Sound | Chapter 6 | 8th Science - Sound Waves | 8th Science : Chapter 6 : Sound
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 6 : Sound
Sound Waves
Sound Waves
Activity 6
Throw a stone into a
pool of still water. It produces waves, which spread rapidly over the surface
of water and they travel in all directions. Do water particles move away from
the point of disturbance? Check it by placing grains of saw dust over the
water. They do not move away. Instead they merely move up and down about their
mean position. Similarly, sound travels in the form of a wave.
Sound is a form of energy. It is
transferred through the air or any other medium, in the form of mechanical
waves. Mechanical wave is a disturbance, which propagates in a medium due to
the repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium, from their mean
position. The disturbance which is caused by the vibrations of the particles is
passed over to the next particle. It means that the energy is transferred from
one particle to another as a wave motion.
A. Characteristic of wave
motion
1. In wave motion, only the energy
is transferred not the particles.
2. The velocity of the wave motion
is different from the velocity of the vibrating particle.
3. For the propagation of a
mechanical wave, the medium must possess the properties of inertia, elasticity,
uniform density and minimum friction among the particles.
How do astronauts
communicate with each other? The astronauts have devices in their helmets which
transfer the sound waves from theirvoices into radio waves and transmit it to
the ground (or other astronauts in space). This is exactly the same as how
radio at your home works.
B. Types of mechanical wave
There are two types of mechanical
wave. They are
1. Transverse wave
2. Longitudinal wave
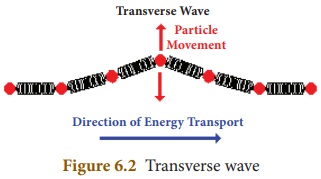
1. Transverse wave
In a transverse wave the particles
of the medium vibrate in a direction, which is perpendicular to the direction
of propagation of the wave. E.g. Waves in strings, light waves, etc. Transverse
waves are produced only in solids and liquids.
2. Longitudinal wave
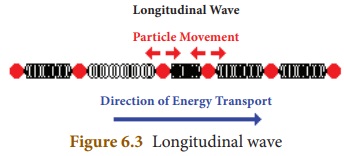
In a longitudinal wave the particles
of the medium vibrate in a direction, which is parallel to the direction of
propagation of the wave. E.g. Waves in springs, sound waves in a medium.
Longitudinal waves are produced in solids, liquids and also in gases.
The seismic wave formed during earthquake is an example for a longitudinal wave. Waves travelling through the layers of the Earth due to explosions, earthquakes and volcanic explosions are called seismic waves. Using a hydrophone and seismometer one can study these waves and record them. Seismology is the branch of science that deals with the study of seismic waves.
Related Topics