Human Organ systems | Term 2 Unit 6 | 6th Science - Questions Answers | 6th Science : Term 2 Unit 6 : Human Organ systems
Chapter: 6th Science : Term 2 Unit 6 : Human Organ systems
Questions Answers
Evalution
I. Choose the appropriate answer
1. Circulatory
system transports these throughout the body
a. Oxygen
b. Nutrient
c. Hormones
d. All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
2. Main organ of
respiration in human body is
a. Stomach
b. Spleen
c. Heart
d. Lungs
Answer: (d) Lungs
3. Breakdown
of food into smaller molecules in our body is known as
a. Muscle
contraction
b. Respiration
c. Digestion
d. Excretion
Answer: (c) Digestion
II. Fill in the blanks
1. A group of
organs together make up an organ system
2. The part of the
skeleton that protects the brain is
3. The process by
which the body removes waste is
4. The skin is the largest sense organ in our body
5. The endocrine
glands produce chemical substances called
III. True or False. If False, give the correct
statement
1. Blood is produced
in the bone marrow.
2. All the waste
products of the body are excreted through the circulatory system.
All the waste products of the body are excreted
through the excretory system.
3. The other name
of food pipe is alimentary canal.
4. Thin tube like
structures which are the component of circulatory system are called blood vessels.
Thin tube like structures which are the component of
circulatory system are called capillaries.
5. The brain, the
spinal cord and nerves form the nervous system.
The brain, the spinal cord, the nerves and the sensory
organs form the nervous system.
IV. Mach the following
1. Ear - Cardiac muscle
2.
Skeletal System - Flat muscle
3.
Diaphragm - Sound
4.
Heart - Air sacs
5.
Lungs - Protection of internal Organs
Answer:
1. Ear - Sound
2. Skeletal System -
Protection of internal Organs
3. Diaphragm - Flat muscle
4. Heart - Cardiac muscle
5. Lungs - Air sacs
V. Arrange in Correct sequence
1. Stomach → Large intestine →
Oesophagus → Pharynx → Mouth → Small Intestine → Rectum → Anus
Mouth → Pharynx → Oesophagus → Stomach → Small Intestine → Large intestine
2. Urethra → Ureter → Urinary Bladder → Kidney
Kidney → Ureter → Urinary → Bladder Urethra
VI. Analogy
1. Arteries : Carry
blood from the heart:: Veins :carry blood to the heart.
2. Lungs: Respiratory system:: Heart : Circulatory system.
3. Enzymes: Digestive glands:: Hormones : Endocrine glands
VII. Give very short answer
1. Describe about skeletal system.
The skeletal system consists of bones, cartilages and joints. Bones
provide a framework for the body. Along with the muscles bones help in movements.
2. Write the functions of epiglottis.
Epiglottis is a flap like structure on top of the windpipe. While
eating, epiglottis closes the wind pipe and thus it prevents the entry of food into
the windpipe.
3. What are the three types of blood vessels?
(i) arteries (ii) veins (iii) capillaries
4. Define the term "Trachea".
The trachea is also called windpipe. It is a tube supported by cartilaginous
rings that connect the pharynx and larynx to the lungs allowing the passage of air.
5. Write any two functions of digestive system.
(i) It is involved in the conversion of complex food substances into
simple forms.
(ii) It is also involved in the absorption of digested food.
6. Name the important parts of the eye.
(i) Cornea (ii) Iris (iii) Pupil
7. Name the five important sense organs.
(i) Eyes (ii) Ears (iii) Nose (iv) Tongue (v) Skin
VIII. Give short answer
1. Write a short note on rib cage.
The rib cage is made up of 12 pairs of curved, flat rib bones. It
protects the delicate vital organs such as heart and lungs.
2. List out the functions of the human
skeleton.
The skeletal system consists of bones, cartilages and joints. Bones
provide a frame work for the body. They give shape and support to the body. Bones
along with muscles help in movements such as walking, running, chewing and dancing
etc.,
3. Differentiate between the voluntary muscles
and involuntary muscles.
Voluntary muscles can be controlled by our will. Example : Muscles
of arm.
Involuntary muscles cannot be controlled by our will. Example: Cardiac
muscles.
IX. Answer in detail
1. List out the functions of Endocrine system
and Nervous system.
Endocrine system regulates various functions of the body and maintains
the internal environment. The two important functions of the nervous system along
with the endocrine system are conduction and co-ordination.
2. Label the diagram given below to show the
four main parts of the urinary system and answer the following questions.
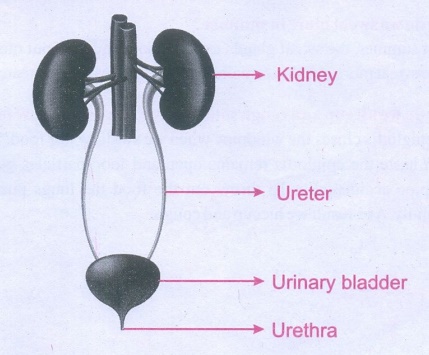
A. Which organ removes extra salts and water
from the blood?
Nephrons
B. Where is the urine stored?
Urinary bladder
C. What is the tube through which urine is
excreted out of the body?
Urethra
D. What are the tubes that transfer urine from
the kidneys to the urinary bladder called?
Ureters
X. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking
Skills
1. What will happen if the diaphragm shows no
movement?
We inhale and exhale gases due to the movement of the diaphragm.
If the diaphragm shows no movement our lungs cannot inhale air from outside; they
cannot exhale impure air from the lungs.
2. Why is the heart divided into two halves by
a thick muscular wall?
The pure blood in one side of the heart should not get mixed with
the impure blood on the other side. So the heart is divided into two halves by a
thick muscular wall.
3. Why do we sweat more in summer?
In hot summer, the sweat glands expand more and give out more sweat.
As we sweat more our skin remains cool and it does not get heated up.
4. Why do we hiccup and cough sometimes when we
swallow food?
The epiglottis closes the windpipe when we swallow our food. When
we eat in haste the epiglottis remains open and food particles go into the windpipe
accidentally. To throw out the food the lungs push out air forcefully. As a result
we hiccup and cough.
Related Topics