Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Cancer Pain Management
What are the differences between alcohol and phenol neurolysis?
What are the differences
between alcohol and phenol neurolysis?
Neurolysis can be accomplished with either
alcohol or phenol. Alcohol for neurolysis is usually used in concen-trations of
50–70%. It causes neurolysis by extracting cholesterol, phospholipids, and
cerebrosides and caus-ing precipitation of lipoproteins and mucoproteins. This
results in damage to both the Schwann cell and the axon. Clinically, alcohol is
painful on injection and is hypobaric if used for intrathecal neurolysis.
Relative to phenol, alco-hol may be more potent with a longer duration of
action.
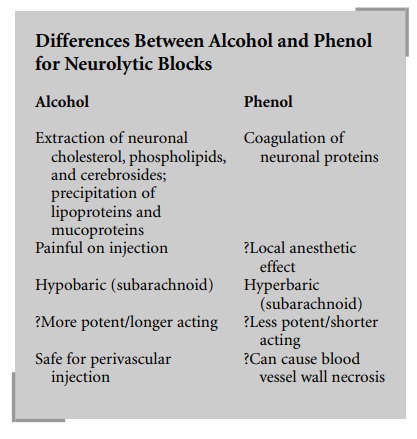
Phenol’s primary neurolytic effect is by
coagulation of proteins. It also causes nonselective damage to neural tissue.
Secondarily, phenol might have a local anesthetic effect. Intrathecally, phenol
is hyperbaric. Phenol has a great affin-ity for vascular tissue and injury to
adjacent blood vessels must be considered when it is used. For this reason,
many pain specialists prefer alcohol to phenol for celiac plexus blocks.
Radiofrequency lesioning, cryoablation, and glycerol are other modalities used
for neurolysis.
Related Topics