Chapter: Biology: Cell Division
Stages of Mitosis
Stages of Mitosis
Mitosisis a continuous process. The process is completed
by a complex method. According to the
sequence and stages, this continuous process is dividedinto five stages. The
stages are:
(1) Prophase, (2) Pro-Metaphase, (3)Metaphase,Anaphase and (5)Telophase.
1. Prophase: At this stage, the nucleus swells up.
Chromosomes begin to be dehydrated. As a result, the chromosomes gradually become shorter
and thicker.
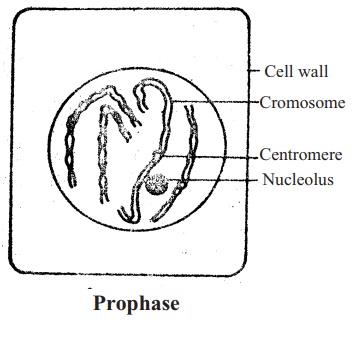
Then they are visible under microscopes. At the end of
this stage nucleolus and nuclear membrane become disappear.
2. Pro-Metaphase : At the beginning ofthis stage. the fibrous protein
converse to form a bi-polar spindle apparatus. Each chromosome is then become
attached to a fibre of the spindle apparatus by its centromere. Each fibre of
the spindle apparatus is called spindle fibre. The fibre to which the
chromosomes are attached is called traction fibre. As they are attached with
the chromosomes so they also called chromosomal fibre. In animal cell aster
rays are radiated from centrioles present at two poles.
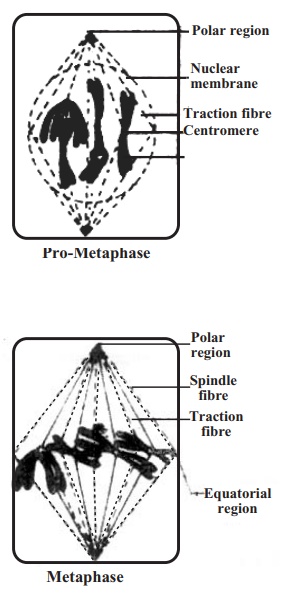
3. Metaphase : Chromosomes are arrangedat the equatorial plane of the
spindle. The centromere of each chromosome remains at the equatorial plane and
the two arms are placed towards two poles. At this stage, the chromosomes
become maximum thick and short. Two chromatids of a chromosome become maximum
thick and short. Two chromatids of a chromosome become clearly visible and the
centromere is divided in to two parts.
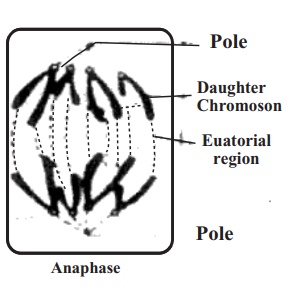
4. Anaphase : Two separate chromatids ofa chromosome move towards the
opposite pole of the spindle apparatus. Centromere goes ahead at the movement
of the chromatids towards the pole and the arms follow them. when the daughter
chromosomes reaches near the poles the anaphase stage ends.
5. Telophase: Daughter chromosomes take position at two opposite
poles.Chromosomes gradually take
water andbecome elongated, thin
and long. Nuclearmembranedevelops encirclingthechromosomes. Nucleolusreappears at
thesecondary constrictionof theSatchromosome.
Spindle apparatus disappears.
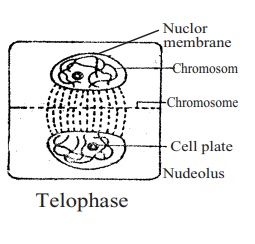
At the end of
this stage,gradually acellwall develops at the equatorial region
of the cell.
As a result, the mother cell divides into two daughter
cells. In case of animal cells, instead of formation of cell wall the cell
membrane is constricted inwardly and the cell divides into two.
Related Topics