Chapter: Security Investigation : Security Investigation
Security Investigation: Attacks
ATTACKS
An attack
is an act of or action that takes advantage of a vulnerability to compromise a
controlled system.
It is
accomplished by a threat agent that
damages or steals an organization’s information or physical asset.
Vulnerability is an identified weakness in a
controlled system, where controls are not
present or are no longer effective.
Attacks
exist when a specific act or action comes into play and may cause a potential
loss.
ü
Malicious
code
The
malicious code attack includes the execution of viruses, worms, Trojan horses,
and active Web scripts with the intent to destroy or steal information.
The state
–of-the-art malicious code attack is the polymorphic or multivector, worm.
These
attack programs use up to six known attack vectors to exploit a variety of
vulnerabilities in commonly found information system devices.
ü
Attack
Replication Vectors
IP scan & attack
Web browsing
Virus
Unprotected shares
Mass mail
Simple Network Management Protocol(SNMP)
ü IP scan & attack
The
infected system scans a random or local range of IP addresses and targets any
of several vulnerabilities known to hackers.
ü Web browsing
If the
infected system has write access to any Web pages, it makes all Web content
files (.html,.asp,.cgi & others) infectious, so that users who browse to
those pages become infected.
ü Virus
Each
infected machine infects certain common executable or script files on all
computers to which it can write with virus code that can cause infection.
ü Unprotected shares
Using
vulnerabilities in file systems and the way many organizations configure them,
the infected machine copies the viral component to all locations it can reach.
ü Mass Mail
By
sending E-mail infections to addresses found in the address book, the infected
machine infects many users, whose mail -reading programs also automatically run
the program & infect other systems.
ü Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
By using
the widely known and common passwords that were employed in early versions of
this protocol, the attacking program can gain control of the device. Most
vendors have closed these vulnerabilities with software upgrades.
Examples
Hoaxes
ü A more
devious approach to attacking the computer systems is the transmission of a
virus hoax with a real virus attached.
ü Even
though these users are trying to avoid infection, they end up sending the
attack on to their co-workers.
Backdoors
ü Using a
known or previously unknown and newly discovered access mechanism, an attacker
can gain access to a system or network resource through a back door.
ü Sometimes
these entries are left behind by system designers or maintenance staff, and
thus referred to as trap doors.
2.5.1 A trap door
is hard to detect, because very often the programmer who puts it in place also
makes the access exempt from the usual audit logging features of the system.
Password Crack
ü Attempting
to reverse calculate a password is often called cracking.
ü A password
can be hashed using the same algorithm and compared to the hashed results, If
they are same, the password has been cracked.
ü The (SAM)
Security Account Manager file contains the hashed representation of the user’s
password.
Brute Force
ü The
application of computing & network resources to try every possible
combination of options of a password is called a Brute force attack.
ü This is
often an attempt to repeatedly guess passwords to commonly used accounts, it is
sometimes called a password attack.
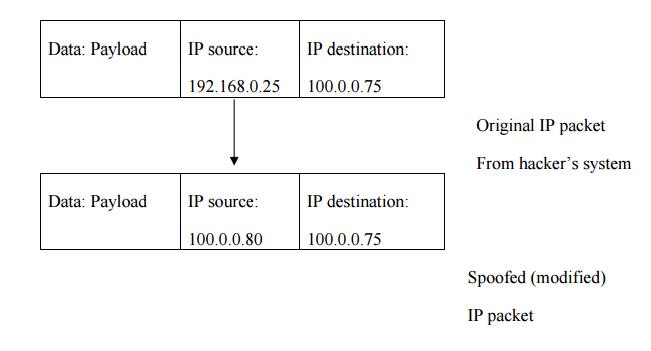
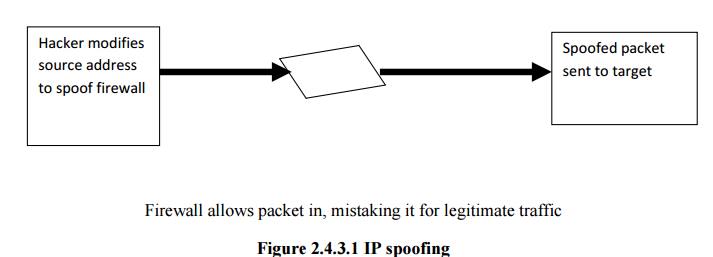
Spoofing
It is a
technique used to gain unauthorized access to computers, where in the intruder
sends messages to a computer that has an IP address that indicates that the
messages are coming from a trusted host.
Dictionary
ü This is another
form of the brute force attack noted above for guessing passwords.
ü The dictionary attack narrows the field by
selecting specific accounts to attack and uses a list of commonly used
passwords instead of random combinations.
Denial –of- Services(DOS) & Distributed Denial
–of- Service(DDOS)
ü The
attacker sends a large number of connection or information requests to a
target.
ü This may
result in the system crashing, or simply becoming unable to perform ordinary
functions.
ü DDOS is
an attack in which a coordinated stream of requests is launched dagainst a
target from many locations at the same.
Man-in-the –Middle
ü Otherwise
called as TCP hijacking attack.
ü An
attacker monitors packets from the network, modifies them, and inserts them
back into the network.
ü This type
of attack uses IP spoofing.
ü It allows
the attacker to change, delete, reroute, add, forge or divert data.
ü TCP
hijacking session, the spoofing involves the interception of an encryption key
exchange.
SPAM
· Spam is
unsolicited commercial E-mail.
· It has
been used to make malicious code attacks more effective.
· Spam is
considered as a trivial nuisance rather than an attack.
· It is the
waste of both computer and human resources it causes by the flow of unwanted
E-mail.
Mail Bombing
ü Another
form of E-mail attack that is also a DOS called a mail bomb.
ü Attacker
routes large quantities of e-mail to the target.
ü The
target of the attack receives unmanageably large volumes of unsolicited e-mail.
ü By
sending large e-mails, attackers can take advantage of poorly configured e-mail
systems on the Internet and trick them into sending many e-mails to an address
chosen by the attacker.
ü The
target e-mail address is buried under thousands or even millions of unwanted
e-mails.
Sniffers
ü A sniffer is a program or device that can
monitor data traveling over a network.
ü Unauthorized
sniffers can be extremely dangerous to a network’s security, because they are
virtually impossible to detect and can be inserted almost anywhere.
ü Sniffer
often works on
TCP/IP networks, where they are sometimes called
“packet
Sniffers”.
Social Engineering
2.5.3 It is the
process of using social skills to convince people to reveal access credentials
or other valuable information to the attacker.
2.5.4 An
attacker gets more information by calling others in the company and asserting
his/her authority by mentioning chief’s name.
Buffer Overflow
ü A buffer
overflow is an application error that occurs when more data is sent to a buffer
than it can handle.
ü Attacker
can make the target system execute instructions.
Timing Attack
ü Works by
exploring the contents of a web browser’s cache.
ü These
attacks allow a Web designer to create a malicious form of cookie, that is
stored on the client’s system.
ü The
cookie could allow the designer to collect information on how to access
password-protected sites.
Related Topics