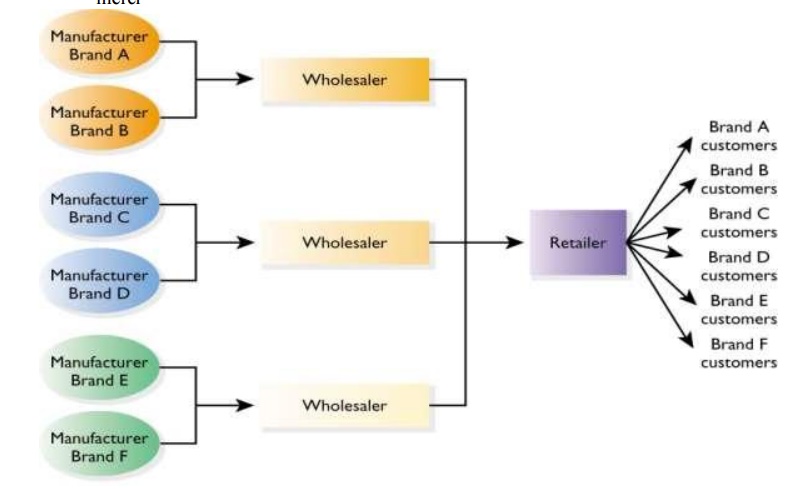
Chapter: Business Science : Marketing Management : Marketing Research and Trends in Marketing
Retail Research Introduction
Retail Research Introduction:
The word
retail has its origin in French word retaillier and means ―to cut a piece‘‘ or
―to break bulk‘.
“Retailing is the sale of goods
and services to the ultimate consumer for personal, family or household use.”
According to Kotler: “Retailing
includes all the activities involved in selling goods or
services to the final consumers
for personal, non business use”
Retailing
may be understood as the final step in the distribution of merchandise for
consumption by the end consumers.
Retailing
is responsible for matching final consumer demand with supplies of different
marketers.
Retailing
is high intensity competition industry, The reasons for its popularity lie in
its ability to provide easier access to variety of products, freedom of choice
and many services to consumers.
The Indian retail is dotted by traditionally market
place called bazaars or haats comprises of numerous small and large shops,
selling different or similar merchandise
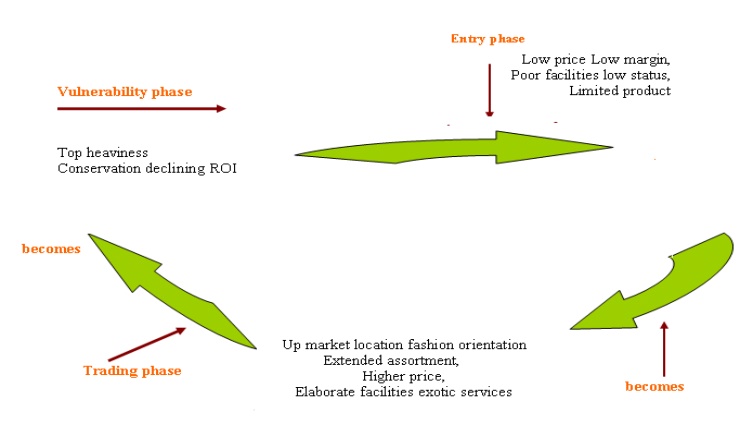
“’Wheel of Retailing”
A better
known theory of retailing ―wheel of retailing‖ proposed by Maclcomb McNair
says,
1.
New retailers often enter the market place with low
prices, margins, and status. The low prices are usually the result of some
innovative cost-cutting procedures and soon attract competitors.
2.
With the passage of time, these businesses strive
to broaden their customer base and increase sales. Their operations and
facilities increase and become more expensive.
3.
They may move to better up market locations, start
carrying higher quality products or add services and ultimately emerge as a
high cost price service retailer.
4.
By this time newer competitors as low price, low
margin, low status emerge and these competitors too follow the same
evolutionary process.
1.
The wheel keeps on turning and department stories,
supermarkets, and mass merchandise went through this cycles.
1.Functions of a retailer
1.
Form: First is
utility regarding the form of a
product that is acceptable to the customer.
The
retailer does not supply raw material, but rather offers finished goods and
services in a form that the customers want.
The
retailer performs the function of sorting the goods and providing us with an
assortment of product in various categories.
2.
Time: He
cerates Time utility by keeping the
store open when the consumers prefer to
shop.
preferable
shopping hours.
3.
Place: By
being available at a convenient location, he creates place utility.
4.
Ownership:
Finally, when the product is sold,
ownership utility is created. Apart
from these functions retailer also performs like:
5.
Arranging
Assortment: manufacturers usually make one or a variety of products and would like to sell their entire
inventory to few buyers to reduce costs. Final consumers, in contrast prefer a
large variety of goods and services to choose from and usually buy them in
small units.
Functions of a retailer
1. Form: First is utility regarding the form of a product that is acceptable to
the customer.
The
retailer does not supply raw material, but rather offers finished goods and
services in a form that the customers want.
The retailer
performs the function of sorting the goods and providing us with an assortment
of product in various categories.
1.
Time: He
cerates Time utility by keeping the
store open when the consumers prefer to
shop. preferable shopping hours.
2.
Place: By
being available at a convenient location, he creates place utility.
3.
Ownership:
Finally, when the product is sold,
ownership utility is created. Apart
from these functions retailer also performs like:
4.
Arranging
Assortment: manufacturers usually make one or a variety of products and would like to sell their entire
inventory to few buyers to reduce costs. Final consumers, in contrast prefer a
large variety of goods and services to choose from and usually buy them in
small units.
I Amount of
Services:
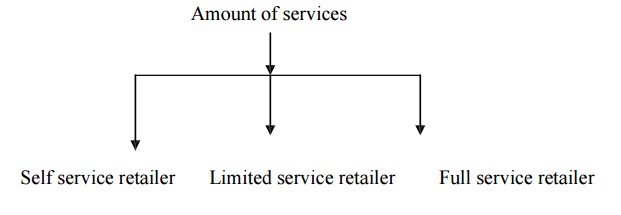
Self service retailer:
Customers
who are willing to perform their own ―locate-compare-select‖ process to save money
Ltd service retailer:
Retailer
provides more sales assistance because they carry more shopping goods. They fix
higher price due to higher operation cost
Full service retailer:
1.Product Line:
1.
Specialty
stores: A retail stores that carries a narrow product line with a deep asswortment within that line. Ex.
Apparel stores, Sporting goods stores, Furniture stores, books stores
2.
Department
stores: A retail organization that carries a wide variety of product lines – typically clothing, home furnishing, and house
hold goods: each line is operated as a separate department managed by
specialist buyers or merchandisers.
Supermarkers: A supermarket
is a large self service retail store that carries a wide variety of consumer
products under one roof , such as complete line of food products , laundry
requirement, household maintenance items. Here large, low – cost, low margin,
high volume
1.
Convenience
stores: A relatively small store located near residential areas, open long hours 7 days a week, and carries a limited line
of high turnover convenience goods at slightly higher price.
2.
Super
stores: A store much larger than a regular supermarket that carries a large assortment of routinely
purchased food and nonfood it4ems and offers services such as dry cleaning,
post offices, photo finishing, check
cashing,
bill paying, lunch counters, car cares, and pet care.
6) Category killer: Giant specialty store
that carriers a very deep assortment of a particular line and is staffed by
knowledgeable employees. Ex. Book, Baby gear, toys, home improvement products.
1. Relative Price:
1.
Discount
stores: these stores are self service, standard general merchandise retailers regularly offering brand name and private
brand items at low price, earn lower margins and push for high sales turnover.
The characteristics of true discount stores include
Selling
products at discounted price
Carry
standard international , national, or store brand toi build image Self service
stores to minimize operational costs
Preferred
store locations are low rent areas.
Like best
known discount store is Wal-Mart. In India almost all retail stores offer
discounts, subhiksha
2) Off – price retailers:
Retailer that buys at less than regular whole sale
prices
and sells at less than retail. Examples are factory outlets, independents and
warehouse club
Independent
off – price retailers: Off-price retailer that is either owned and run by entrepreneurs or is a
division of a larger retail corporation.
Factory
Outlet: Off-price retailing operation that is owned and operated by a manufacturer and that normally carries
the manufacturer‗s surplus, discontinued, or irregular goods.
Warehouse
club: Off-price retailer that sells a limited selection of brand-name grocery
items, appliances, clothing, and hodgepodge of other goods at deep discounts to
members who pay annual membership fees.
IV Organisational Approach:
Chain
stores: Two or more outlets that are owned and controlled in
common,
have central buying and merchandising, and sell similar lines of merchandise.
Franchise:
A contractual
association between a manufacturer, wholesaler, or service organization (a franchiser)and independent business
people (franchisees) who buy the right to own and operate one or more units in
the franchise system.
2.Factors Influencing the retail
Shoppers
1. Range of Merchandise:
The range
of merchandise is one of the most important reasons for customers to patronize
a particular outlet.
Initial
curiosity about the store draw a consumer to retail store.
But
convert the customer into buyer and retain them over a period of time is
dependent on the quality and the range of merchandise offered by the store.
Range of
merchandise includes categories like Books & Music, apparel and other
lifestyles products
2. Convenience of shopping at a particular outlet.
This
element is fast gaining prominence in the world of organized retail.
Example
patient prefer medicine shops, fresh juice and fruits shops near clinic or
hospitals.
3. Time of
Travel:
Time
requires to reach a particular location is again become critical.
big
cities where traveling takes too much time like Delhi, Mumbai because of this
we can see many local areas developing in terms of shopping to facilitate
buying
4. Socio
economic background and culture:
Background
of the consume largely determines his /her lifestyles. And this influences the
kind of
store that he may be comfortable shopping in.
Consumer
buying behavior varies largely market to market influence by culture and
environment.
5. The stage of the family life cycles.
The stage
of the family life cycle the customer belongs to also influences their needs.
Example
Need for young bachelors differ from the requirements of the old age or senior
citizen.
1.
Retail
Location
“A store is place , real or
virtual , where the shoppers comes to buy goods & services. The
sales
transaction occurs at this junction.‖
1.
The location of retail store has for along time
been considered the most important ‗P‗ in retailing.
2.
Locating the retail store in the right place was
considered to be adequate for success.
Types of Retail Location
Typically a store location may
be:
1.
Freestanding /Isolated store.
2.
Part of Business District/Centers (unplanned
Business Districts).
3.
Part of a Shopping Center (Planned Shopping
Centers)
Freestanding /Isolated store
1.
Where there are no other outlets in the vicinity of
the store and therefore store depends on its own pulling power and promotion to
attract customers.
• A biggest advantage for freestanding stores
is that there is no competition around.
2.
This type of location has several advantages
including no competition, low rent, and often better visibility from the road,
easy parking and lower property.
Part of Business District/Centers (unplanned
Business Districts).
1.
A retail store can also be located as a part of a business
district. Or we can refer this as unplanned business centers
2.
A business district is place of commerce in a city
which developed historically as the center of trade and commerce in the city or
town.
3.
A business districts can be a central, secondary or
a Neighborhood business district.
4.
A Central business District CBD is the main center of commerce and trade in the city.
(high
land rates , intense development)
• CBD
served different sections of population for Examples of Cannaught place in
Delhi, Colaba in Mumbai, Commercial Street and in Bangalore are up market CBD’s.
Part of a Shopping Center
(Planned Shopping Centers)
• A
shopping center has been defined as ― a group of retail and other commercial
establishments that is planned , developed, owned and managed as a single
property‖
1.
The basic configuration of a shopping centre is a
―Mall ‖ or Strip centre.
2.
A mall is typically enclosed and climate
controlled. A walkway is provided in front of the stores.
3.
A strip centre is a row of stores with parking
provided in the front of the stores.
4.
In India we can planned shopping centre can
categorize in two category
Regional shopping centers or
Mall: Regional shopping centers or mall are the largest planned shopping centers..
1.
Often they are anchored by two or more major
department stores have enclosed mall serve a large trading area and have high
rents. (ansal plaza,spencers plaza crossroads, DLF city in Gurgaon)
2.
Neighborhood/community/shopping
centers: Neighborhood /community centers usually
have a balanced mix of stores including a few grocery stores , a chemist, a
verity store and a few other stores selling convenience goods to the residents
of the neighborhood.
3.Step involved in choosing a Retail Location
1.
In order to arrive at the decision on where to
locate the retail store a retailer needs to first on the region that he wants
to locate the store.
2.
After identifying the region the following steps
Have to be followed .
3.
Identifying the market in which to locate the
store.
4.
Evaluate the demand and supply within that market.
i.e. determine the market potential.
5.
Identify the most attractive sites
4) Select
the best site available.
1. Market Identification:
• The
first step in arriving at a decision on retail location is to identify the
market attractiveness to a retailer.
This is important that retail needs to
understand the market well.
2. Determining the market
Potential::
The retailer need to take into consideration
various elements as shown in format. (features of population)
Demographic features of the population
The characteristics of the household in the
area (average household income)
Competition and compatibility (Need to know
compatibility & competition in market)
1.
Laws & regulations:( good understanding of the
laws
2.
Trade area analysis:
3.
A trade area is the geographic area that generates
the majority of the customers for the store.
4.
Primary
trade area: primary trading covers between 50-80% of the
store‗s customers.
5.
Secondary
Trading Area: this area contains the additional 15- to 25% of
the store’s customers.
6.
Tertiary
trading area covers the balance customers
7.
These trading areas are dependent on distance and do
not always have to be concentric in naturel
3 & 4 Identify Alternate
sites and select the site:
After
taking decision on the location and market potential the retailer has to select
the site to locate the store based on these
·
Traffic
·
Accessibility of the market is also a key factor
·
The total number of stores and the type of store
that exist in the area
·
Amenities
·
To buy or to lease
·
The product mix to be offered by the retailer
Research prior to setting up a
retail store
Demographic
Data.
Population
GDP
Customer
Data.
Research after setting up a
retail store
1.
Merchandise and service offered.
2.
New product development.
3.
Acceptability of products.
4.
Acceptability of pricing.
5.
Understanding consumer profiles.
Seven Secrets
of Retail
1.
STORE –Place – Business Development.
2.
STOCK –Product –Visual Merchandising.
3.
STAFF –People –Training & Development.
4.
SERVICE –PersistenCe –CRM.
5.
SALE –Priority –Sales & Marketing.
6.
SUCCESS –Passion –Your Profession.
7.
SMILE –Permanent –Pass it On…!
Related Topics