Chapter: Mechanical : Manufacturing Technology : Metal Casting Process
Special Casting Process
SPECIAL CASTING PROCESS
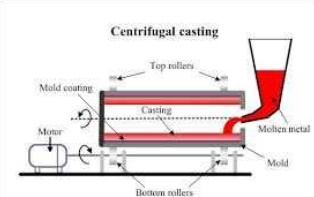
1.Centrifugal casting
Centrifugal casting uses a permanent mold that is rotated about its axis at a speed between300 to 3000 rpm as the molten metal is poured.Centrifugal forces cause the metal to be pushed out towards the mold walls, where it solidifies after cooling.Centrifugal casting has greater reliability than static castings. They are relatively free from gas and shrinkage porosity. Surface treatments such as case carburizing, flame hardening and have to be used when a wear resistant surface must be combined with a hard tough exterior surface.One such application is bimetallic pipe consisting of two separate concentric layers ofdifferent alloys/metals bonded together.
2. CARBON DI OXIDE PROCESS MOULDING.
Working Principle
The highly flowable mixture of pure dry silica sand and sodium silicate binder is rammed or blown into the mould or core box. Carbon –dioxide gas at a pressure of about 1.5 bar is diffused through the mixture (of sand and sodium silicate) to initiate the hardening reaction which takes from a few seconds to a few minutes depending upon the size of core or mould.Passage of carbon-dioxide through the sand containing sodium silicate produces carbonic acid in the aqueous solution, this causes a rise in the SiO2- Na2O ratio and the formation of a colloidal silica gel which hardens and forms a bond between the sand grains. The reaction is represented by the following equation.
NaSiO3 (Sodium Silicate) + CO2 -------à NaCO3 + SiO2 (Silica Gel)
Carbon Dioxide Moulding Operation
This sand is mixed with 3 to 5 % sodium silicate liquid base binder in Muller for 3 to 4 minutes. Additives such as coal powder, wood flour sea coal, and dextrin may be added to b improve its properties. Aluminium oxid e Kaolin clay may also added to the sand. Patterns use d in this method may be coated with Zinc of 0.05 mm to 0.13 mm and then spraying a layer of aluminium or brass of about 0.25 mm thickness for good surface finish and good results.
Advantages
• Operation is speedy since we can use the mould and cores imm ediately after processing.
• Heavy and rush orders
• Floor space requirement is less
• Semi skilled labor may be used.
Disadvantages
Difficult in reus ing the moulding sand.
Investment Casting
Investment casting produces very high surface quality and dim ensional accuracy. Investm ent casting is commonly used for precision equipment such as surgical e quipment, for complex geometries and for p recious metals.
This process is co mmonly used by artisans to produce highly detailed artwork. The first step is to produce a pattern or replica of the finished
mould. Wax is most commonly used to form the pattern, alth ough plastic is also used.
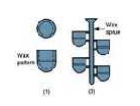
Patterns are typically mass-produced by injecting liquid or semi-liquid wax into a perm anent die.
Prototypes, small production runs and specialty projects can also be undertaken by carving wax models.
![]()
Cores are typica lly unnecessary but can be used for complex internal structures. Rapid prototyping techniques have been developed to produce expendable patter ns.
![]() Several replicas are often attached to a gating system constr ucted of the same material to form a tree assembly. In this way multipl e castings can be produced i n a single pouring.
Several replicas are often attached to a gating system constr ucted of the same material to form a tree assembly. In this way multipl e castings can be produced i n a single pouring.
Advantages
– Parts of great complexity and intricacy can be cast
– Close dimensional control and good surface finish
– Wax can usually be r ecovered for reuse
– Additional machining is not normally required - this is a net shape process
Disadvantages
– Many processing step s are required
– Relatively expensive process
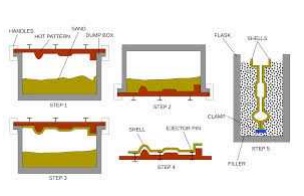
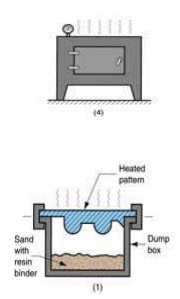
Shell-molding
Shell-mold casting yields better surface quality and tolerances.
The 2-piece pattern is made of metal (e.g. aluminum or steel), it is heated to between 175°C- 370° C, and coated with a lubricant, e.g. silico ne spray. Each heated half-pattern is covered with a mixture of sand and a thermoset resin/epoxy binder. The binder gl ues a layer of sand to the pattern, forming a shell. The process may be repeate d to get a thicker shell.The assembly is baked to cure it.The patterns are removed, and the two half-shells joined together to f orm the mold; metal is poured into th e mold. When the metal solidifies, the shell is broken to get the part.
Advantages of shell m oulding
Smoother cavity surface permits easier flow of molten meta l and better surface finish on casting
![]()
Good dimensiona l accuracy Machining often not required
Mold collapsibili ty usually avoids cracks in casting Can be mechaniz ed for mass production
Disadvantages of shell moulding.
More expensive metal pattern
Difficult to justif y for small quantities
Related Topics