Chapter: Digital Principles and System Design : Synchronous Sequential Logic
Synchronous Sequential Logic
SYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL LOGIC
PRE-REQUISITE DISCUSSION
Digital electronics is classified into
combinational logic and sequential logic. Combinational logic output depends on
the inputs levels, whereas sequential logic output depends on stored levels and
also the present inputs.
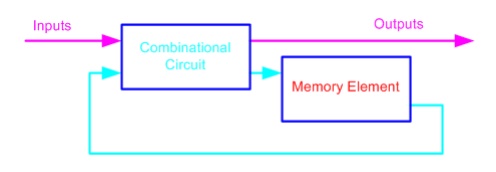
The memory elements are devices
capable of storing binary info. The binary info stored in the memory elements
at any given time defines the state of the sequential circuit. The input and
the present state of the memory element determine the output. Memory elements
next state is also a function of external inputs and present state. A
sequential circuit is specified by a time sequence of inputs, outputs, and
internal states.
There are two types of sequential circuits. Their
classification depends on the timing of their signals:
•
Synchronous sequential circuits
•
Asynchronous sequential circuits
ü
ASYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT
This is a system whose outputs depend upon the
order in which its input variables change and can be affected at any instant of
time. Gate-type asynchronous systems are basically combinational circuits with
feedback paths. Because of the feedback among logic gates, the system may, at
times, become unstable. Consequently they are not often used.
ü SYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
This type of system uses storage elements called
flip-flops that are employed to change their binary value only at discrete
instants of time. Synchronous sequential circuits use logic gates and flip-flop
storage devices. Sequential circuits have a clock signal as one of their
inputs. All state transitions in such circuits occur only when the clock value
is either 0 or 1 or happen at the rising or falling edges of the clock
depending on the type of memory elements used in the circuit. Synchronization
is achieved by a timing device called a clock pulse generator. Clock pulses are
distributed throughout the system in such a way that the flip-flops are
affected only with the arrival of the synchronization pulse. Synchronous
sequential circuits that use clock pulses in the inputs are called
clocked-sequential circuits. They are stable and their timing can easily be
broken down into independent discrete steps, each of which is considered
separately.
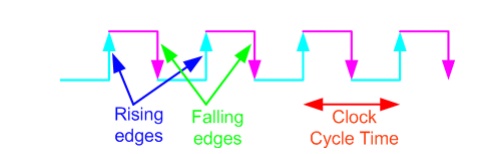
A clock signal is a periodic square wave that
indefinitely switches from 0 to 1 and from 1 to 0 at fixed intervals. Clock
cycle time or clock period: the time interval between two consecutive rising or
falling edges of the clock.
Clock
Frequency = 1 / clock cycle time (measured in cycles per second or Hz)
Example: Clock
cycle time = 10ns clock frequency = 100M
Related Topics