Chapter: Programming and Data Structures : Linear Data Structures : Stacks, Queues
Stacks ADT - Linear Data Structures
STACK ADT
STACK
:
“A stack is an ordered list in which all
insertions and deletions are made at one end, called the top”stacks. are
sometimes referred to as Last In First Out (LIFO) lists
Stacks have some useful terminology
associated with them:
Push
To add an element to the stack
Pop
To remove an element from the stock
Peek
To look at elements in the stack without removing them
LIFO
Refers to the last in, first out behavior of the stack
FILO
Equivalent to LIFO
stack (data structure)
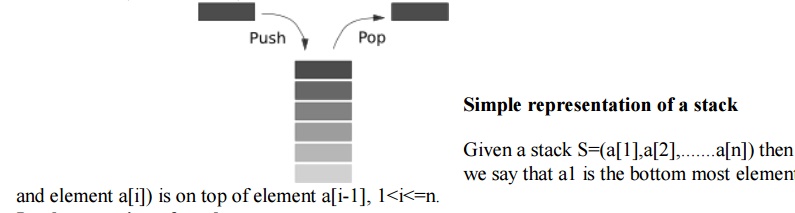
Simple
representation of a stack
Given a stack S=(a[1],a[2],.......a[n])
then we say that a1 is the bottom most element
and element a[i]) is on top of element
a[i-1], 1<i<=n.
Implementation
of stack :
1. array
(static memory ).
2. linked
list (dynamic memory)
The
operations of stack is
1. PUSH
operations
2. POP
operations
3. PEEK
operations
The
Stack ADT
A
stack S is an abstract data type (ADT) supporting the following three methods:
push(n)
: Inserts the item n at
the top of stack
pop()
: Removes the top element from the stack
and returns that top element. An error
occurs
if the stack is empty.
peek():Returns
the top element and an error occurs if the stack is empty.
1.
Adding an element into a stack. ( called
PUSH operations )
Adding element into the
TOP of the stack is called PUSH operation.
Check
conditions :
TOP = N ,
then STACK FULL where N is maximum size of the stack.
Adding into stack ( PUSH
algorithm )
procedure
add(item
: items);
{add item to the global stack stack ; top is the
current top of stack and n is its maximum size}
begin
if top = n then stackfull;
top := top+1;
stack(top) := item;
end: {of add}
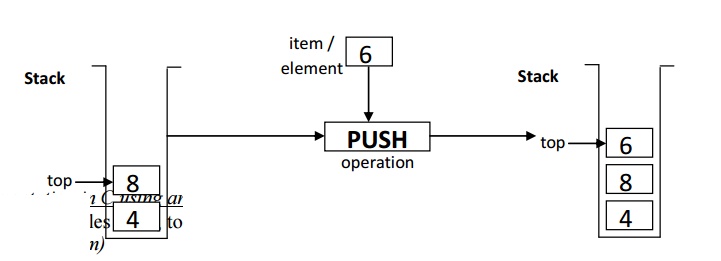
Implementation in C
/* here, the variables top and size are
global variables */
void push (int item)
{
if (top == size-1)
printf(“Stack is Overflow”);
else
{
top = top + 1; stack[top] = item;
}
}
2. Deleting an element from a
stack. (
called POP operations )
Deleting
or Removing element from the TOP of the stack is called POP operations.
Check Condition:
TOP = 0, then STACK EMPTY
Deletion in stack ( POP Operation )
procedure
delete(var
item : items);
{remove top element from the stack stack and put it
in the item} begin
if top = 0 then stackempty;
item := stack(top);
top := top-1; end; {of delete}
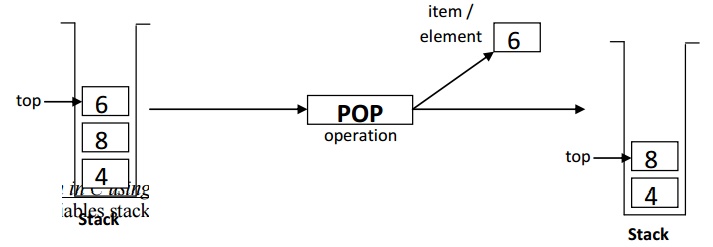
Implementation in using array:
/* here, the variables stack, and top
are global variables */
int pop ( )
{
if (top == -1)
{
printf(“Stack is Underflow”); return
(0);
}
else
{
return (stack[top--]);
}
}
3.
Peek Operation:
ü Returns
the item at the top of the stack but does not delete it.
ü This
can also result in underflow if the stack is empty.
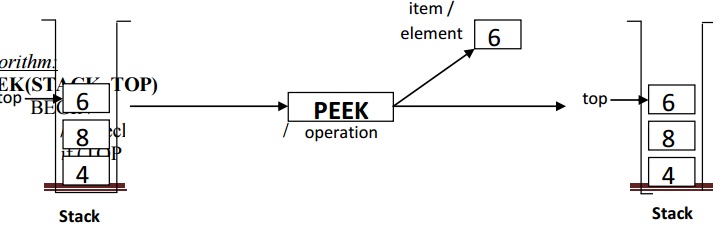
Algorithm:
PEEK(STACK, TOP)
BEGIN
/* Check, Stack is empty? */
if (TOP == -1) then
print “Underflow” and return 0. else
item
= STACK[TOP] / * stores the top element into a local variable */
return
item / * returns the top element
to the user */
END
Implementation in C using array:
/* here, the variables stack, and top
are global variables */ int pop ( )
{
if
(top == -1)
{
printf(“Stack is Underflow”); return
(0);
}
else
{
return
(stack[top]);
}
}
Applications of Stack
1. It
is very useful to evaluate arithmetic expressions. (Postfix Expressions)
2. Infix
to Postfix Transformation
3. It
is useful during the execution of recursive programs
4. A
Stack is useful for designing the compiler in operating system to store local
variables inside a function block.
5. A
stack (memory stack) can be used in function calls including recursion.
6. Reversing
Data
7. Reverse
a List
8. Convert
Decimal to Binary
9. Parsing
–It is a logic that breaks into independent pieces for further processing
10.
Backtracking
Note :
1. Infix notation A+(B*C)
equivalent Postfix notation ABC*+
2. Infix notation (A+B)*C
Equivalent Postfix notation AB+C*
Related Topics