Chapter: Biochemistry: Inborn Errors of Metabolism
Alkaptonuria: Causes, Symptoms
Alkaptonuria
This is a rare inborn error of metabolism of
phenylalanine and tyrosine.
Estimated incident is 2-5 per million live
births.
Cause
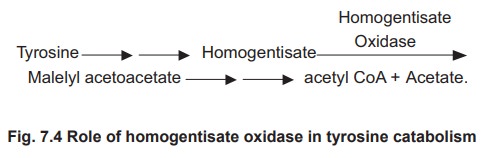
The disease is characterised by the deficiency
of homogentisate oxidase which catalyses the conversion of tyrosine to acetyl
coA and acetate. In this reaction sequence homogentisic acid (homogentisate) is
an intermediate which is oxidised by the enzyme homogentisate oxidase.This results
in the accumulation of homogentisic acid as shown in the figure 7.4.
Symptoms
Homogentisic acid accumulates in the tissues and
blood and also appears in urine. Most striking clinical manifestation is
occurrence of dark urine on standing in air. Homogentisic acid like many
derivatives of tyrosine is readily oxidized to black pigments. These pigments
are called as alkaptons. Urine in an exposed air slowly turns black from top to
bottom.
In long standing cases, deposition of
homogentisic acid derivatives in cartilages of ears and other exposed places
leading to generalized pigmentation of connective tissues and deposition in
joints leading to arthritis, a condition is called ochronosis. This is due to
the of oxidation homogentisate by polyphenol oxidase, forming benzoquinone
acetate, which polymerizes and binds to connective tissue macromolecules.
Related Topics