (tontanelle) will be closed by the end of
two years.
Muscles and Fat
Muscle fibers are present at birth but in very
under developed forms. They grow slowly during babyhood and are weak. The fat
tissue develops rapidly during babyhood due partly to the high fat content of
milk.
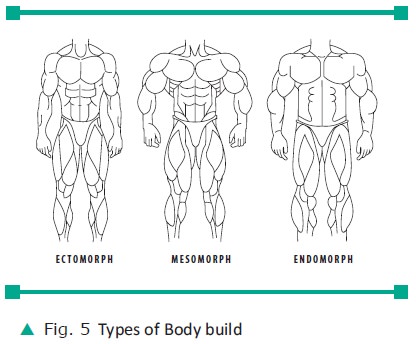
Body Builds
Babies begin to form characteristic body
builds from during their second year of life. The three most common forms of
body build are ectomorphic, which tends to be long and slender, endomorphic,
which tends to be round and fat, and mesomorphic which tends to be heavy, hard
and rectangular.
Teeth
By the end of one year the baby has four to
six temporary teeth and sixteen by the age of two. The teeth present in the
front will emerge first and the molars which are situated at the back appears
last.
Nervous System
The brain weight is one-eighth of the baby’s
total weight at birth. During the first 2 years, brain weight is gained and
this leads to the baby’s top heavy appearance. The cerebellum and the cerebrum
triple its weight in one year. Immature cells, present at birth, con-tinue to
develop after birth but rela-tively few new cells are formed.
By three months, the eye muscles are well
developed and babies can see things clearly. They can also see colours. Hearing
develops rapidly during this stage. Smell and taste are improved during
babyhood. Babies are highly responsive to all skin stim-uli because all sense
organs relating to touch, pressure, pain, and temperature are present in
well-developed forms.
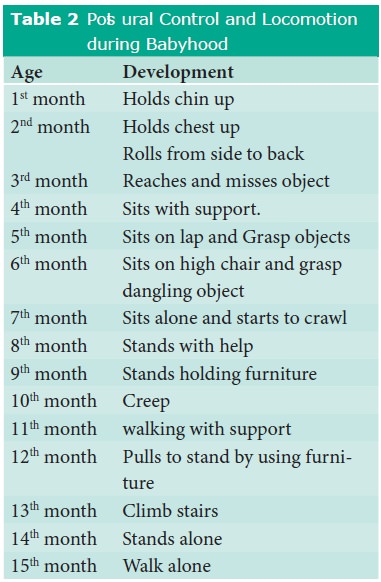
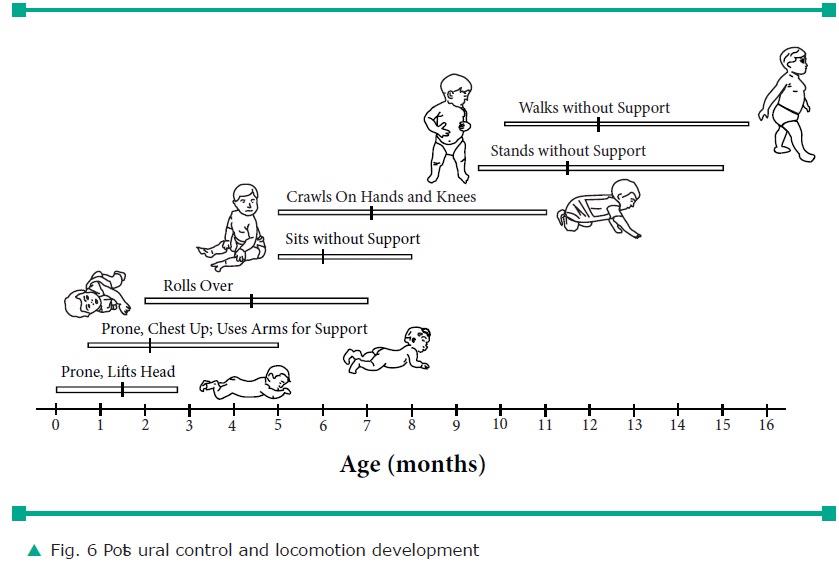
b. Motor Skills Development during Babyhood.
After the fast growth spurt in infancy, the
growth rate of the baby is slow. Motor development means the ability to control
movement of several parts of the body through coordinated movement of mus-cles
and limb. The sequences of postural control and locomotion among babies as
reported by Schiamberg are as follows
In this sequence of development it can noted
that the development proceeds from head to foot as shown in figure 6
c. Social Development
The baby begins to communicate with others by
gestures and also develops close relation with care givers like mother and
father. At about five weeks of age, the baby smiles in response to patting. By
the sec-ond month it recognizes his/her mother and by the third month the baby
will turn its head in response to human voice. Once the babies get attached to
their mother they show fear on separation.
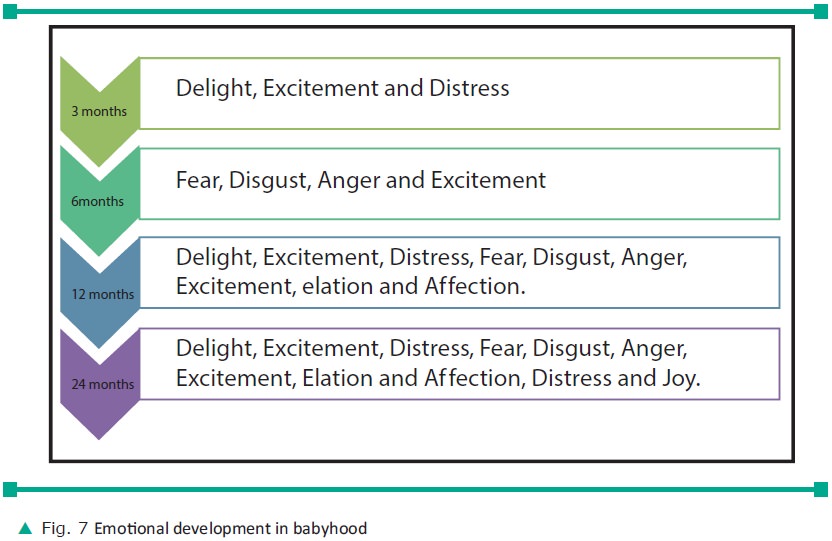
d. Emotional Development
Until use of language begins, it is emo-tions
that make adults know the needs of baby. As age increases, emotions become less
diffused and more specific and differ-entiated in relation to cause, and they
can be aroused by a wide variety of stimuli. It is shown in figure 7
e. Cognitive Development
According to Piaget’s theory babyhood is the
“sensory motor” stage. Babies under-stand the permanence of objects and
peo-ple. They visually follow the displacement of objects and begin to use
instruments and tools. They also understand discipline and what behaviour is
appropriate and in appropriate. They also understand the con-cepts of words
like “please” and “thank you”.
f. Language Development
Language development is an important means of
becoming independent for the baby. It gives him a new power to commu-nicate
their feeling to others.
· Before the baby speaks words, they show the ability to produce vowel and consonants sounds.
·
By the third month the baby coos and babbles before he/she
speaks words. These two along with gestures are known as pre -speech forms.
·
By six months he/she produces most of the vowels and few
consonants sounds.
Cooing – quick burst of
squealing noise.
Babbling – production of
inartic-ulate meaningless speech sounds which are sequences of vowels and
consonants such as da-da-da.
g. Physiological Function
Babyhood is the time when the fundamen-tal physiological patterns of eating, sleep-ing and elimination should be established, even though the habit formation may not be completed when babyhood ends.
Related Topics