Chapter 2 | Economics | 8th Social Science - Definition, History, objectives of Public Sector | 8th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 2 : Public and Private Sectors
Chapter: 8th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 2 : Public and Private Sectors
Definition, History, objectives of Public Sector
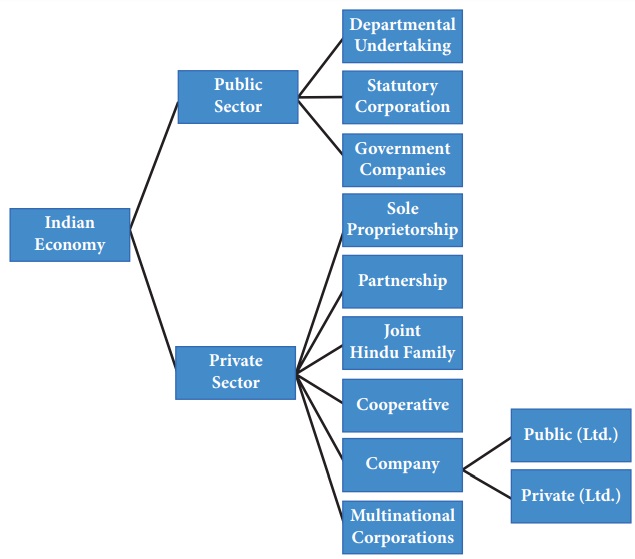
Definition of Public Sector
The sector, which is engaged in the
activities of providing government goods and services to the general public is
known as Public Sector. The enterprises, agencies, and bodies are fully owned,
controlled and run by the government whether it is central government, state
government or a local government.
History of public Sector
When India achieved independence in
1947, it was primarily an agricultural country with a weak industrial base.
There were only eighteen Indian Ordnance Factories in the country which the
British had established for their own economic interest and rule the
subcontinent with brute force. The national consensus was in favour of rapid
industrialisation of the economy which was seen as the key to economic
development, improving living standards and economic sovereignty.
Building upon the Bombay Plan
(1940), which noted the requirement of government intervention and regulation,
the first Industrial Policy Resolution announced in 1948 laid down broad
contours of the strategy of industrial development. Subsequently, the Planning
Commission was formed by a cabinet resolution in March 1950 and the Industrial
Act was enacted in 1951 with the objective of empowering the government to take
necessary steps to regulate industrial development.
Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru
promoted an economic policy based on import substitution industrialisation and
advocated a mixed economic system. He believed that the establishment of basic
and heavy industry was fundamental to the development and modernisation of the
Indian economy. India's second five year plan (1956–60) and the Industrial
Policy Resolution of 1956 emphasised the development of public sector
enterprises to meet Nehru's national industrialisation policy. His vision was
carried forward by Dr. V. Krishnamurthy known as the "Father of Public
sector undertakings in India". Indian statistician Prof. P.C. Mahalanobis
was instrumental to its formulation, which was subsequently termed the
Friedman– Mahalanobis model.
The 1991 industrial policy was
radically different from all the earlier policies where the government was
deliberating disinvestment of public sector and allowing greater freedom to the
private sector. At the same time, foreign direct investment was invited from
business houses outside india. Thus, multinational corporations, which operate
in more than one country gained entry into the Indian economy. Thus, we have
public sector units, private sector enterprises and multinational corporations
coexisting in the Indian economy.
The objectives of Public Sector
*
To promote rapid economic development through creation and expansion of
infrastructure
*
To generate financial resources for development
*
To promote redistribution of income and wealth
*
To create employment opportunities
*
To promote balanced regional growth
*
To encourage the development of small-scale and ancillary industries, and
*
To accelerate export promotion and import substitution
Related Topics