Chapter: Biochemistry: Biological Oxidation
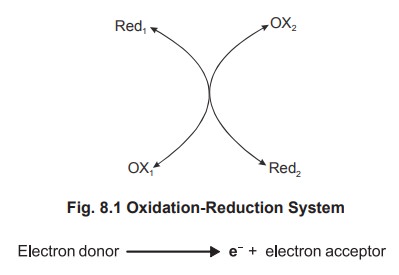
Redox Couple
Redox Couple
Always every oxidation is accompanied by a reduction
process. All such reactions are termed as oxidation-reduction reactions
and shortly referred as redox. These redox reactions are
associated with movements of electron. The electron donor is called as
reductant or reducing agent and the electron acceptor, the oxidant or oxidizing
agent. The system which transfer its electron is changed into oxidant form
while the system which accepts electrons gets converted to the reductant form.
Oxidation reduction system is simplified and shown below (fig 8.1)
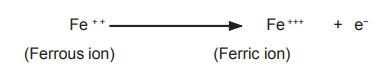
A specific example is oxidation of ferrous iron
to ferric iron indicates the removal of electron (e-)from ferrous iron.
Since, the electron is not stable in the free
form it gets attached to another molecule and thus every oxidation is followed
by a reduction. Always these redox reactions are energy yielding. A direct
transfer of electrons from substrate to the oxidant would liberate a sudden
burst of energy and most of it will be wasted by dissipation. Normally when the
electrons of hydrogen combine with oxygen results in explosion. In biological
system this oxidation reduction process takes place smoothly without increasing
the temperature because the transfer of hydrogen pairs occurs in a step by step
process till it reacts with oxygen. This permits the liberation of energy in
small amounts so that it can be captured and saved.
Redox Potential
In oxidation and reduction reactions the free
energy exchange is proportionate to the tendency of reactants to donate or to
accept electrons. The affinity for the electron by the oxidant is called the
electron affinity or redox potential. In biochemistry, the oxygen has the
highest redox potential or electron affinity (E0) and therefore the
electron pass from the systems of hydrogen donors which have lower potentials.
It is usual to compare the redox potential of a system (E0) against
the potential of the hydrogen electrode, which is at pH 0 designated as 0.0
volts. However, in a biological system it is normal to express the redox
potential (E0) at pH 7.0 at which the electrode potential of
hydrogen electrode is - 0.42volts. In the biological system, the enzymes
concerned with this oxidation reduction processes are designated as
oxidoreductases. Some of the redox potentials are given in the table 8.1.
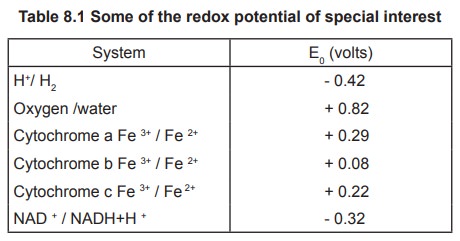
A positive value for the standard reduction
potential means that a compound in question preferentially is reduced when
involved in a redox reaction with hydrogen. A negative value means that a
compound in question is preferentially oxidized. However, listings of standard
reduction potentials are always given in the form of a reduction reaction.
Related Topics