Chapter: Optical Communication and Networking : Optical Networks
SONET/SDH
SONET/SDH
ü SONET is the TDM optical network standard for North America
ü SONET is called Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) in the rest of the world
ü SONET is the basic phycal layer standard
ü Other data types such as ATM and IP can be transmitted over SONET
ü OC-1 consists of 810 bytes over 125 us; OC-n consists of 810n bytes over 125 us
ü Linear multiplexing and de-multiplexing is possible with Add-Drop-Multiplexers
ü The SONET/SDH standards enable the interconnection of fiber optic transmission equipment from various vendors through multiple-owner trunk networks.
ü The basic transmission bit rate of the basic SONET signal is
ü In SDH the basic rate is 155.52 Mb/s.
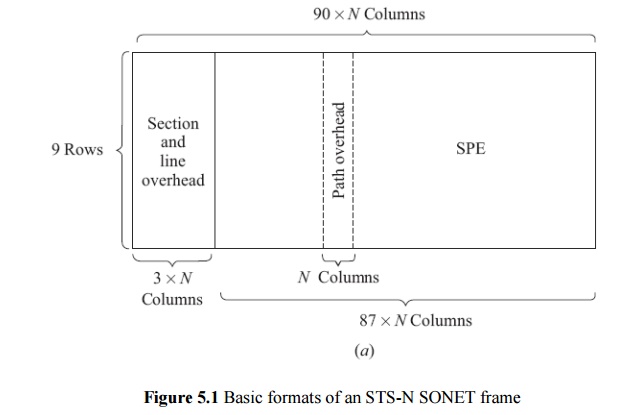
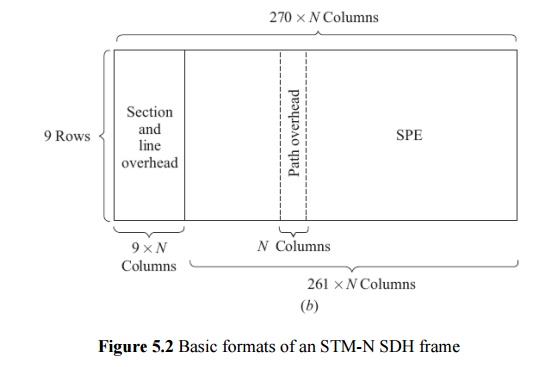
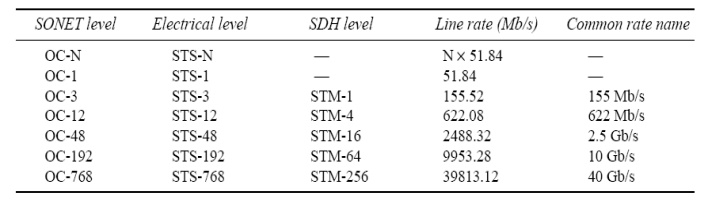
Common values of OC-N and STM-N:
ü OC stands for optical carrier. It has become common to refer to SONET links as OC-N links.
ü The basic SDH rate is 155.52 Mb/s and is called the synchronous transport module—level 1 (STM 1).
SONET Add Drop Multiplexers:
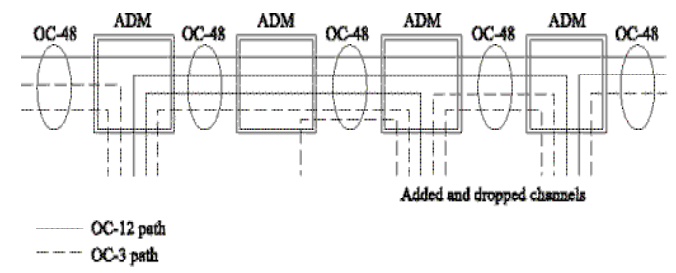
SONET ADM is a fully synchronous, byte oriented device, that can be used add/drop OC sub-channels within an OC-N signal
Ex: OC-3 and OC-12 signals can be individually added/dropped from an OC-48 carrier
SONET/SDH Rings:
ü SONET and SDH can be configured as either a ring or mesh architecture
ü SONET/SDH rings are self-healing rings because the traffic flowing along a certain path can be switched automatically to an alternate or standby path following failure or degradation of the link segment
ü Two popular SONET and SDH networks:
– 2-fiber, unidirectional, path-switched ring (2-fiber UPSR)
– 2-fiber or 4-fiber, bidirectional, line-switched ring (2-fiber or 4-fiber BLSR)
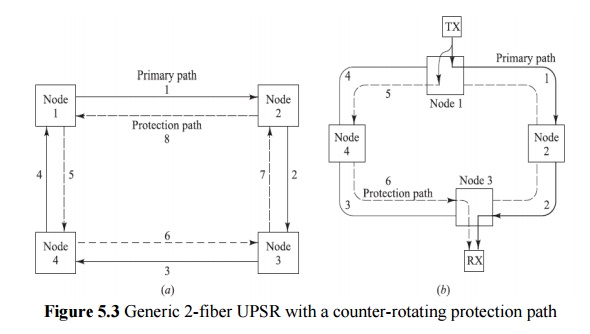
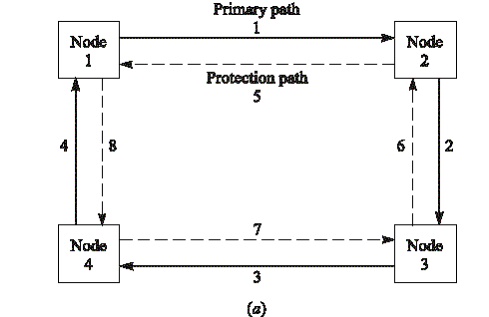
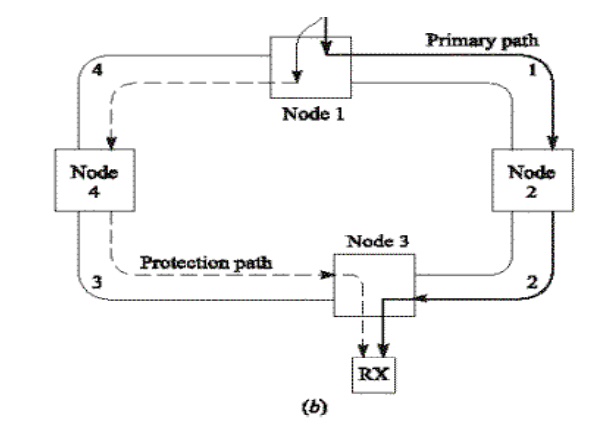
Ex: Total capacity OC-12 may be divided to four OC-3 streams, the OC-3 is called a path here
2-Fiber UPSR Protection:
ü Rx compares the signals received via the primary and protection paths and picks the best one
ü Constant protection and automatic switching
BLSR Recovery from Failure Modes:
ü If a primary-ring device fails in either node 3 or 4, the affected nodes detect a loss-of-signal condition and switch both primary fibers connecting these nodes to the secondary protection pair
ü If an entire node fails or both the primary and protection fibers in a given span are severed, the adjacent nodes switch the primary-path connections to the protection fibers, in order to loop traffic back to the previous node.
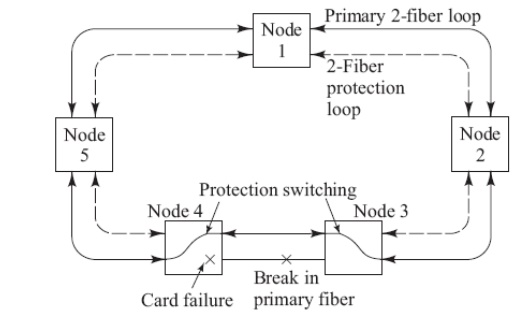
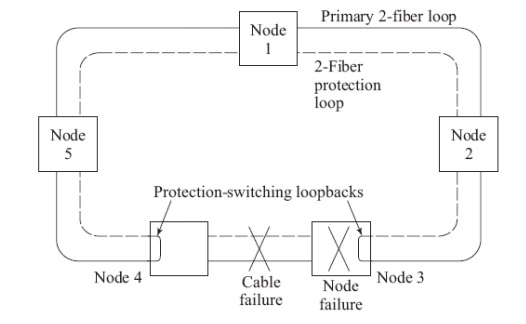
4-Fiber BLSR Basics:
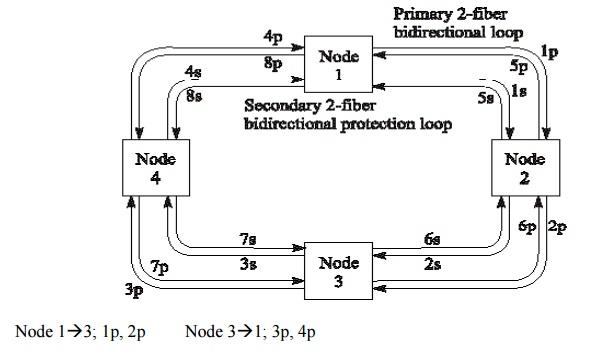
BLSR Fiber-Fault Reconfiguration:
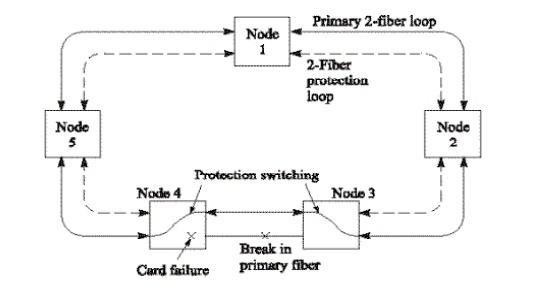
In case of failure, the secondary fibers between only the affected nodes (3 & 4) are used, the other links remain unaffected
BLSR Node-Fault Reconfiguration:
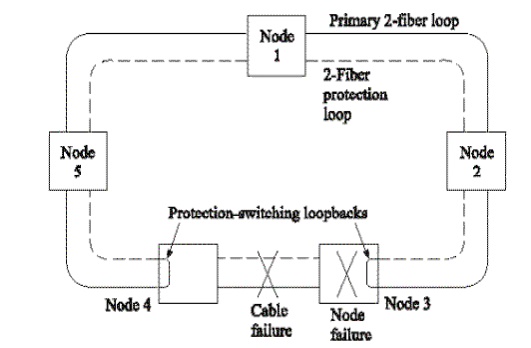
If both primary and secondary are cut, still the connection is not lost, but both the primary and secondary fibers of the entire ring is occupied
Related Topics