Nutrition - Types of Diet | 12th Nursing : Chapter 4 : Nutrition
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 4 : Nutrition
Types of Diet
TYPES
OF DIET
Modification of diet
means changing the constituents of the diet as per the metabolic rate of the
person. In disease condition, the body’s metabolic rate keeps on changing hence
the diet of a normal person cannot fulfill the basic needs of providing enough
calories.
Diet can be classified
Based on the consistency
Liquid Diet
Clear liquid diet: clear liquid diet is
free from any solid particles. Ex: Clear soups, tea or coffee without
cream etc. This is given for the patient who cannot chew or swallow the food.

Full liquid diet: Full liquid diet is
composed of solids which are easily digestible, mixed in liquid. This
diet is prescribed for patients who are severely ill, not able to chew or
swallow but need good calories. This diet is given in between a clear liquid
diet and soft diet. Ex: eggs, vegetable soup, kheer, milk etc.
Soft Diet
Soft diet is easy for
chewing and easily digestible. This diet contains all the required nutrients
especially proteins and carbohydrates. It is soft in consistency, easy to chew,
made up of simple, easily digested foods, containing limited fibre and does not
contain rich or highly flavoured foods.

Bland Diet
Bland diet is free from
all spices and condiments and is basically used to prevent peptic ulcers.

Normal Diet
A Normal diet is defined
as one which consists of any and all foods eaten by a person in health. As
there is no restriction of any kind of food, this diet is well balanced and
nutritionally adequate.

On the basis of Consistency and Constituents
·
Low fibre diet
·
High fibre diet
·
High calorie and low calorie diet
·
High fat and low fat diet
·
High protein and low protein diet
·
Low sodium diet
Modification in diet is
done for various diseases in different pattern.
Special Feeding Techniques
Food consumption in the
clients with different diseases is altered. Different techniques used in
hospitals for such patients are:
·
Tube feeding
·
Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)
Tube Feeding
Tube feeding is commonly
done by using nasogastric tubes of different sizes. Nasogastric tube is
inserted from nose to stomach. The tube is inserted gently upto the marking
roughly estimated. Then it is strapped at the forehead. Then placement of tube
is assessed either using stethoscope or aspiration of gastric juice from
stomach. Feed is given through the tube until the patient is able to eat by
mouth. This method is easier, simple method for helpless patients who are not
able to take the food orally. Full fluid diets or commercial formulas may be
administered through this route.
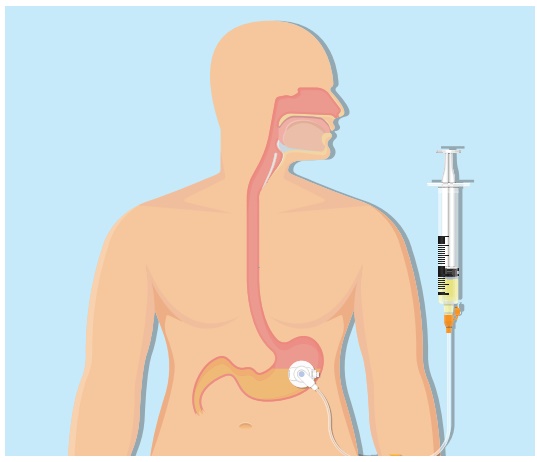
The tube may be passed
through the nose into the stomach (nasogastric), duodenum (nasoduodenal) or
jejunum (nasojejunal).
When there is an
obstruction in the esophagus, enteral feeding is done by passing a tube
surgically through an incision in the abdominal wall into the stomach
(gastrostomy), duodenum (duodenostomy) or jejunum (jejunostomy).
Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)
The delivery of
nutrients directly into the circulation through the peripheral or central vein
is termed as parenteral nutrition. This technique is used for long term purpose.
In this method, a cannula is inserted in large veins to reach superior vena
cava in the heart.
Related Topics