Chapter: Network Programming and Management : Socket Options, Elementary UDP SOC Sockets
Elements of UDP Socket
ELEMENTS OF UDP SOCKET
The significant difference between TCP and UDP
applications are in the Transport layer. UDP is connectionless, unreliable,
datagram protocol. However, there are needs for such requirements in
applications such as DNS, NFS and SNMP. Typical functions calls of UDP client
server are shown below:
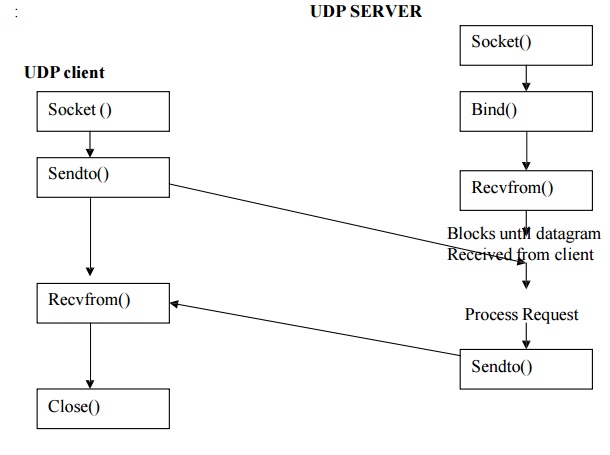
IN this, client does not establishes connection with server, rather
it sends datagram using send to function along with destination address.
Similarly, the server does not accept connection from a client, instead the
server just calls recvfrom function which waits until data arrives from some
client. Recvfrom returns the protocol address of the client along with the
datagram so the server can send a response to the correct client.
Recvfrom and sendto functions
: #include <sys/socket .h>
ssize_t recvfrom ( int sockfd, void *buff,
size_t nbytes, int flags, struct sockaddr *from, socklen_t *addrlen)
ssize_t sendto ( int sockfd, const void *buff,
size_t nbytes, int flags, struct const sockaddr *to, socklen_t *addrlen)
sockfd,
buff and nbytes are identical to the first three arguments for read and write:
descriptors, pointer to buffer to read into or write from, and number of bytes
to read or write.
The
flags are meant are normally used with recvmsg and sendmsg functions. IN this
function they are defaulted to the value of 0. The to argument for the sendto
is a socket address structure containing protocol address (IP and port) of
where data is to be sent. The recvfrom functions fills in the socket address
structure pointed to by from with the protocol address of who sent the
datagram. The number of bytes stored in this socket address structure is also
returned to the caller in the integer pointed to by the addlen.
Final
argument to sendto is an integer value, while the final argument to recvfrom is
a pointer to an integer value (a value result - argument.)
The
final two argument of recvfrom is similar to the two argument to accept : the
contents of the socket address structure upon return tell us who sent the
datagram (in case of UDP)or who initiated the connection in the case of TCP.
Both function return the length of the data that was read or written as the
value of the funtion.
In the
case of writing a datagram of length 0 is OK. IN UDP, this means, 20 byte
length of IP header of IPV4, 8 byte UDP header and no data. It is accepted
unlike TCP where in a 0 is consider as EOF.
UDP Echo Server : Main function: The function
call of UDP client and server is shown in the following figure.
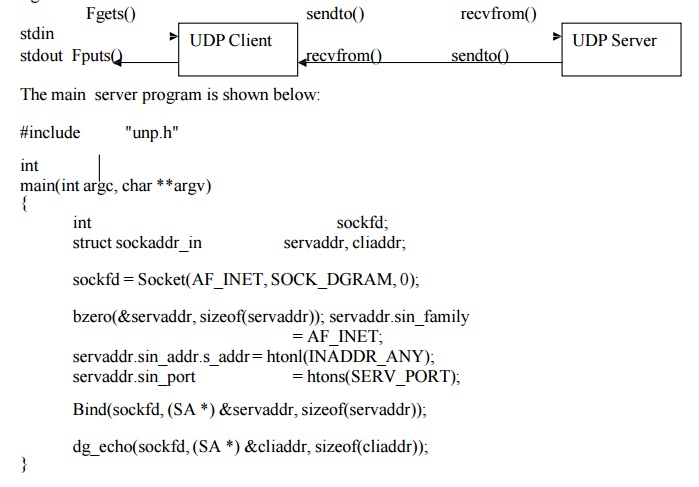
IN this UDP socket is created by giving
SOCK_DGRAM . The address for the bind is given as INADDR_ANY for multihomed
server. And the const SERVER_PORT is the well known port.
UDP Echo Server : dg_echo function: The
programme is given below:
void
dg_echo(int sockfd, SA *pcliaddr, socklen_t
clilen)
{
int n;
socklen_t len;
char mesg[MAXLINE];
for ( ; ; ) {
len = clilen;
n = recvfrom(sockfd, mesg, MAXLINE, 0,
pcliaddr, &len); sendto (sockfd, mesg,n,0,pcliaddra, len);
}
}
The important details to consider are:
1. The function never terminates ( exit (0) is not
called) as it is connection less protocol
2. The main function is iterative server not
concurrent. There is no call tofokr, so a single server process handles any and
all clients.
3. There is implied queuing takes place in the UDP
layer for the socket. Each datagram that is arrived is received in a buffer
from where the recvfrom receives the next datagram in FIFO manner. The size of
the buffer may be changed by changing the value of SO_RCVBUF

The main function in figure is the protocol
dependent ( it creates a ![]() socket of protocol AF_INET) and
allocates and initializes an IPv4 socket address structure. But the dg_echo
function is protocol independent as it is provided with the socket address
structure and its length by the main function. It is the recvfrom that fills in
this structure with the IP address and prot number of the client and as the
same pointer is passed to sendto as the destination address.
socket of protocol AF_INET) and
allocates and initializes an IPv4 socket address structure. But the dg_echo
function is protocol independent as it is provided with the socket address
structure and its length by the main function. It is the recvfrom that fills in
this structure with the IP address and prot number of the client and as the
same pointer is passed to sendto as the destination address.
Related Topics