Term 3 Unit 3 | Geography | 6th Social Science - Understanding Disaster | 6th Social Science : Geography : Term 3 Unit 3 : Understanding Disaster
Chapter: 6th Social Science : Geography : Term 3 Unit 3 : Understanding Disaster
Understanding Disaster
Unit 3
Understanding Disaster

Learning
Objectives
• To understand the meaning of
disaster.
• To know about the types of
disasters.
• To know a few key concepts in
Disaster Management and orient them to the words used in media.
• To understand Tsunami and flood.
• To understand about Forecasting,
Emergency Operation Centre etc.,
This lesson explains about the various natural
disasters and man-made disasters. It also deals with the precautionary and
mitigation measures taken to avoid the loss of lives and materials.
Disaster is a very common phenomenon in the human
society. It has been experienced by people since time immemorial. Though its
form may be varied, it has been a challenge for society. The latest development
which has been discovered in the World Disaster Reports recently is that, the
disasters have increased in frequency and intensity. India is one of the most
disaster prone countries in the world. It has some of the world’s most severe
droughts, famines, cyclones, earthquakes, chemical disasters, rail accidents
and road accidents. The high density of population in the developing countries,
especially in the high risk coastal areas, results in millions of people
getting affected by natural disasters, especially in recurring disasters like
floods, cyclones, storm surges, etc.
Disaster
‘A disaster is a serious disruption of the
functioning of a society involving human and material loss. Disaster is broadly
classified into natural and man-made disasters.
1. Natural Disasters

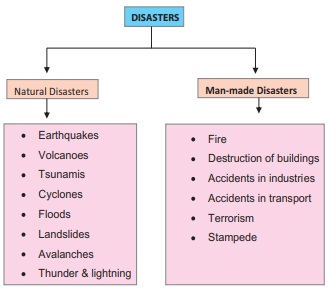
Earthquake
The sudden shaking
of the earth at a place for a short spell of time is called an earthquake. The
duration of the earthquake may be a few seconds to some minutes. The point
where an earthquake originates is called its ‘focus’. The vertical point
at the surface from the focus is called ‘epicentre’.
Volcanoes
Volcanoes are openings or vents where lava, small
rocks and steam erupt onto the earth’s surface.
Tsunami
Tsunami are waves generated by earthquake,
volcanic eruptions and underwater landslides.
Cyclones:
A low pressure area which is encircled by
high-pressure wind is called a cyclone.
Floods
An overflow of a large amount of water, beyond its
normal limits, especially on the rainfed areas is called a flood.
Landslide
The movement of a mass of rocks, debris, soil
etc., downslope is called a landslide.
Avalanche
A large amount of ice, snow and rock falling
quickly down the side of a mountain is called an Avalanche.
Thunder and
lightning
Thunder is a series of sudden electrical discharge
resulting from atmospheric conditions. This discharge results in sudden flashes
of light and trembling sound waves which are commonly known as thunder and
lightning.
2. Man-made disasters

Fire
Massive forest
fires may start in hot and dry weather as a result of lightning, and human
carelessness or from other causal factors.
Destruction
of buildings
Demolition of buildings by human activites.
Accidents in
industries
Chemical, biological accidents that occur due to
human error. (e.g.) Bhopal gas tragedy
Accidents in
Transport
Violation of road rules, carelessness cause
accidents.
Terrorism
The social unrest or differences in principles
leads to terrorism.
Stampede
The term stampede
is a sudden rush of a crowd of people, usually resulting in injuries and death
from suffocation and trampling.
Tsunami and floods
A killer Tsunami hit the south east Asian
countries on the 26th of December, 2004. A massive earthquake with a magnitude
of 9.1 -9.3 in the Richter scale epicentre in the Indonesian island of Sumatra.
It triggered one of the biggest Tsunamis the world had ever witnessed. The
massive waves measuring up to 30 metres that killed more than 2,00,000 people
of Asia.

In India, over 10,000 people were killed by this
disaster. Tamil Nadu alone accounted for 1,705 deaths. All the coastal
districts were affected, Nagapattinam was the worst hit in the state of Tamil
Nadu. Fishermen, tourists, morning walkers, children playing in beach and
people living on the coast were unprepared for the waves. So they lost their
life and the most of the loss of lives and damage to property was within 500
metres of the shore. After that the Indian government set up a Tsunami Early
Warning System at Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services
(INCOIS), Hyderabad in 2007.
Tsunami -
Do’s and Don’ts
• You should find out if your home, school etc.,
are in valunarable areas along sea shore.
• Know the height of your street above sea level.
• Plan evacuation routes and practise your
evacuation routes.
• Discuss tsunamis with your family. Review safety
and preparedness measures with your family.
• If you see the sea water receding, you must
immediately leave the beach and go to higher ground far away from the beach.
• Don't go to the coast to watch the Tsunami.
• Dont try to surf the tsunami waves.
• Be aware facts about tsunami.
Floods
Floods are high stream flows, which overlap
natural or artificial banks of a river or a stream and are markedly higher than
the usual flow as well as inundation of low land.
Types of
floods
Flash floods: Such
floods that occur within six hours during heavy rainfall.
River floods: Such
floods are caused by Precipitation over large catchment areas or by melting of
snow or sometimes both.
Coastal floods:
Sometimes floods are associated with cyclone high tides and tsunami.
Causes of
floods
• Torrential Rainfall.
• Encroachment of rivers bank.
• Excessive rainfall in catchment.
• Inefficient engineering design in the
construction of embankments, dams and canals.
Effects of
floods
• Destruction of drainage system
• Water pollution
• Soil erosion
• Stagnation of water
• Loss of agricultural land and cattle
• Loss of life and spread of contagious diseases.
Do’s
• To find out if the settlement area is to be affected
by flood or not.
• Keeping radio, torch and additional batteries,
storing drinking water, dry foods items, salt and sugar. Safeguarding materials
like kerosene, candle, match box, clothes
and valuable things.
• Keeping umbrella and bamboo poles.
• Keeping first aid box and strong ropes to bind
things.
• To dig canals from the farm land, to drain the
excessive water keeping sand bags etc.,
Don’ts
• Try to connect electricity once it is cut.
• Operate vehicles
• Swim against floods
• Avoid going on excursions.
• Neglect flood warning messages
During
floods
• Cut off gas connection and electricity.
• Keep sand bags on drainage holes and bathroom
holes.
• Leave immediately through the known passage or
prescribed passage
• Drink hot water.
• Use bleaching powder to keep your environment
hygienic.
• Before using match sticks and candles, ensure
that there is no gas leakage.
• Don’t eat more food when you are affected by
diarrhoea.
• Don’t try to take anything that floats in flood.
Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR)
Disaster Risk Reduction: The practice of reducing
disaster risks through systematic efforts to analyze and manage the causal
factors of disasters. There are four key approaches to public awareness for
disaster risk reduction. Campaigns, participatory learning, informal education,
and formal school based interventions.
CASE STUDY
Chennai
flood – 2015

Chennai is one of the largest
metropolitan cities in India, which lies on the south eastern coast. The north
east monsoon along with tropical cyclone hits Chennai every year and gives
heavy cyclonic rainfall. In 2015, November and December due to heavy rain, the
devastating floods that hit Chennai and other parts of Tamil Nadu claimed more
than 400 lives and caused enormous economic damage. The Government of India and
Tamil Nadu have taken a lot of action to reduce loss of life and minimize human
sufferings.
Forecasting and Early Warning
Weather forecasting, Tsunami early warning system,
cyclonic forecasting and warning provide necessary information which help in
reducing risks during disasters.
School Disaster Management Committee, Village
Disaster Management Committee, State and Central government institutions take
mitigation measurestogether during disaster.
Newspaper, Radio, Television and social media
bring updated information and give alerts on the vulnerable area, risk,
preparatory measures and relief measures including medicine.
Glossary
1. Mitigation: The
lessening of the adverse impacts of hazards and related disasters.
2. Forecast:
Definite statement or statistical estimate of the likely occurrence of a future
event or conditions for a specific area.
3. Rainfed: Supplied primarily with
rainwater.
4. Magnitude: A
measure of the amount of energy released by an earthquake.
5. Contagious:
Transmissible by direct or indirect contact .
6. Catchment: The
action of collecting water, especially the collection of rainfall over a
natural drainage area.
ICT CORNER
Geography
- Understanding Disaster
Through this activity you will know about prevention activities before cyclone through a game.

Steps:
Step -1 Use the URL or scan the QR code to open
the “storm safe” game page.
Step -2 Click the “play” icon to enter the game
page
Step -3 Click the “continue” button start the
game.
Step -4 Drag and put weightless things in the
house.

*Pictures are indicatives only.
Browse in the link
Web:
http://www.vicses.com.au/stormsafe-game/
(or)scan the QR Code
Related Topics