Chapter 2 | Economics | 8th Social Science - Socio-Economic Development | 8th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 2 : Public and Private Sectors
Chapter: 8th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 2 : Public and Private Sectors
Socio-Economic Development
Socio-Economic Development
Socio-economic development is the
process of social and economic development in a society. Socio-economic
development is measured with indicators, such as GDP, life expectancy, literacy
and levels of employment.
The new “Think Tank” is NITI Aayog
can form a suitable platform in integrating the social sector initiatives of
the Centre, state and the local bodies.



INDICATORS OF SOCIO- ECONOMIC
DEVELOPMENT
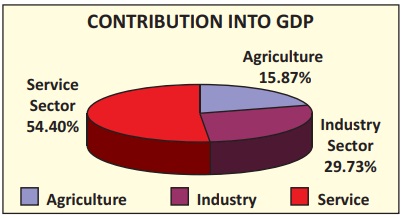
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
GDP supports in developing socio -
Economic Development. The proportion of GDP by the industrial sector both
private and public sector has been increased. It results increasing government
funds and increase public spending.
Life Expectancy
According to 2011 Census of India,
Life expectancy in India is 65.80 years for men and 68.33 years for women.
Government provides high degree of health measures through various programmes.
The Government announced in the Union Budget 2018-19 the “National Health
Production Scheme” (NHPS) to serve poor and vulnerable families.
Literacy
Educational skill plays a vital role
in the Socio Economic Development. Sarva Siksha Abhiyan(SSA) is government of
India’s flagship programme. It is implemented for making free and Compulsory
Education to the children of 6-14 years with life skills. The Government also introduced
RMSA, Smart class, e-learning, free computer skill classes and eco-friendly
studying environment, Digital India for increasing the level of quality in
education.
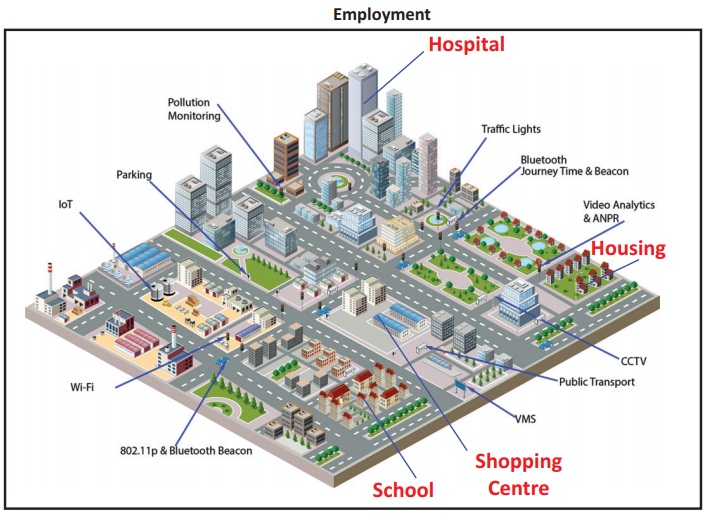
Employment
There is a clear shift in employment
to secondary and tertiary sector from the primary sector. A growing number of
people moved urban areas in search of employment. It increased urban
population, hence government started the ‘Smart city’ Scheme which provides the
city with many facilities like hospitals, schools, housing facilities and
shopping centers. To promote rural and backward areas in terms of employment
the government encourages private sectors to start an industry in backward
areas by providing tax benefit electricity at a lower tariff, etc., It removes
regional inequality.
Provision of House , Clean
Drinking Water and Sanitation
Government sector provides housing
facilities, clean drinking water facilities and sanitary facilities under clean
India Planning. Providing clean water and sanitary facilities overcome diseases
and malnutrition. By providing these facilities the Life Cycle of the people
increases.
Related Topics