Classification/Division - Types of Companies | 11th Commerce : Chapter 6 : Joint Stock Company
Chapter: 11th Commerce : Chapter 6 : Joint Stock Company
Types of Companies
Types of Companies
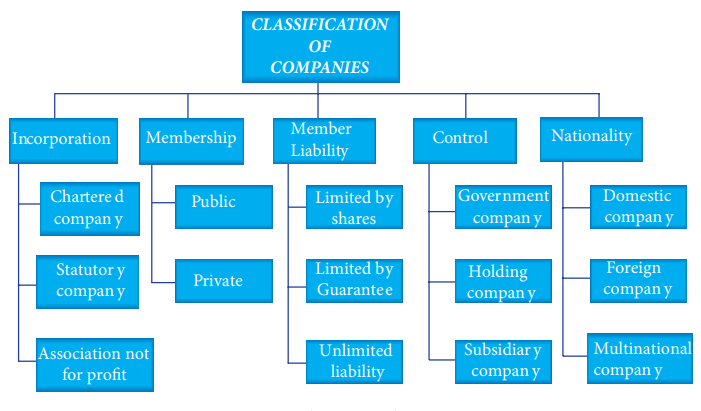
1. Classification of Companies on the Basis of Incorporation
a. Chartered Companies
Chartered companies are established
by the King or Queen of a country.
Powers and privileges of chartered company are specified in the charter. Power
to cancel the charter is vested with
King/Queen. Examples: East Indian Company,
Bank of England, Hudson’s Bay
Company. The Companies Act does not apply to them. Such companies cannot be
started in India.
b. Statutory Companies
Companies are established by a Special Act made in Parliament/State
Assembly. Constitution of company is specified
in the Memorandum of Association
(MOA). Rules relating to day-to-day management of statutory companies are specified
in the Articles of Association
(AOA). Audit of statutory company is
conducted by Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAGI). The report of
CAGI is placed in Parliament/State Assemblies concerned. Examples: Food
Corporation of India, LIC, GIC, RBI, SBI, IDBI, Railways, Electricity, ONGC.
Statutory companies enjoy autonomous status. It need not use the word ‘Limited’
next to its name.
c. Association Not for Profit
According to Section 25, the Central
Government may, by license, grant that an association may be registered as a
company with limited liability, without using the words ‘limited’ or ‘private
limited’ as part of its name. The license will be granted only in the case of
‘association not for profit’. In other words, the Central Government will grant
the license only if it is satisfied that:
(i) The association about to be formed
as a limited company aims at the promotion of Sports, Commerce, Art, Science,
Religion, Charity or any other useful object.
(ii) It intends to apply its profits, if
any, for promoting its objects.
(iii) It prohibits the payment of
dividend to its members.
Such companies may be public or private
companies and may or may not have share capital.
2. Classification of Companies on the Basis of Membership
a. Private Company
Private limited company is a type of
company which is formed with minimum two shareholders and two directors, The
minimum requirement with respect to authorised or paid up capital of Rs. 1,00,000
has been omitted by The Companies (Amendment) Act, 2015 w.e.f. 29th of May,
2015. Another crucial condition of a private limited company is that it by its
articles of association restricts the right to transfer its shares & also
prohibits any invitation to the public to subscribe for any securities of the
company. Maximum of 200 persons can become shareholders in a private company.
The name of private company should be suffixed with pvt ltd or (p) ltd. Ex.
Scientific publishing services private Limited, Chennai. A private Limited
company can be formed in three variations.
(a) as a private limited company; (b) As
a small private limited company; (c) As a One Person Company (OPC).
b. Public Company
Public Company means a company which is
not a private company. A public company may be said to be an association which
i. consists of at least 7 members.
ii. has a minimum paid-up capital of Rs. 5,00,000
or such higher paid up capital as may be prescribed.
iii. is a subsidiary of a company which
is not a private company.
iv. does not restrict the right to
transfer its shares.
v. does not prohibit any invitation to
subscribe for any shares or debentures of the company.
vi. does not prohibit any invitation or
acceptance of deposits. (The name of public company should be suffixed with
ltd. Ex.National Aluminium company Limited, Chennai )
3. Classification of Companies on the Basis of Liability
A company limited by shares is a company
in which the liability of its members is limited by its Memorandum to the
amount (if any) unpaid on the shares respectively held by them. The companies
limited by shares may be either public companies or private companies. If a
member has paid the full amount of shares, then his liability shall be nil.
Thus two main features of a company
limited by shares are as follows:
i. The liability of its members is
limited to the amount (if any) remaining unpaid on the shares held by them.
ii. Such liability can be enforced
either during the lifetime of the company or during the winding up of the
company.
b. Company Limited by Guarantee
A company limited by guarantee is a
company in which the liability of its members is limited by its Memorandum to
such an amount as the members may respectively undertake to contribute to the
assets of the company in the event of its being wound up. Such companies are
generally formed for the promotion of Commerce, Art, Science, Religion, Charity
or any other useful object. The companies limited by guarantee may be either
private companies or public companies.
c. Unlimited Company
An unlimited company is a company in
which the liability of its members is not limited by its Memorandum. In other
words, the liability of members is unlimited i.e., there is no limit on the
liability of members. The members of such companies may be required to pay
company’s losses from their personal property. Because such companies have
separate legal entity, its creditors cannot file a suit against the members
directly. The creditors will have to apply to the court for the winding up of
the company and then the liquidator will direct the members to contribute to
the assets of the company to pay off its liabilities.
4. Classification of Companies on the Basis of Membership
a. Government Companies
A public enterprise incorporated
under the Indian Companies Act,
1956 is called a government company.
These companies are owned and managed by the central or the state government.
Section 617 of the Companies Act, 1956 defines “Government Companies” as any
company in which not less than 51% of the [paid-up share capital] is held by.
1.
The Central Government; or
2.
Any State Government or Governments; or
3.
Partly by the Central Government and
partly by one or more State Governments.
A subsidiary of a Government company
shall also be treated as a Government company. These companies are registered
as private limited companies though their management and their control vest
with the government. This is a type of organization where both the government
and private individuals are shareholders. Sometimes these companies are called
as a mixed ownership company.
Examples:
Steel
Authority of India, Indian Oil Corporation, Oil and Natural Gas Corporation,
Bharath Heavy Electricals.
b. Holding Companies
As per Section 2(87) “subsidiary
company” or “subsidiary”, in relation to any other company (that is to say the
holding company), means a company in which the holding company—
i.
controls the composition of the Board of
Directors; or
ii.
exercises or controls more than one-
half of the total share capital either at its own or together with one or more
of its subsidiary companies:
Provided that such class or classes of
holding companies as may be prescribed shall not have layers of subsidiaries
beyond such numbers as may be prescribed.
c. Subsidiary Companies
“Subsidiary company” or “Subsidiary”, in
relation to any other company (that is to say the holding company), means a
company in which the holding company.
i. controls the composition of the Board
of Directors; or
ii. exercises or controls more than one-
half of the total share capital either at its own or together with one or more
of its subsidiary companies:
Examples:
H Ltd., holds more than 50% of the equity share capital of S Ltd. Now H Ltd.,
is the holding company of S Ltd., and S Ltd., is the subsidiary of H Ltd.
5. Classification of Companies on the Basis of Nationality
a. Domestic Companies
A company which cannot be termed as
foreign company under the provision of the Companies Act should be regarded as a
domestic company.
b. Foreign Companies
A foreign company means a company which
is incorporated in a country outside India under the law of that country. After
the establishment of business in India, the following documents must be filed
with the Registrar of Companies within 30 days from the date of establishment.
(i) A certified copy of the charter or
statutes under which the company is incorporated, or the Memorandum and
articles of the company translated into English.
(ii) The full address of the registered
office of the company.
(iii) A list of directors and secretary
of the company.
(iv) The name and address of any person resident of India who is authorised to accept, on behalf of the company, service of legal process and any notice served on the company.
(v) The full address of the company’s
principal place of business in India.
c. Multi National Companies
A Multi National Company (MNC) is a huge
industrial organisation which,
i. Operates in more than one country
ii. Carries out production, marketing
and research activities on international Scale in those countries.
iii. Seeks to maximise profits world
over.
A domestic company or a foreign company
can be a MNC.
Examples:
Microsoft
Corporation, Nokia Corporation, Nestle, Coca-Cola, International Business
Machine, Pepsico, Sony Corporation.
Related Topics