Chapter: Clinical Dermatology: Medical treatment
Therapeutic options
Therapeutic
options
Some
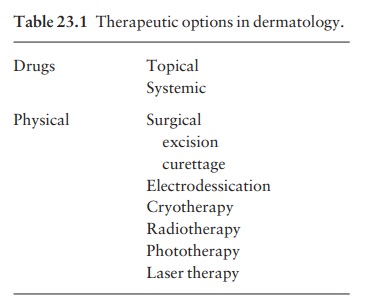
of the treatments used in dermatology are listed in Table 23.1
Topical vs. systemic therapy
The
great advantage of topical therapy is that the drugs are delivered directly to
where they are needed, at an optimum concentration for the target organ.
Systemic side-effects from absorption are less than those expected from the
same drug given systemically: with topical treatment, vital organs such as the
marrow, liver and kidneys are exposed to lower drug concen-trations than is the
skin. However, topical treatment is often messy, time-consuming and incomplete,
and takes time to apply, whereas systemic treatment is clean and quick and its
effect is uniform over the entire skin surface. Cost must also be considered.
Some
drugs can only be used topically (e.g. gamma benzene hexachloride for scabies
and mupirocin for bacterial infections), while others only work systemic-ally
(e.g. dapsone for dermatitis herpetiformis and griseofulvin for fungal
infections).
When
a choice exists, and both possibilities are equally effective, then local
treatment is usually to be preferred. Most cases of mild pityriasis versicolor,
for example, respond to topical antifungals alone so sys-temic itraconazole is
not the first treatment of choice.
Related Topics