Chapter: Security Investigation : Security Investigation
Security Investigation: Threats
THREATS
To
protect an organization’s information, you must
Know yourself
(i.e) be familiar wit the information to be
protected, and the systems that store, transport and process it.
2. Know
the threats you face
To make sound decisions about information security,
management must be informed about the various threats facing the organization,
its application, data and information systems.
A threat
is an object, person, or other entity, that represents a constant danger to an
asset.
1 Threats to Information Security

2 Threats
ü Acts of Human Error or Failure:
Acts
performed without intent or malicious purpose by an authorized user.
because
of in experience ,improper training,
Making of
incorrect assumptions.
One of
the greatest threats to an organization’s information security is the
organization’s own employees.
ü Entry of
erroneous data
ü accidental
deletion or modification of data
ü storage
of data in unprotected areas.
ü Failure to protect information
can be prevented with
Training
Ongoing
awareness activities -Verification by a second party
Many
military applications have robust, dual- approval controls built in .
Compromises to Intellectual Property
ü Intellectual Property is
defined as the ownership of ideas and control over the tangible or virtual representation of those
ideas.
ü Intellectual
property includes trade secrets, copyrights, trademarks, and patents.
ü Once
intellectual property has been defined and properly identified, breaches to IP
constitute a threat to the security of this information.
ü Organization
purchases or leases the IP of other organizations.
ü Most
Common IP breach is the unlawful use or duplication of software based
intellectual property more commonly known as software Piracy.
ü Software
Piracy affects the world economy.
ü U.S
provides approximately 80% of world’s software.
In addition
to the laws
surrounding software piracy,
two watch dog
organizations
investigate
allegations of software abuse.
Software and Information Industry Association
(SIIA) (i.e)Software Publishers Association
Business Software Alliance (BSA)
Another effort to combat (take action against)
piracy is the online registration process.
Deliberate Acts of Espionage or Trespass
ü Electronic
and human activities that can breach the confidentiality of information.
ü When an
unauthorized individual’s gain access to the information an organization is
trying to protect is categorized as act of espionage or trespass.
ü Attackers
can use many different methods to access the information stored in an
information system.
Competitive Intelligence[use web browser to get
information from market research]
Industrial espionage(spying)
3. Shoulder
Surfing(ATM)
Trespass
Can lead
to unauthorized real or virtual actions that enable information gatherers to
enter premises or systems they have not been authorized to enter.
Sound
principles of authentication & authorization can help organizations protect
valuable information and systems.
Hackers-> “People who use and create
computer software to gain access to information illegally”
There are
generally two skill levels among hackers.
Expert Hackers-> Masters of several
programming languages, networking protocols, and operating systems .
Unskilled Hackers
ü Deliberate Acts of information Extortion (obtain by
force or threat)
Possibility
of an attacker or trusted insider stealing information from a computer system
and demanding compensation for its return or for an agreement not to disclose
the information.
ü Deliberate Acts of sabotage or Vandalism
Destroy
an asset or
Damage
the image of organization
Cyber
terrorism-Cyber terrorists hack systems to conduct terrorist activities through
network or internet pathways.
ü Deliberate Acts of Theft
Illegal
taking of another’s property-- is a constant problem.
Within an
organization, property can be physical, electronic, or intellectual.
Physical
theft can be controlled by installation of alarm systems.
Trained
security professionals.
Electronic
theft control is under research.
ü Deliberate Software Attacks
Because
of malicious code or malicious software or sometimes malware.
These
software components are designed to damage, destroy or deny service to the
target system.
More
common instances are
Virus,
Worms, Trojan horses, Logic bombs, Backdoors.
“The
British Internet Service Provider Cloudnine” be the first business “hacked out
of existence”
ü Virus
Segments
of code that performs malicious actions.
Virus
transmission is at the opening of Email attachment files.
Macro virus-> Embedded in automatically
executing macrocode common in word processors,
spreadsheets and database applications.
Boot Virus-> infects the key operating
files located in the computer’s boot sector.
ü Worms
A worm is
a malicious program that replicates itself constantly, without requiring
another program to provide a safe environment for replication.
Worms can
continue replicating themselves until they completely fill available resources,
such as memory, hard drive space, and network bandwidth.
Eg:
MS-Blaster, MyDoom, Netsky, are multifaceted attack worms.
Once the
worm has infected a computer , it can redistribute itself to all e-mail
addresses found on the infected system.
Furthermore,
a worm can deposit copies of itself onto all Web servers that the infected
systems can reach, so that users who subsequently visit those sites become
infected.
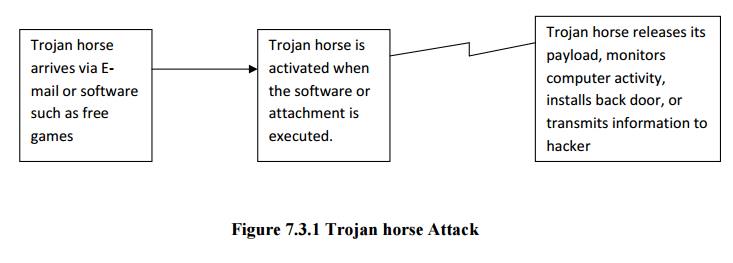
ü Trojan Horses
Are
software programs that hide their true nature and reveal their designed
behavior only when activated.
Back Door or Trap Door
ü A Virus
or Worm has a payload that installs a backdoor or trapdoor component in a
system, which allows the attacker to access the system at will with special
privileges.
Eg: Back
Orifice
Polymorphism
ü A Polymorphic threat is one that changes
its apparent shape over time, making it undetectable by techniques that look
for preconfigured signatures.
ü These
viruses and Worms actually evolve, changing their size, and appearance to elude
detection by antivirus software programs.
Virus & Worm Hoaxes
Types of Trojans
· Data
Sending Trojans
· Proxy
Trojans
· FTP
Trojans
· Security
software disabler Trojans
· Denial of
service attack Trojans(DOS)
Virus
A program
or piece of code that be loaded on to your computer, without your knowledge and
run against your wishes.
Worm
1. A program
or algorithm that replicates itself over a computer network and usually
performs malicious actions.
Trojan Horse
ü A
destructive program that masquerade on beginning application, unlike viruses,
Trojan horse do not replicate themselves.
Blended threat
ü Blended
threats combine the characteristics of virus, worm, Trojan horses &
malicious code with server and Internet Vulnerabilities.
Antivirus Program
A Utility
that searches a hard disk for viruses and removes any that found.
ü Forces of Nature
Fire: Structural fire that damages the
building. Also encompasses smoke damage from
a fire or water damage from sprinkles systems.
Flood: Can sometimes be mitigated with
flood insurance and/or business interruption
Insurance.
Earthquake: Can sometimes be mitigated with
specific causality insurance and/or
business interruption insurance, but is usually a separate policy.
Lightning: An Abrupt, discontinuous
natural electric discharge in the atmosphere.
Landslide/Mudslide: The
downward sliding of a mass of earth & rocks directly damaging all parts of the information systems.
Tornado/Severe Windstorm
Huricane/typhoon
Tsunami
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Dust Contamination
Since it
is not possible to avoid force of nature threats, organizations must implement
controls to limit damage.
They must
also prepare contingency plans for continued operations, such as disaster
recovery plans, business continuity plans, and incident response plans, to
limit losses in the face of these threats.
ü Deviations in Quality of Service
A product
or service is not delivered to the organization as expected.
The
Organization’s information system depends on the successful operation of many
interdependent support systems.
It
includes power grids, telecom networks, parts suppliers, service vendors, and
even the janitorial staff & garbage haulers.
This
degradation of service is a form of availability
disruption.
Internet Service Issues
ü Internet
service Provider(ISP) failures can considerably undermine the availability of
information.
ü The web
hosting services are usually arranged with an agreement providing minimum
service levels known as a Service level
Agreement (SLA).
ü When a
Service Provider fails to meet SLA, the provider may accrue fines to cover
losses incurred by the client, but these payments seldom cover the losses
generated by the outage.
Communications & Other
Service Provider Issues
ü Other
utility services can affect the organizations are telephone, water, waste water,
trash pickup, cable television, natural or propane gas, and custodial services.
ü The loss
of these services can impair the ability of an organization to function.
ü For an
example, if the waste water system fails, an organization might be prevented from
allowing employees into the building.
ü This
would stop normal business operations.
Power Irregularities
ü Fluctuations
due to power excesses.
ü Power
shortages &
ü Power
losses
This can
pose problems for organizations that provide inadequately conditioned power for
their information systems equipment.
When
voltage levels spike (experience a
momentary increase),or surge (
experience prolonged increase ), the extra voltage can severely damage or
destroy equipment.
The more
expensive uninterruptible power supply (UPS) can protect against spikes and
surges.
ü
Technical
Hardware Failures or Errors
Resulting
in unreliable service or lack of availability
Some
errors are terminal, in that they result in unrecoverable loss of equipment.
Some
errors are intermittent, in that they resulting in faults that are not easily
repeated.
ü
Technical
software failures or errors
This
category involves threats that come from purchasing software with unknown,
hidden faults.
Large
quantities of computer code are written, debugged, published, and sold before
all their bugs are detected and resolved.
These
failures range from bugs to untested failure conditions.
ü
Technological
obsolescence
Outdated
infrastructure can lead to unreliable and untrustworthy systems.
Management
must recognize that when technology becomes outdated, there is a risk of loss
of data integrity from attacks.
Related Topics