Chapter: Biochemistry: Inborn Errors of Metabolism
TaysachŌĆÖs Disease: Causes, Symptoms
TaysachŌĆÖs Disease
Gangliosides are glycosphingolipids which are
present in small amounts in the membranes of a wide variety of tissues. Nervous
tissues are particularly rich in gangliosides. Generally, the carbohydrate
segments of glycolipids are removed by lysosomal hydrolases in the early phases
of the turn over of these compounds. Several inborn errors due to the
deficiency of these hydrolases have been well documented.
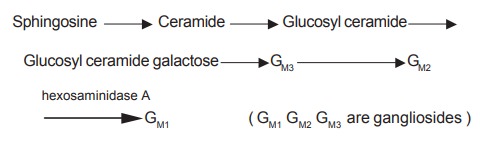
Cause
TaysachŌĆÖs disease is due to the absence of
N-acetyl hexosaminidase A that leads to the accumulation GM2 in
brain and spleen. Hence the ganglioside GM2 is called as TaysachŌĆÖs
ganglioside.
In this condition GM2 is not degraded
to GM1 and accumulates in large amounts in lysosomes, particularly
in the brain cells. The amount sometimes exceeds 100 - 300 times the normal
content causing degeneration of the nervous system.
Symptoms
Muscle weakness, retardation in development and
difficulty in eating are typical early symptoms. Mental retardation and
blindness are the characteristic symptoms in this rare genetic disorder. Death
between 2 -5 years is unavoidable. More than 90 % of the patients have a
characteristic cherry red spot in the retina.
TaysachŌĆÖs disease can be diagnosed by taking
amniotic fluid from the mother and assaying the hexosaminidase A activity.
Related Topics