Chapter: Web or internet Programming : Server Side Programming
Servlets
Servlets
• A Java
program which resides and executes on a server to provide functionality to the
server or processing of data on the server.
Lifecycle:
• The life
cycle of a servlet is controlled by the container in which the servlet has been
deployed. When a request is mapped to a servlet, the container performs the
following steps.
1. If an
instance of the servlet does not exist, the Web container
a. Loads the
servlet class.
b. Creates
an instance of the servlet class.
c. Initializes
the servlet instance by calling the init method. Initialization is covered in
Initializing a Servlet.
2. Invokes
the service method, passing a request and response object. Service methods are
discussed in the section Writing Service Methods.
3. If the
container needs to remove the servlet, it finalizes the servlet by calling the
servlet's destroy method. Finalization is discussed in Finalizing a Servlet.
Example:
import
java.io.*;
import
javax.servlet.*;
import
javax.servlet.http.*;
public
class HelloWorld extends HttpServlet
{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException
{
PrintWriter
pw = response.getWriter(); pw.println("Hello World");
}
}
Servlet API (refer
java complete ref)
Two packages contain the classes and interfaces
that are required to build servlets. These are javax.servlet and
javax.servlet.http. They constitute the Servlet API. Keep in mind that these packages are not part of the Java core
packages. Instead, they are standard extensions. Therefore, they are not
included in the Java Software Development Kit. You must download Tomcat to
obtain their functionality.
The Servlet API has been in a process of ongoing
development and enhancement. The current servlet specification is version is
2.3 and that is the one used in this book. However, because changes happen fast
in the world of Java, you will want to check for any additions or alterations.
This chapter discusses the core of the Servlet API, which will be available to
most readers.
The javax.servlet package contains a number
of interfaces and classes that establish
the
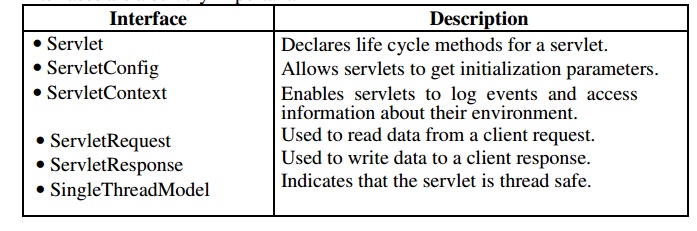
framework in which servlets operate. The following table summarizes the core interfaces
that are provided in this package. The most significant of these is Servlet. All servlets must implement
this interface or extend a class that implements the interface. The ServletRequest and ServletResponse interfaces are also very important.
The
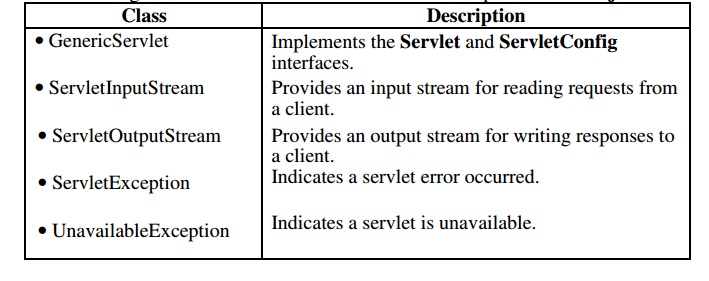
following table summarizes the core classes that are provided in the javax.servlet package.
Related Topics