Chapter: Plant Biochemistry: Phosphoglycolate formed by the oxygenase activity of RubisCO is recycled in the photorespiratory pathway
Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate is recovered by recycling 2-phosphoglycolate
Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate is recovered by recycling 2-phosphoglycolate
Figure 7.1 gives an overview of the reactions of the photorespiratory path-way and their localization. The oxygenation of two molecules of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate yields two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate and two mol-ecules of 2-phosphoglycolate. The latter are recycled to yield another mole-cule of 3-phosphoglycerate. This recycling begins with the hydrolytic release of phosphate byglycolate phosphate phosphatase present in the chloroplast stroma (Fig. 7.2). The resultant glycolate leaves the chloroplasts via a spe-cific translocator located in the inner envelope membrane and enters the peroxisomes via pores in the peroxisomal boundary membrane, probably facilitated by a porin .
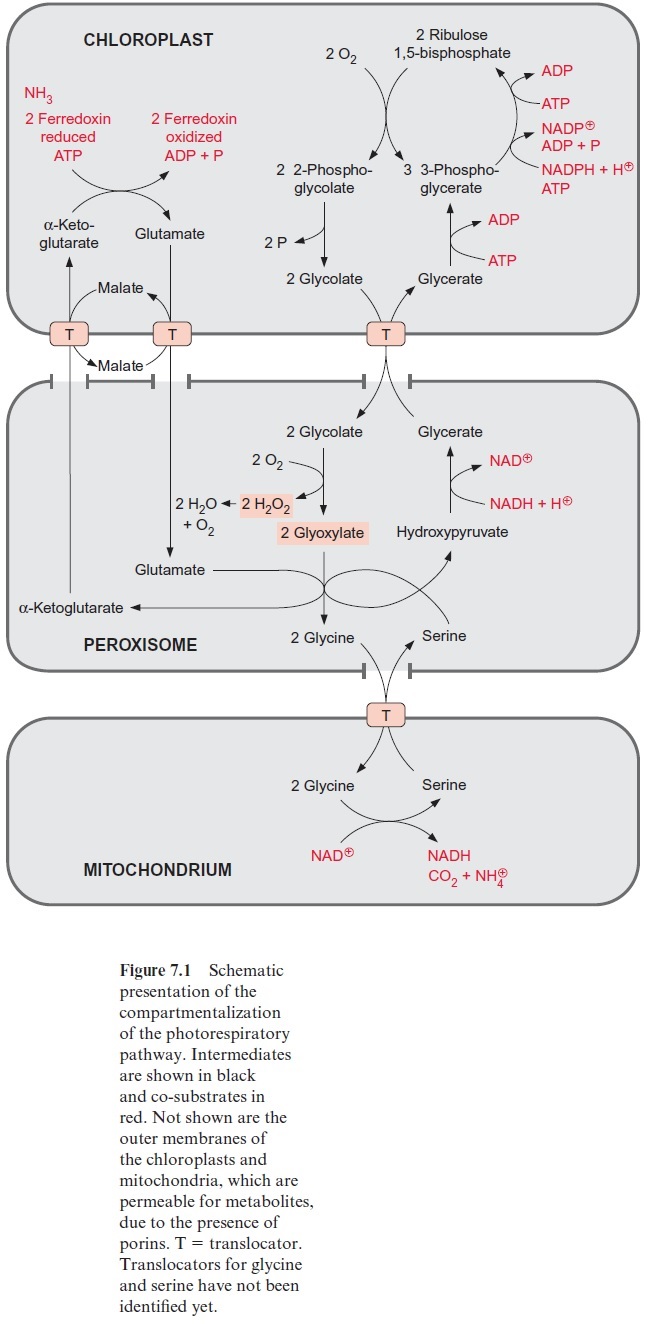
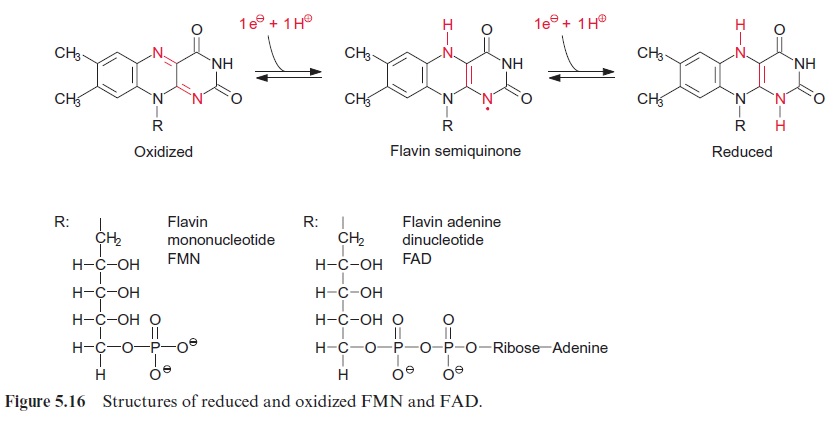
In the peroxisomes the alcoholic group of glycolate is oxidized to a carb-onyl group in an irreversible reaction catalyzed by glycolate oxidase, result-ing in the synthesis of glyoxylate. The reducing equivalents are transferred to molecular oxygen to produce H2O2 (Fig. 7.2). Like other H2O2 forming oxidases, the glycolate oxidase contains a flavin mononucleotide cofactor (FMN, Fig. 5.16) as redox mediator between glycolate and oxygen. H2O2 is then converted to water and oxygen by the enzyme catalase, which is present in the peroxisomes. Thus, in total, 0.5 mol of O2 is consumed for the oxidation of one mole of glycolate to glyoxylate.
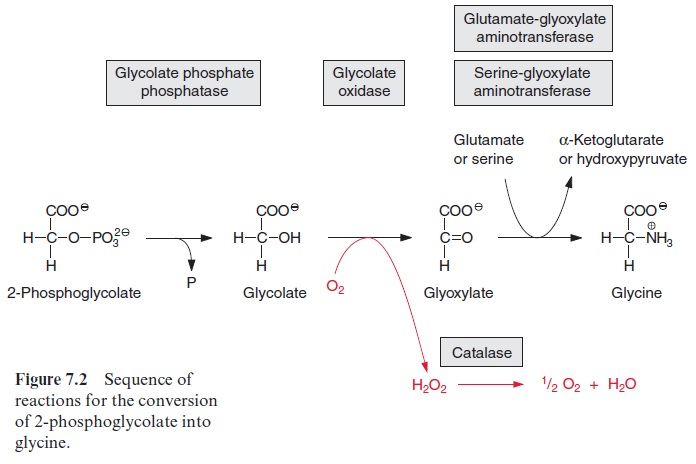
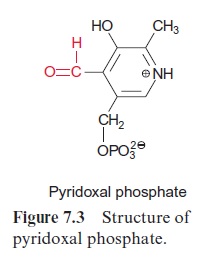
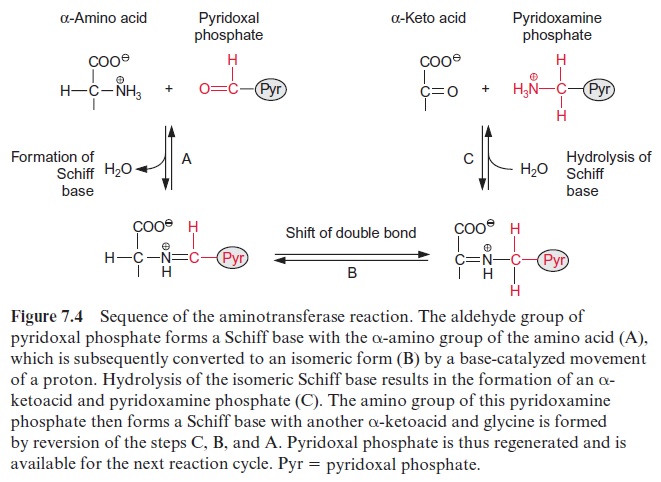
The glyoxylate is converted to the amino acid glycine by two different reactions proceeding in the peroxisome simultaneously at a 1:1 ratio. The enzyme glutamate-glyoxylate aminotransferase catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from the donor glutamate to glyoxylate. This enzyme also reacts with alanine as amino donor. In the other reaction, the enzyme serine-glyoxylate aminotransferase catalyzes the transamination of glyoxylate by serine. These two enzymes, like other aminotransferases (e.g., glutamate-oxaloacetate aminotransferase) contain bound pyridoxal phosphate with an aldehyde function as reactive group (Fig. 7.3).Figure 7.4 presents the reaction sequence of transamination reactions.
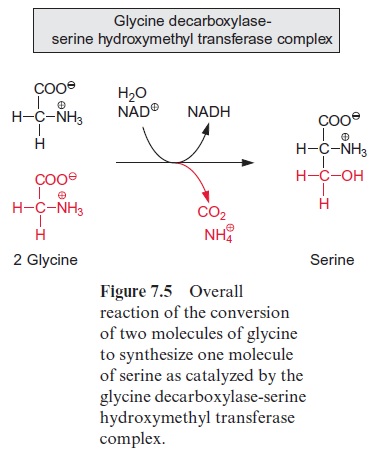
The glycine thus formed leaves the peroxisomes via pores and is trans-ported into the mitochondria. Although this transport has not yet been characterized in detail, it is to be expected that it is facilitated by a specific translocator. In the mitochondria two molecules of glycine are oxidized yielding one molecule of serine with release of CO2 and NH4+ and a trans-fer of reducing equivalents to NAD+ (Fig. 7.5).
Related Topics