Chapter: Information Security : Security Investigation
Risk Assessment
RISK ASSESSMENT
ü Assigns a
risk rating or score to each Information asset.
ü It is
useful in gauging the relative risk to each
Vulnerable asset.
1 Valuation of Information assets
ü Assign
weighted scores for the value to the organization of each Information asset.
ü National
Institute of Standards & Technology (NIST) gives some standards.
ü To be
effective, the values must be assigned by asking he following questions.
ü Which
threats present a danger to an organization’s assets in the given environment?
ü Which
threats represent the most danger to the organization’s Information?
ü How much
would it cost to recover from a successful attack?
ü Which of
the threats would require the greatest expenditure to prevent?
2 Likelihood
ü It is the
probability of specific vulnerability within an organization will be
successfully attacked.
ü NIST
gives some standards.
ü 0.1 = Low 1.0 = High
ü Eg:
Number of network attacks can be forecast based on how many network address the
organization has assigned.
3 Risk Determination
Risk = [
( Likelihood of vulnerability occurrence ) X (Value of information Asset )] __
( % of risk mitigated by current controls) + uncertainty of current knowledge
of the Vulnerability
ü
For the purpose of relative risk assessment, risk
equals:
–
Likelihood
of vulnerability occurrence TIMES value (or impact)
–
MINUS
percentage risk already controlled
–
PLUS an
element of uncertainty
Eg:
Information Asset A has a value score of 50 & has one vulnerability:
Vulnerability 1 has a likelihood of 1.0 with no current controls, estimate that
assumptions and data are 90% accurate.
Solution:
Risk = [(1.0)
x 50] – 0% + 10%
= (50 x 1.0) – ((50 x 1.0)x 0.0) + ( (50 x 1.0) x
0.1)
= 50 – 0 + 5
= 55
4 Identify Possible Controls ( For Residual Risk)
Residual
risk is the risk that remains to the information asset even after the existing
control has been applied.
Three
general categories of controls
Policies
Programs
Technologies
3
Policies
ü
General Security Policy
ü
Program Security Policy
ü
Issue Specific Policy
ü
Systems Specific Policy
4
Programs
- Education
- Training
- Awareness
1
Security Technologies
6
Technical Implementation Policies
Access Controls
ü Specially
addresses admission of a user into a trusted area of the organization.
ü Eg: Computer rooms, Power Rooms.
ü Combination
of policies , Programs, & Technologies
Types of Access controls
Mandatory
Access Controls (MACs)
Give users and data owners limited control over access to information
resources.
Nondiscretionary
Controls
ü Managed
by a central authority in the organization; can be based on individual’s role
(role-based controls) or a specified set of assigned tasks (task-based
controls)
Discretionary
Access Controls ( DAC)
Implemented at discretion or option of the data
user Lattice-based Access Control
Variation
of MAC - users are assigned matrix of authorizations for particular areas of access.
5 Documenting the Results of Risk Assessment
By the
end of the Risk Assessment process, you probably have a collection of long
lists of information assets with data about each of them.
The goal
of this process is to identify the information assets that have specific
vulnerabilities and list them, ranked according to those most needing
protection. You should also have collected some information about the controls
that are already in place.
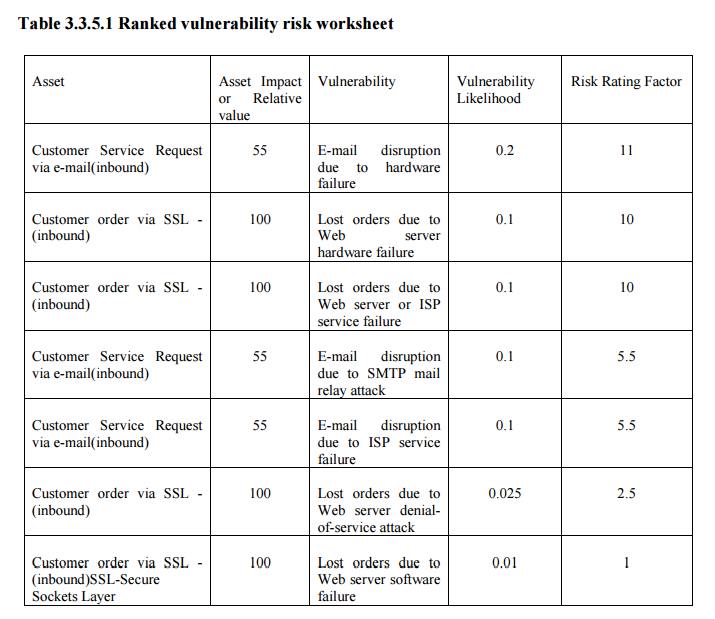
The final summarized document is the ranked vulnerability risk
worksheet, a sample of which is shown in the following table.
Table
3.3.5.1 Ranked vulnerability risk worksheet
Related Topics