Chapter: Mechanical : Computer Aided Design : Visual Realism
Z - buffer algorithm
Z - buffer algorithm
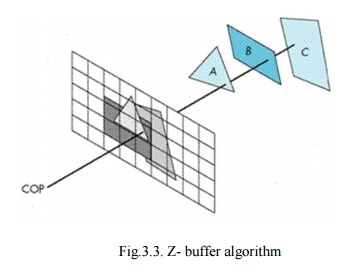
Fig.3.3. Z- buffer algorithm
In Z-buffering, the depth of ‘Z’value is verified against available depth value. If the present pixel is behind the pixel in the Z-buffer, the pixel is eliminated, or else it is shaded and its depth value changes the one in the Z-buffer. Z-buffering helps dynamic visuals easily, and is presently introduced effectively in graphics hardware.
· Depth buffering is one of the easiest hidden surface algorithms
· It keeps follow of the space to nearest object at every pixel position.
· Initialized to most negative z value.
· when image being drawn, if its z coordinate at a position is higher than z buffer value, it is drawn, and new z coordinate value is stored; or else, it is not drawn
· If a line in three dimensional is being drawn, then the middle z values are interpolated: linear interpolation for polygons, and can calculate z for more difficult surfaces.
Algorithm: loop on y;
loop on x;
zbuf[x,y] = infinity;
loop on objects
{
loop on y within y range of this object
{
loop on x within x range of this scan line of this object
{
if z(x,y) < zbuf[x,y] compute z of this object at this pixel & test zbuf[x,y] = z(x,y) update z-buffer
image[x,y] = shade(x,y) update image (typically RGB)
}
}
}
Basic operations:
1. compute y range of an object
2. compute x range of a given scan line of an object
3. Calculate intersection point of a object with ray through pixel position (x,y).
Related Topics