Chapter: 9th Social Science : History: State and Society in Medieval India
State and Society in Medieval India
State and Society in Medieval India
Introduction
We begin this chapter by
defining the term ‘medieval’. The periodization of history into
‘ancient/classical’, medieval’ and ‘modern’ is conventionally used with
reference to European history. In the context of Indian history, the use of
these terms is more problematic. Therefore, historians have debated their
relevance in defining different periods of Indian history. For instance, the
historian Burton Stein, uses the term ‘classical’ to describe the period up to
the Gupta empire, and dates the ‘medieval’ period from the 7th century A.D.(CE)
till the beginning of Mughal rule in the 16th century. The Mughal era, from the
16th to 18th century is referred to as the early modern peroid.

The political scenario
in all parts of India underwent momentous, definitive changes which transformed
the social and economic fabric and development of the country. Historians have now
moved away from thinking of history as a linear narrative of kings and
dynasties, and the events – mainly wars and military campaigns – which happened
during their rule. History is now thought of inter-disciplinary terms to
comprise social and economic change. Nevertheless, such change does not happen
autonomously without any reference to changes in the political structure. This
is especially true for the period covered in this chapter.
Major Political Changes
·
The expansion of the Chola empire from the time of Rajaraja which eclipsed the
Pandyan and Pallava kingdoms, extending north till Orissa.
·
From the twelfth century, the beginning of several centuries of
Muslim rule in Delhi, extending throughout north India and the spread of Islam
to different parts of the country.
·
By the end of the 13th century the eclipse of the great empire of the Cholas and the consequent rise
of many Religious kingdoms in south India. This ultimately culminated in the
rise of the Vijayanagar empire ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
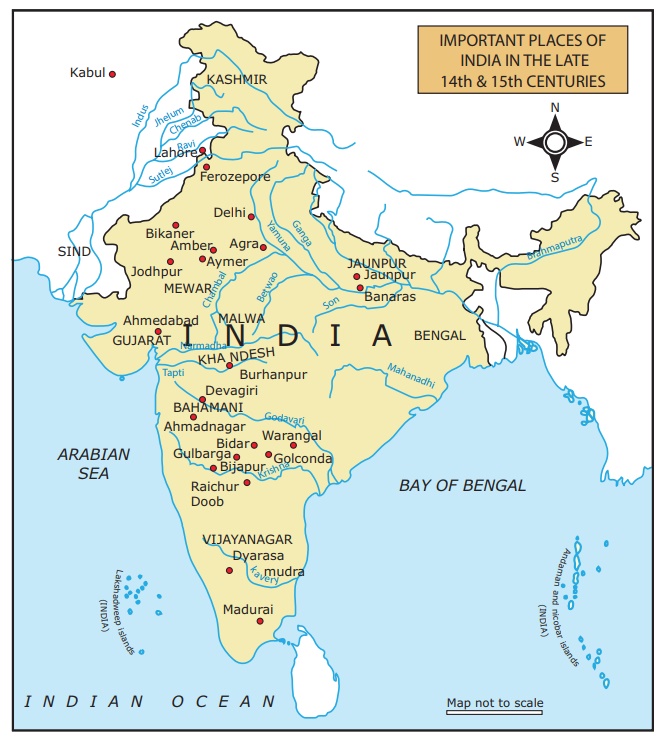
·
The consolidation of Muslim rule under the Mughals in the north, beginning in
1526 A.D. (C.E.) with the defeat of the Ibrahim Lodi by Babur. At its height,
the Mughal empire stretched from Kabul to Gujarat to Bengal, from Kashmir to
south India.
·
The coming of the Europeans, beginning with the Portuguese who
arrived on the west coast of India in 1498.
Related Topics