Chapter: Network Programming and Management : Socket Options, Elementary UDP SOC Sockets
Generic Socket Options
GENERIC SOCKET OPTIONS:
These socket options are protocol independent meaning that the protocol independent code within the kernel handles these and not particular module of any protocol. Some options apply to only certain types of sockets. For example, SO-BROADCAST socket options applied only to datagram socket although it is listed under GENERIC Sockets.
SO_BROADCAST
Socket Option: This socket option enables or
disables the ability of the process to send
broadcast messages. Broadcasting is supported for only datagram sockets and
only on net works such as ethernet, token ring etc but not point to point
networks. This option controls whether datagrams may be broadcast from the
socket. The value has type int; a nonzero value means ―yes.
SO_DEBUG:The option is supported by TCP only. When
enabled for a TCP socket, the kernal keeps
track of all the packets sent or received by TCP for the socket.
SO_DONTROUTE
Socket option: The option specifies that
outgoing packets are to bypass the normal
routing mechanism of the underlying ptotocol. With Ipv4, the packet is
directed to the appropriate local
interface, as specifried by the network and
subnet protions of the destination address.
If the local
interface cannnot be determined from
destination address, ENETUNREACH is
returned.
SO_ERROR
options: This option can be used with
getsockoptonly. It is used to reset the error status of the socket. When a errors occurs on a socket, the protocol module
sets a variable named so_error for that socket to one of the standard unix
values. The processs is immediately notified. The process can then obtain the
values of so-error by fetching the SO_ERROR socket option. After the receipt,
the so_error value is reset to 0 by the kernel.
SO_KEEPALIVE
socket option: When the keep alsive socket option
is set for a TCP socket, and if no
data is exchanged across in either direction for two hours TCP automatically
sends a keepalive probe to the peer. The probe is a
TCP segment to which the peer must respond. The possible three scenarios ae ;
•
The peer
responds with expected ACK. The application is no notified but the TCP sens
another
probe after
2 hours.
•
The peer
responds with RST which tells the local TCP that the peer host has crashed and
rebooted..
The
socket‘s pending error is set to ECONNRESET and
the socket is closed.
•
There is
no response from the peer. TCP sends eight additional probes, 75 sec apart . If
there is no response within 11 min a dn 15 se after first probe, the socket is
sent with ETIMEOUT and the socke tis
closed.
The purpose of this option is to detect if the
peer host crashes. IF the peer host crashes, its TCP will send
FIN
across the connection which can easily detect
with select. SO_LINGER Socket Option :
The option specifies how the close function
operates for a connection oriented protocol (TCP). BY default,
close returns immediately, but if there is any
data still remaining in the socket send buffer, the system will try to deliver
the data top the peer.
The SO_LINGER socket option lest us change this
default. This option requires the folowing structure to be passed between the
user process and the kernel. It is is defined by including <sys/socket.h>
Struct linger {
Int l_onoff; /*0=off,
nonzero = on */
Int l_linger ; /* liner time, posix 1g
specifies uits as sec*/
}
Calling setsockopt leads to one of the
following three scenarios depending on the values of the two structure.
1.
if
l_onoff is 0, the option is turned off. The value of l_linger is ignored and
the reviously discussed TCP defaults applies. Close returns immediately.
2. IF l_onoff is nonzero and l_linger is 0, TCP aborts the connection when it is closed. That is TCPdiscards any data still remaining in the socket send buffer and an RST to the peer.
3.
IF
l_onoff is nonzero and l_linger is nonzero, the kernel will linger when the
socket is closed. Thst is if ther is any data still remaining in the socket
send buffer, the porcess is put to sleep until either a) all the data is send
and acknowledged by the peer. B) the linger time expires.
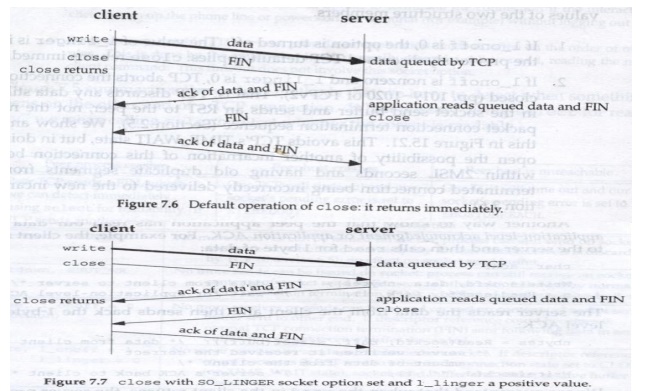
Let us understand when the close on a socket
returns, given the various scenarios that we have seen so far. Assue that the
client writes data to the socket and then calls close as shown in the folowing
figure.
When the clidnt data arrives, the server is
temporarily busy, so the data is added to the socket receive buffer by its TCP.
Similarly the next segment, the client‘s FIN is also addded to the socket
receive buffer. But by default, the client‘s close returns immediately.
SO-OOBINLINE
socket option:
When This option is set, out of band data will
be placed in the normal input queue. Whne this occurs, the
MSG_OOB flag to the receive functions cannot be
used to read the out of band data.
SO_RCVLOWAT and SO_SNDFLOWAT Socket Options:
Every socket has a receive low mark and a send
low water mark. These are used in select function. These two socket opitons les
us to change these options.
Receive low water mark is the amount of data that must be in the socket receive buffer for select function to be readable. If defalut to 1 for a TCP and UDP sockets. The send low water mark is the amount of available space that must exist in the socket send buffer for a select function to return writable. This low watermarl bnormally defaults to 2048 for TCP sockets.
SO_CVTIMEO AND SO_NDTIMO socket options: These
two socket options allow us to place a timeout on socket receives and sends.
Notice that the arguments to the two sockopt functionsis a pointer to a timeval
structure, the same one used with select. This lets specify the timeout in
seconds and microseconds.
The receive timeout afffects the five input
functions : read, readv, recv, recvfrom and recvmsg. The send timeout affects
the five output functions : write, writev,send, sendto, and sendmsg.
Related Topics