Chapter: Network Programming and Management : Socket Options, Elementary UDP SOC Sockets
Socket-Level Options
Socket-Level Options
— Constant: int SOL_SOCKET
Use this constant as the level argument to
getsockoptor setsockoptto manipulate the socket-level options described in this
section.
Here is a table of socket-level option names;
all are defined in the header file sys/socket.h.
SO_REUSEADDR
This option controls whether bind (see Setting Address) should permit reuse of local addresses for this
socket. If you enable this option, you can actually have two sockets with the
same Internet port number; but the system won't allow you to use the two
identically-named sockets in a way that would confuse the Internet. The reason
for this option is that some higher-level Internet protocols, including FTP,
require you to keep reusing the same port number.
The value has type int; a nonzero value means
―yes‖.
SO_KEEPALIVE
This option controls whether the underlying
protocol should periodically transmit messages on a connected socket. If the
peer fails to respond to these messages, the connection is considered
broken. The value has type int; a nonzero value
means ―yes‖.
SO_DONTROUTE
This option controls whether outgoing messages
bypass the normal message routing facilities. If set, messages are sent
directly to the network interface instead. The value has type int; a nonzero
value means ―yes‖.
SO_LINGER
This option specifies what should happen when
the socket of a type that promises reliable delivery still has untransmitted
messages when it is closed; see Closing a Socket. The value has type
struct linger.
— Data Type: struct linger
This structure type has the following members:
int l_onoff
This field is interpreted as a boolean. If
nonzero, closeblocks until the data are transmitted or the timeout period has
expired.
int l_linger
This specifies the timeout period, in seconds.
SO_BROADCAST
This option controls whether datagrams may be
broadcast from the socket. The value has type int; a nonzero value means ―yes‖.
SO_OOBINLINE
If this option is set, out-of-band data
received on the socket is placed in the normal input queue. This permits it to
be read using reador recvwithout specifying the MSG_OOB flag. See Out-of-
Band Data.The value
has type int; a nonzero value means ―yes‖.
SO_SNDBUF
This option gets or sets the size of the output
buffer. The value is a size_t, which is the size in bytes.
SO_RCVBUF
This option gets or sets the size of the input
buffer. The value is a size_t, which is the size in bytes.
SO_STYLESO_TYPE
This option can be used with getsockoptonly. It
is used to get the socket's communication style. SO_TYPEis the historical name,
and SO_STYLEis the preferred name in GNU. The value has type intand its value
designates a communication style; see Communication Styles.
SO_ERROR
This option can be used with getsockoptonly. It
is used to reset the error status of the socket. The value is an int, which
represents the previous error status.
SO_RCVBUF /SO_SNDBUF
•
Integer
values options - change the receive and send buffer sizes.
•
Can be
used with STREAM and DGRAM sockets.
•
With
TCP, this option effects the window size used for flow control – must be
established before connection is made.
SO_REUSEADDR
Boolean option: enables binding to an address
(port) that is already in use.
•
Used by
servers that are transient - allows binding a passive socket to a port
currently in use (with active sockets) by other processes.
Can be used to establish separate servers for
the same service on different interfaces (or different IP addresses on the same
interface).
Virtual Web Servers can work this way.
KEEPALIVE socket Option: The purpose of this
option is to detect if the peer host crashes. This option is usually used by
servers, although client can also use this option. Server uses this option
because they spend most of their time blocked wiating for the input across the
TCP connection, that is waiting for the client request. But if the client host
crashes, the server process will never know about it and it will wiat
continuosly for input data that can never arrriver. This is called half open
connection. The keep alive option will detect these half open connections and
terminates them.
3. If there is no response from the peer to the
keepalive probe, TCP sends eight additional probes, 75 sec apart trying to
elicit response. TCP will give up if ther is no response within 11 minutes and
15 seconds after sending the first probe. If there is no response at all to
TCPs keepalive probes, the socket‘s pending error is sent to ETIMEDOUT and the
socket is closed. But if the socket receives an ICMP response to one of the
keepalive probes, the socket corresponding error is returned instead such as
EHOSTUNREACH error.
SO_LINGER Socket option: This option specifies
how the close function operates for a connection oriented protocol (that is for
TCP) By default, close function returns immediately with ack, but if there is
any data still remaining the in the socket sedn buffer, the system will try to
deliver the data to the peer.
The
SO_LINGER socket option les us change this default. This option requires the
folowing structure to be passed between the user process and the kernel. It is
defined as
Struct linger {
Int l_onoff; /* 0 for Off and Nonzero for ON*/
Int l_linger; /*Linger time Posix 1g
specification as seconds*/
}
Calling
setsocket leads to one of the folowing threee scenarios depending on the values
of the two structure memebrs.
1. If l_onoff is 0, the option is turned off. The
value of l_linger is ignored and the preveiously discussed TCP default applies:
close returns immediately.
2. If l_onoff is non zero and l_linger is 0, TCP
aborts the connection when it is closed. That is TCP discards any data still
remaining in the socket send buffer amd sends an RST to the peer.
(Not the four step termination sequence) This avoids the TCP‘s IME_WAIT state.
3. If l_onoff is nonzero and l_linger is non zero,
then the kernel will linger when the socket is closed . That is, if ther is any
bdata stilol remaining in the socket send buffer, the process is put to sleep
until either i) all the data is sent and acknolodged by the peer TCP ii) the linger
time expires
When using this feature of the SO-LINGER
option, it is important for the application to check the return value from
close because if the linger time expires before the remianing data is sent and
acknowledged, claose returns EWOULDBLOCK and any remaining data in the send
buffer is discarded.
SO_RCVBUF and SO_SNDBUF Socket Option:
The
receive buffer are used by the TCP and UDP to hold received data until it is
read by the application. With TCP, the available room in the socket receive buffer
is the window that TCP avertises to the other end. Hence the the peer sends
only that amount of data and any data beyond that limit is discarded. In case
of UDP, the bufffer size is not advertised hence, any data that do not fit ito
the buffer, are dropped However, the abovementioned socket options allows one
to change the default sizes. The default values for the TCP and UDP differ for
different implementation. It is normally 4096 for TCP and send buffer for UDP
is 9000 and 40000 bytes for receive buffer.
SO_REUSEADDR and
SO_REUSEPORT:
The SO_REUSEADDR serves four purposes :
This option allows a listening server to start
and bind its well known port even if previously established connections exists
that use this port as their local port. As the server is in listening state,
when connection request comes from a client, a child process is spawned to
handle that client. Wqith this listening server terminates. Once again when the
listening is restarted buy calling socket, bind and listen, the call to bind
fails because the listening server is trying to bind a port that is part of
exisitng connection. But if the srver is sets the SO_REUSEADDR socket option
between the calls to socket and bind, the latter function will succeed.
This
allows multiple instances of the same service to be started on the same port as
long as each instance binds a different local IP address. It is common of a a
site to host multiple http servers using the IP alias techniques. If the
primary address is 198.69.10.2 and it has two aliases as 198.69.10.129 and
198.69.10.128. Three HTTP servers are started. Whne the first connection
request comes, the server binds the call with 198.69,10.128 and a local port of
80. The second request is connected to 198.69.10.129 provided the SO_REUSEADDR
is set before the call to bind.
Simlarly for the final http server also.
It also
allows a single process to bind the same port to multiple socket as slong as
each bind specifies a different loacl IP address It also allows completely
duplicate binding: a bind of an IP address and port, when the same IP address
and port are already bound to another socket. This happens with the protocol
that support multicasting (UDP)
SO_ TYPE socket
Option: This option returs the socket ytpe. The integer value returned is a
value such as SOCK _ STREAM or
SOCK_DGRAM.
SO_USELOOPBACK Socket
Option: When this option is set, the socket receives a copy of everything send on the socket.
IPv4 Socket options: The level of this options are IPPROTO_IP.
IP_HDRINC Socket
Option : If this socket is set for a raw socket, we must buid our own IP header
for all datagrams that we send on
the raw socket. Normally kernel builds the headers for datagrams sent on raw
socket. But for some applications, build there own IP address to override that
IP would place into certain header fields. (Traceroute).
IP_OPTIONS Socket
Options: Setting this option allows us to set the IP option in the Ipv4 header.
This requires intimate knlowledge of
the format of the IP options in the IP header.
IP_RECVDSTADDR Socket
Options :
This
socket options causes the destination IP address of a received UDP datqgram to
be returned as ancillary data by recvmsg.
IP_RECVIF Socket
Options :
This
socket option causes the index of the interface on which a UDP datagram is
received to be returned as an ancillary data by recvmsg.
IP_TOS Socket
Option :
This options lets us set the type of field
service in the IP header for a t
CP or UDP socket. The different value to which
this o[tions can be set are given below: Constant description
IPTOS_LOWDELAY minimize delay.
IPTOS_THROUGHPUT maximize throughput
IPTOSRELIABILITY maximize reliability.
IPTOS_LOWCOST Minimize cost.
For
telnet login shoul;d specify IPTOS_LOWDEAY while the data portion of an FTP
transfer should specify IPTOS_ THROUGHPUT
IP_TTL Socket
Option :
With
this option we can set and fetch the default TTL (time to live field) that the
system will use for a given socket (*64 for TCP and 255 for UDP)
ICMPv6 Socket
Option : The level is of IPPROTO_ICMPV6
ICMP6_FILTER: This
option lets us fetch and set an icmp6_filter structure that specifies which of the 255 possible ICMPV6 message types
are passed to the process on a raw socket.
IPv6 Socket Options:\
These are processed by IPv6 and have a level of
IPPROTO_IPV6.
IPV6_ADDRFORM Socket
Option:
This option allows a socket to be converted from IPv4 to IPv6 or vice
versa.
IPV6_CHECKSUM Socket Option: This socket option specifies the byte offset into the user data
of where the checksum field is
located. If this value is nonnegative, the kernel computes and store the
checksum for all outgoing pockets. And verify the received checksum on input,
discarding packets with invalid checksum. If the value is set to -1, the kernel
will calculate and store the checksum for outgoing packets.
IPV6_DSTOPTS Options : This options lets any received IPv6 destination options are to be
returned as ancillary data by recvmsg.
IPV6_HOPOPTS: Setting
this option specifies that the received IPv6 hop by hop options are to be returned as ancillary data by recvmsg.
IPV6_HOPLIMIT : Setting this option specifies that the received hop limit field be
returned as ancillary data by recvmsg.
IPV6_NEXTMSG : This is
a not a socket option but the type of an ancillary data object that can be specified to sendmsg. This opjet specifies the next hop address for a datagram
as a socketaddress structure.
IPV6 _PKTINFO:
Setting this option specifies that the following two pieces of information
about a received IPv^ datagram ae to
be returned as ancillary data by recvmsg.
IPV6_PKTOPTIONS: Most
of the IPv6 socket options assume a UDP socket with the information being passed between the kernel and
the application using ancillary data with recvmsg
and sendmsg. A TCP socket fetches and stores these values using the IPV6_PLTOPTIONS
socket options.
IPV6_RTHDR: Setting this options specifies that a
received IPV6 routing header is to be returned as ancillary data by recvmsg.
IPV6_UNICAST_HOPS : This IPv6 option is similar to the IPv4 IP_TTL socket option.
Setting the socket option specifies
the default hop limit for outgoing datagram sent on the socket, whcile fetching
the socket options returns the value for the hop limit that the kernel use fo
the socket. To obtain actual hop limit field, IPV^_HOPLIMIT socket option is
used.
TCP SOCKET OPTIONS: The leve is IPPROTO_TCP
TCP_KEEPALIVE socket
options : It specifies the idle time in seconds for the connections before TCP starts sending keepalive probes.
Default value is 7200 sec (2 hours) This is effective when SO_
KEEP ALIVE option is enabled.
TCP_MAXRT Socket
Options : It specifies the amount of time in seconds before a connections is broken once TCP starts transmitting
data. A value of 0 means touse the system default. And a value of –I means to
rettransmit forever. If a positive value is specified, it may be rounded up to
the implementations next transmission time.
TCP_MAXSIZE Socket
Option: This socket option allows us to fetch or set the maximum segment size for a TCP connection. Often it is
the MSS value announced by the peer process.
TCP_NODELAY Socket Option :
If this option is set, TCP‘s Nagle‘s algorithm
is disabled.
Nagle‘s Algorithm: The algorithm states that if
a given connection has outstanding data ( that is, data that our TCP has sent
and for which it is currently awaiting an ack), then no small packet will be
sent on the connection until the existing data is acknowledged. Small packet is
any size less than MSS. The purpose is to prevent a connection from having
multiple packets outstanding at any time. This situation becomes more
prominenet in a WAN with Telnet.
Consider the example where in we type Hello to
Telnet client. Let this take 250 ms between each letter (as shown below) The
RTT to the server and back is 600 ms and the server immediately sends the echo
of the character. We assume that ACK of the client character is sent back to
the client along with the character echo and we ignore the ACKs that the client
sends for the server echo. Assuming Nagle‘s algorithm disabled, we have the
following figure:
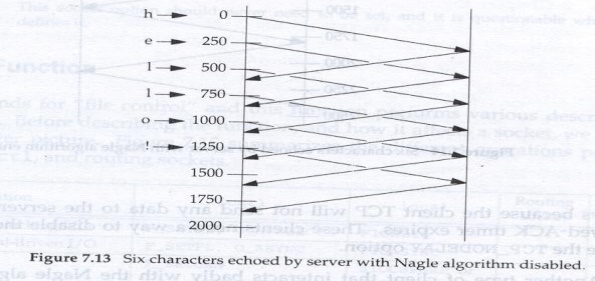
IN this each packet is sent in a packet itself.
But if the Nagle‘s algorithm is enabled
(default), we have the six packets as shown in the following figure:
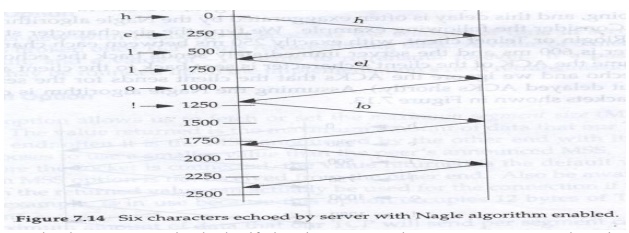
The first packet is sent as a packet by
itself., but the next two characters are not sent, since the connection has
small packet outstanding. At time 600 ms when the ACK of the first packet is
received, along with the echo of the first character, theset two characters are
sent. Until this packet ACKed at time 1200, no more small packets are sent.
When the Nagles algorithm oftern interacts with another TCP algorithm called ‗delayed ACK‘ algorithm. This algorithm causes the TCP to not send an ACK immediately whne it receives data; instead TCP will wait some small amount of time and only then send ACK. The hope is that in this small time (50 – 200 ms) there will be more data to be sent back to the peer and the ACK can piggy back on the data saving the TCP segment. This is the normally case with Telnet. Therefore, they wait for the echoed data
to piggy back.
In all these cases, the TCP_NODELAY socket
option is set.
TCP_STDURG socket option: If this is set, then
the the urgent pointer will point to the data byte sent with the MSG_OOB flag
fcntrl Function : This stands for file control. This control performs various
deascriptors control operations.
Following table summarised some of the key file operations. These are preferred
way under Posix 1g.
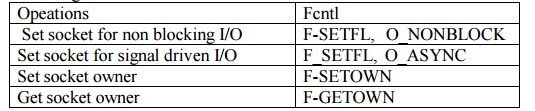
These features are provided in the following
way.
•
Non
blocking I/O: We can set the O_NONBLOCK file status flag using the F_SETFL
command to set a socket nonblocking.
• Signal
Driven I/O : We can set the O_SYNC file status by using F-SETFL command which
caused the SIGIO signal to be generated when the status of a socket changes.
•
The F_SETDOWN
command lets us set the socket owner to receive the SIGIO and SIGURG signals.
SIGIO is generated when the signal driven I/O is enabled for a socket and the
latter is generated with new out of band data arrives for a socket. The
F-GETOWN command returns the current owner of the the socket.
#include <fcntl.h>
int fcntl (int fd, int cmd, …) returns: depends
on cmd if OK, -1 on error.
Related Topics